Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Hook plate fixation for volar plate avulsion fractures of the middle phalanges in Korea: a case series
- Kang-San Lee, Sang-Woo Son, Hee-June Kim, Hyun-Joo Lee, Dong Hee Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2026;39(1):48-53. Published online January 25, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00339

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
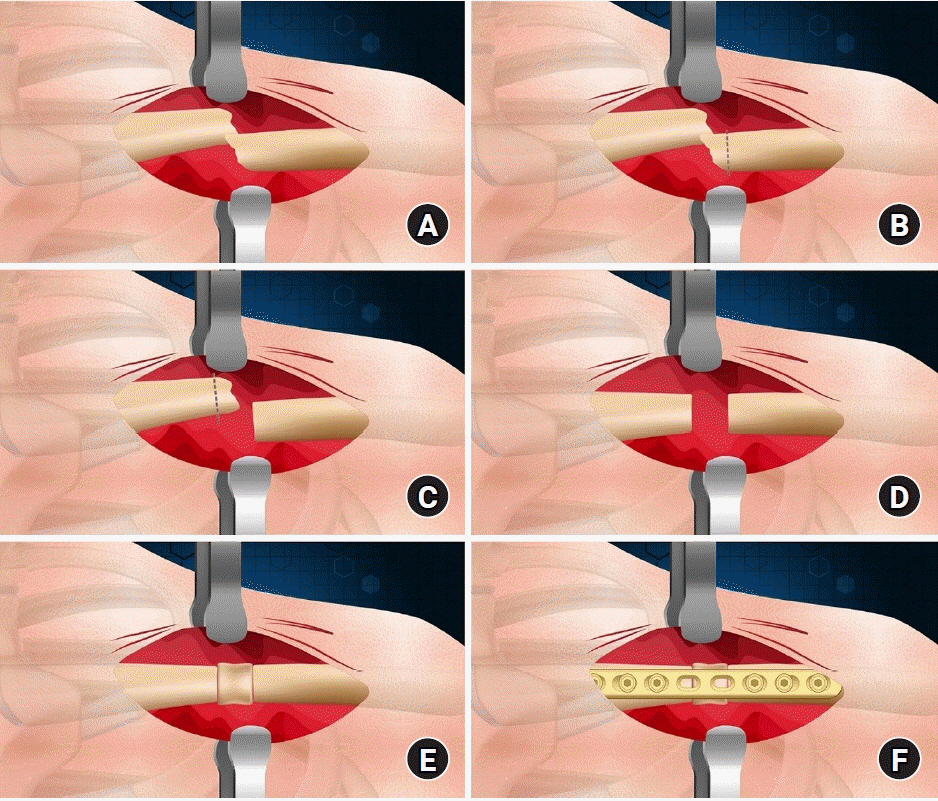
Volar plate avulsion fractures in phalanges are relatively common injuries. While surgical treatment can help reduce limitations in motion after injury, the small size of the fracture fragment can make the procedure challenging. In this study, we used hook plate fixation as a surgical technique for treating volar avulsion fractures in phalanges and evaluated its radiological and clinical outcomes.
Methods
The medical records of eight patients (nine digits) with volar plate avulsion fractures of the middle phalanx were retrospectively reviewed. All fractures were treated with a 1.5-mm hook plate after open reduction. Radiologic evaluations were performed using simple radiographs, and clinical outcomes were assessed through range of motion, instability, and pain.
Results
The mean follow-up period was 4.89 months (range, 1–9 months). All nine digits achieved bone union at the final follow-up. The mean union time was 2.2 months (range, 1–4 months). In all patients, the range of motion in the proximal interphalangeal joint was 85° (range, 70°–100°) before implant removal and 89.4° (range, 80°–100°) after implant removal. All patients demonstrated no joint instability and no residual pain.
Conclusion
Using a hook plate for volar plate avulsion fractures presents a promising alternative to existing fixation methods. Its biomechanical advantages and ease of fabrication make it a valuable tool in hand surgery. Level of evidence: IV.
- 191 View
- 8 Download

- Three-dimensional computed tomography-based differentiation of engaged versus displaced intertrochanteric fractures using the anterior fracture line: a cross-sectional study from Korea
- Jae-Suk Chang, Jin Yeob Park, Sang-Ok Chun, Chul-Ho Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2026;39(1):30-37. Published online January 25, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00318

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
With the advent of an aging society, osteoporotic fractures—particularly hip fractures—are increasing, with a 1-year mortality rate of 17%. Achieving stable fixation that enables early ambulation is essential but remains challenging because complex intertrochanteric (IT) fracture patterns are often underestimated on plain radiographs. Using three-dimensional computed tomography (3D-CT), this study analyzed whether the anterior fracture line lies medial or lateral to the IT line and examined its relationship with displacement or distal medullary canal engagement, highlighting the potential influence of the joint capsule and capsular ligaments on fracture morphology and fixation stability.
Methods
A retrospective review was conducted on 96 osteoporotic IT fractures in patients aged ≥60 years treated between April 2013 and December 2022 at National Police Hospital and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. Fractures were classified as engaged, completely displaced, and partially displaced based on 3D-CT findings. The anterior fracture-line position (medial or lateral to the IT line) and the status of the lesser trochanter (LT) were evaluated. The chi-square or Fisher exact test was used for statistical comparisons.
Results
In total, 96 patients were analyzed. Of these, 49 cases (51.0%) were classified as engaged type, 27 cases (28.1%) as completely displaced type, and 20 cases (20.8%) as partially displaced type. When comparing fracture pattern with anterior fracture-line position, the completely displaced type showed a significantly higher proportion of lateral anterior fracture lines than the other two types (P<0.001). However, no significant association was identified between fracture pattern and LT displacement. When the anterior fracture-line position and LT displacement were evaluated together, only the engaged type demonstrated a possible association between a lateral anterior fracture line and LT displacement, though the statistical significance was weak (P=0.047).
Conclusions
Fracture lines lateral to the IT line were strongly associated with displacement in IT fractures; however, their relationship with LT involvement, reflecting iliopsoas tendon traction, was not clearly demonstrated. Although the factors contributing to the engaged-type fracture remain uncertain, the statistical association between fracture pattern and anterior fracture-line position suggests that capsular structures may play a stabilizing role in select fracture configurations. Further studies are needed to clarify these anatomical interactions. Level of evidence:
- 151 View
- 5 Download

Review Article
- Complications of hand fractures: strategies for prevention and management
- Jong Woo Kang
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2026;39(1):1-11. Published online January 25, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00304

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Various complications can occur after hand fractures. Among them, joint stiffness and malunion are the most common and significant complications, which are often accompanied by tendon adhesions and joint contracture. Careful evaluations of injury characteristics, such as fracture patterns, alignment, and soft tissue injury, are the first step to select appropriate management strategies and prevent complications of hand fractures. Close observation of its clinical prognosis is also essential for early detection and preemptive management of complications. Management of complications includes immobilization, rehabilitation, and various surgical techniques such as tenolysis or capsular release for joint stiffness, corrective osteotomy for malunion, and revisional fixation with bone graft for nonunion. The authors discuss prevention, early recognition, and management strategies for complications of hand fractures in this review.
- 321 View
- 11 Download

Original Articles
- Epidemiological changes and surgical trends of distal radius fractures in adults over 50 years during the COVID-19 pandemic in Korea: a nationwide repeated cross-sectional study
- Han-Kook Yoon, So Ra Yoon, Kee-Bum Hong, Youngsu Jung, SeongJu Choi, Jun-Ku Lee
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2026;39(1):12-19. Published online January 25, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00297

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
The COVID-19 pandemic is likely to have affected bone health in older adults in Korea. This study aimed to analyze changes in the epidemiology and management of distal radius fractures (DRFs) in older adults before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods
Patients with DRF aged over 50 years in 2017, 2018, 2020, and 2021 were included in this study. Patients were classified into a group with DRF occurring between 2017 and 2018 (before COVID-19) and a group with DRF occurring between 2020 and 2021 (during COVID-19). We calculated the incidence rates of DRF and compared them between the two groups. We also analyzed and compared demographic data (age, sex, income, residence) and the operation rate for DRF between the two groups. Patient selection and treatment were based on International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision codes.
Results
A total of 140,634 patients with DRF (before COVID-19, 69,794; during COVID-19, 70,840) were included. The incidence of DRF before COVID-19 (184.4/100,000 person-years) was higher than during COVID-19 (169.8/100,000 person-years). The operation rate was higher during COVID-19 (86.9%) than before COVID-19 (83.3%).
Conclusion
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the incidence of DRF decreased in South Korea. However, the rate of surgical treatment increased and exceeded the global surgical rate. Level of evidence: III.
- 212 View
- 6 Download

- Association between decreased bone mineral density and Pauwels angle in femoral neck fractures: a cross-sectional study
- Soo-Hwan Jung, Yong-Uk Kwon, Ji-Hun Park
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2026;39(1):20-29. Published online January 25, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00269

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Progressive osteoporosis reduces the trabecular structures of the proximal femur, whereas the primary compression trabeculae (PCTs) are relatively preserved. We hypothesize that the loss of the vertically oriented PCTs in osteoporosis, which act as a mechanical barrier, affects fracture line propagation and influences the Pauwels angle. This study investigated the association between bone mineral density (BMD) and Pauwels angles in low-energy femoral neck fractures (FNFs).
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 150 patients (mean age, 75.3 years; range, 50–94 years) diagnosed with intracapsular FNFs between May 2019 and May 2023. BMD was measured within 1 month of the injury date using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, and modified Pauwels angles were assessed using a computed tomography-based multiplanar reconstruction program. Multiple linear regression analysis was performed to evaluate the factors influencing the Pauwels angles. The dependent variable was the Pauwels angle, while the independent variables included sex, age, height, body weight, body mass index, American Society of Anesthesiologists score, Charlson comorbidity index score, smoking status, alcohol use, preinjury walking ability, and femoral neck BMD T-scores.
Results
Higher femoral neck BMD T-scores were significantly associated with increased Pauwels angles (β=3.449, P<0.001). Greater body weight was independently associated with increased Pauwels angles (β=0.213, P=0.007).
Conclusions
The Pauwels angle demonstrated a significant association with BMD, with lower BMD associated with less steep Pauwels angles. In the absence of BMD measurement, the Pauwels angle may indicate osteoporosis severity in patients with low-energy FNFs. Level of evidence: III.
- 137 View
- 4 Download

- Computed tomography plane reformatting to reduce projection error in measuring Pauwels angle of femoral neck fractures: a cross-sectional study
- Gyu Min Kong, Jae-Young Lim, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2026;39(1):38-47. Published online January 25, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00038

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to assess fracture verticality in both coronal and axial planes after eliminating projection error in femoral neck fractures among non-older adults, and to demonstrate its clinical utility using computed tomography (CT)-based modeling at actual size.
Methods
This retrospective observational study enrolled 57 patients (30 males and 27 females), aged 20–65 years, with displaced femoral neck fractures. Based on CT images, an actual-size fracture model was constructed. The CT scanning plane was reformatted with the neck-shaft fragment realigned vertically to the ground and parallel to the femoral neck axis. Three consecutive images were used to generate coronal reformats at the centerline and posterior border to measure central and posterior coronal plane verticality as Pauwels’ angle (PA). The central image of the reformatted axial plane was used to assess axial plane verticality. Differences in verticality were analyzed using analysis of variance.
Results
Three coronal morphology types were identified: linear (n=30), concave (n=25), and convex (n=2). Two axial morphology types were observed: cephalad (n=35) and trochanteric (n=22). The mean central PA, posterior PA, and axial verticality were 55.43°±13.79°, 51.44°±11.13°, and 85.74°±18.41°, respectively. Only the central PA showed a significant difference (P<0.001). The PA was significantly higher in the linear coronal type between images (P<0.05) and in the trochanteric axial type (P<0.05).
Conclusions
After reformatting the scanning plane, the central PA showed significant variation between images. Femoral neck fractures of the linear type in the coronal plane and the trochanteric type in the axial plane demonstrated greater verticality than other morphological types. Level of evidence:
- 147 View
- 4 Download

- Surgical outcomes of the coracoid process fracture associated with the acromioclavicular joint injury in Korea: a case series
- Dongju Shin, Sung Choi, Sangwoo Kim, Byung Hoon Kwack
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2026;39(1):54-61. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00346
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
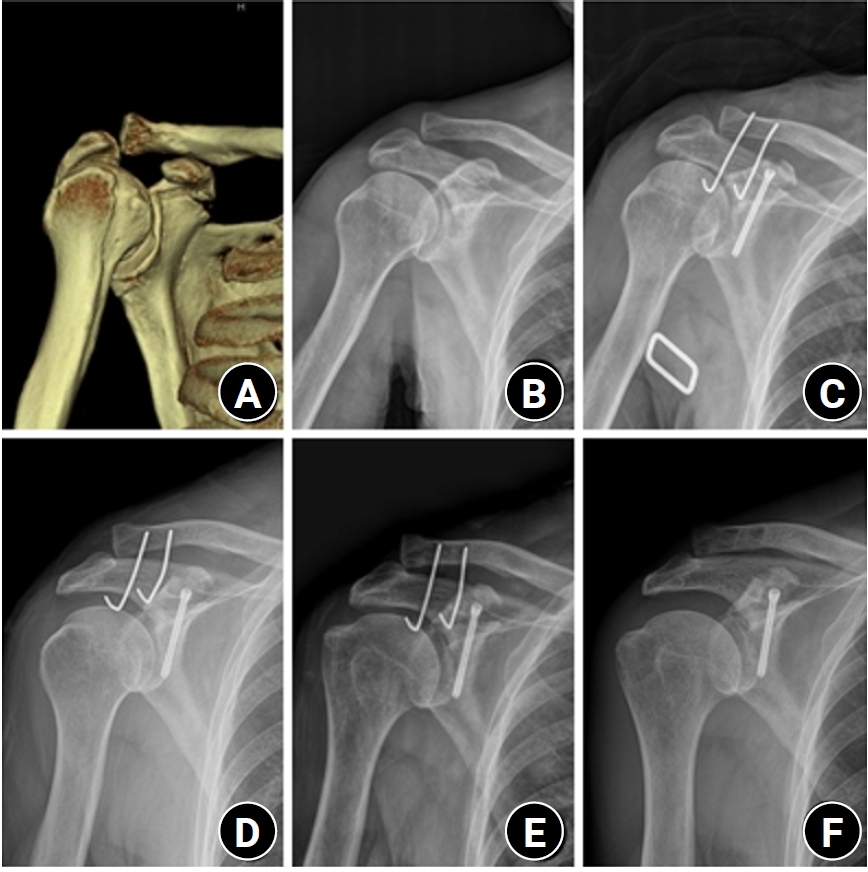
Excluding technical reports and isolated case reports, there are no published studies evaluating coracoid process fixation with or without an acromioclavicular joint (ACJ) stabilization procedure for coracoid process fractures associated with ACJ injury. The purpose of this study was to assess the surgical outcomes of coracoid process fractures associated with ACJ injuries and to determine the usefulness of coracoid process fixation with or without an ACJ stabilization procedure.
Methods
From February 2006 to December 2015, patients with coracoid process fractures associated with ACJ injuries were enrolled. Radiological and clinical outcomes were analyzed in 12 patients who underwent coracoid process fixation with or without an ACJ stabilization procedure. A 3.5-mm cannulated screw with a washer or a 3.0-mm headless compression screw was used for coracoid process fixation, and either a clavicle hook plate or Kirschner (K)-wires were used for ACJ injuries when additional fixation was necessary.
Results
Bone union was achieved in 11 patients (91.7%), while one case was determined to be a nonunion at 6 months. Radiological union occurred at an average of 3 months (range, 1.5–4 months) in all patients except the nonunion case. At the final follow-up, the average clinical scores were a visual analogue scale (VAS) pain score of 1.5 (range, 0–4) and a UCLA score of 30.9 (range, 28–35). Clinical outcomes were satisfactory in all patients, including the patient with nonunion.
Conclusion
The clinical and radiological outcomes of treating coracoid process fractures associated with ACJ injuries using coracoid process fixation with or without ACJ stabilization were favorable. A cannulated screw with a washer and clavicle hook plate fixation may provide sufficient stability for both the coracoid process fracture and the ACJ injury when feasible. Level of evidence: IV.
- 182 View
- 6 Download

Technical Note
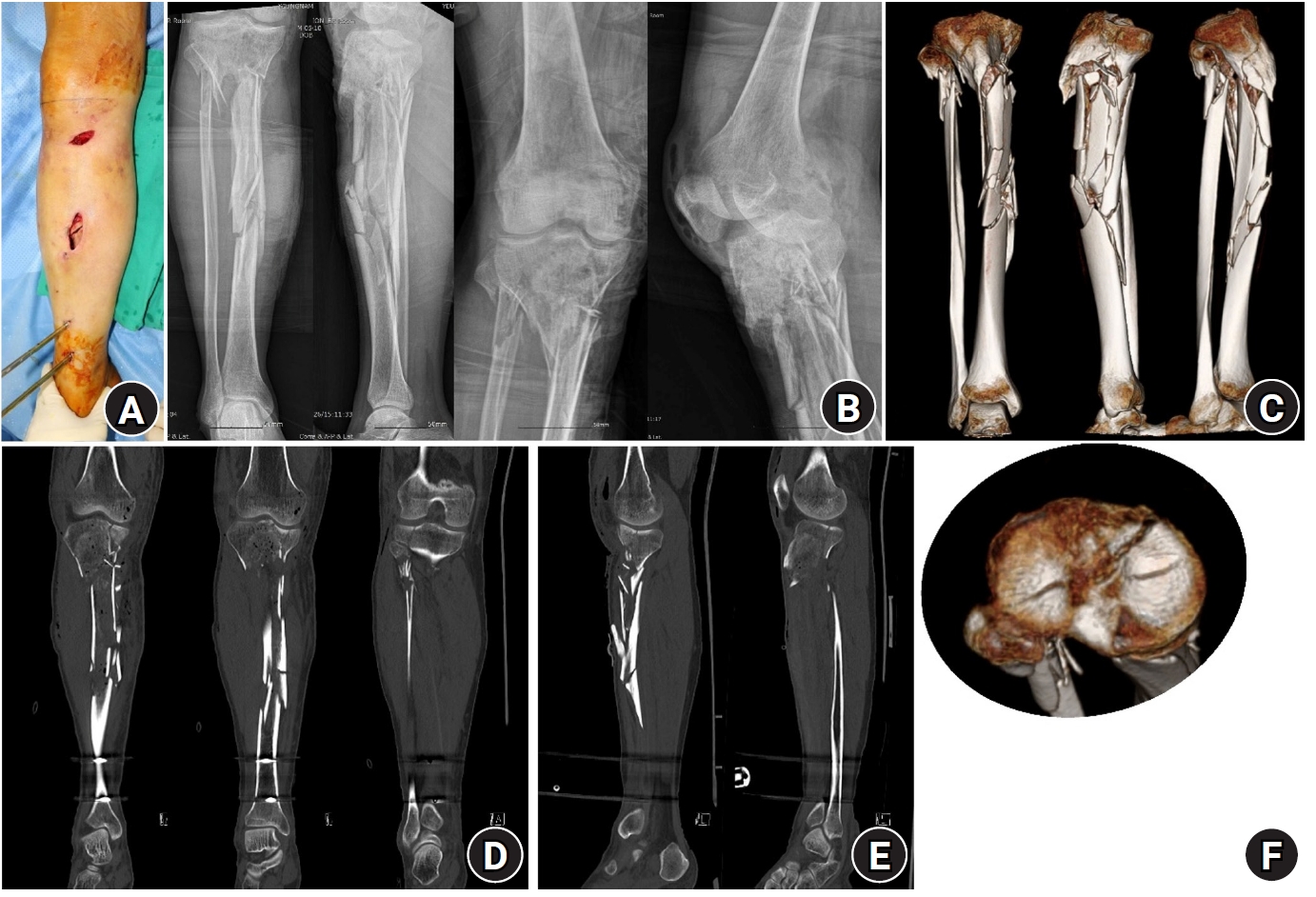
- Rim plate-assisted intramedullary nail and plate combination technique for complex tibial plateau-to-diaphysis fractures: a technical note and case series
- Whee Sung Son
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2026;39(1):62-71. Published online December 4, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00290
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Complex tibial plateau-to-diaphysis fractures present a significant surgical challenge due to their intricate fracture patterns and frequent association with severe soft tissue damage and concomitant injuries. This technical note introduces a novel fixation strategy: the rim plate-assisted intramedullary nail-plate combination (NPC) technique. In this approach, a rim plate simplifies the conventional NPC procedure by unifying the tibial plateau fracture into a single structural segment. This modification eliminates the need to address the articular and diaphyseal components simultaneously while enhancing articular stability. Furthermore, the technique preserves soft tissue integrity and promotes early rehabilitation. Clinical case examples demonstrate its successful application in managing complex tibial plateau-to-diaphysis injuries. Level of evidence: V.
- 521 View
- 22 Download

Original Article
- Comparative results of the femoral neck system versus the dynamic hip screw for stable femoral neck fractures in older adults in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
- Byung-Chan Choi, Byung-Woo Min, Kyung-Jae Lee, Jun-Sik Hong
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):203-211. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00276
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study aimed to compare the clinical and radiological outcomes of the femoral neck system (FNS) and the dynamic hip screw (DHS) for the internal fixation of stable femoral neck fractures in older adults.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study included 48 matched older adult patients based on sex, age, BMI, and osteoporosis status, who had undergone internal fixation with either FNS or DHS for stable femoral neck fractures between January 2010 and December 2022. To minimize selection bias, a 1:1 case-control matching was performed based on sex, age, body mass index (BMI), and the presence of osteoporosis. A total of 48 patients (24 in each group) were included. We compared perioperative data (operation time, hemoglobin change, transfusion rate), functional outcomes using the Koval score, and radiological outcomes, including union rate, femoral neck shortening, and complication rates.
Results
The mean operation time was significantly shorter in the FNS group than in the DHS group (60.9 minutes vs. 70.8 minutes; P=0.007). There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in the union rate (87.5% in FNS vs. 95.8% in DHS), femoral neck shortening, final Koval score distribution, or overall complication rates (12.5% in both groups).
Conclusions
For treating stable femoral neck fractures in older adults, the FNS demonstrated comparable clinical and radiological outcomes to the DHS, with the distinct advantage of a shorter operation time. While these findings suggest that the FNS is a promising and safe alternative that may reduce the surgical burden, definitive conclusions are precluded by the small sample size, warranting further research to corroborate these results. Level of evidence: IV.
- 1,681 View
- 21 Download

Review Article
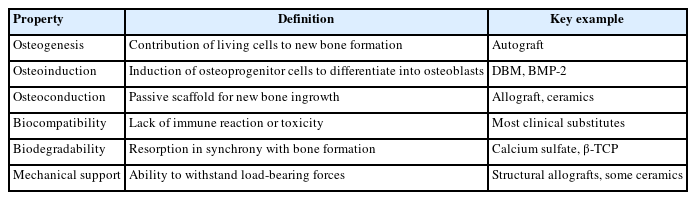
- Current concepts and applications of bone graft substitutes in orthopedic surgery
- Jae Ho Cho, Hyung Keun Song
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):169-177. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00248
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Bone defects, which often arise from high-energy injuries, infections, tumor resections, or nonunions, represent a persistent challenge in orthopedic trauma surgery. Autologous bone grafting remains the gold standard due to its unique combination of osteogenic, osteoinductive, and osteoconductive properties. However, issues such as donor site morbidity, limited graft volume, and increased surgical time have driven the development of bone graft substitutes. These substitutes vary widely in origin, composition, biological activity, and mechanical characteristics, encompassing allografts, xenografts, synthetic materials, and biologically enhanced constructs. This review outlines the fundamental biological principles underlying bone regeneration—including osteogenesis, osteoinduction, and osteoconduction—and addresses additional key factors such as biocompatibility, biodegradability, and mechanical strength. Current bone graft materials are classified by biological origin and functional characteristics, with an emphasis on their use in trauma surgery. Particular attention is given to the clinical applications, indications, and limitations of allograft-based solutions (such as structural allografts and demineralized bone matrix), synthetic ceramics (including calcium phosphate and bioactive glass), and biologically enhanced options, such as recombinant growth factors and stem cell therapies. In trauma settings, graft selection must be tailored to the characteristics of the defect, mechanical demands, the biological environment, and patient-specific factors. Integration with surgical technique and fixation is crucial for optimizing outcomes. Although modern substitutes show promise, none fully replicate the complex biology of autografts. Looking ahead, emerging technologies such as 3D printing, nanotechnology, and smart biomaterials offer exciting possibilities but face translational challenges. This review aims to provide practicing orthopedic surgeons with a concise, evidence-based overview of bone substitute options and their roles in trauma care. By applying core biological principles and clinical judgment, surgeons can better navigate the expanding array of graft materials to improve outcomes for patients with complex skeletal defects.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Safety and Efficacy of rhBMP-2 for Treating Acute Traumatic Fractures of the Upper and Lower Extremities: A Multicenter Prospective Study
Seungyeob Sakong, Seokjun Hong, Wonseok Choi, Seonghyun Kang, Jae-Woo Cho, Whee Sung Son, Jeong-Seok Choi, Chang-Jin Yon, Won-Tae Cho, Jong-Keon Oh
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2026; 15(3): 1176. CrossRef
- Safety and Efficacy of rhBMP-2 for Treating Acute Traumatic Fractures of the Upper and Lower Extremities: A Multicenter Prospective Study
- 4,310 View
- 100 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- Hook plate versus periarticular-type volar locking plate for distal radius fractures involving the volar lunate facet in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
- Hyun-Jae Park, Joo-Hak Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):221-228. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
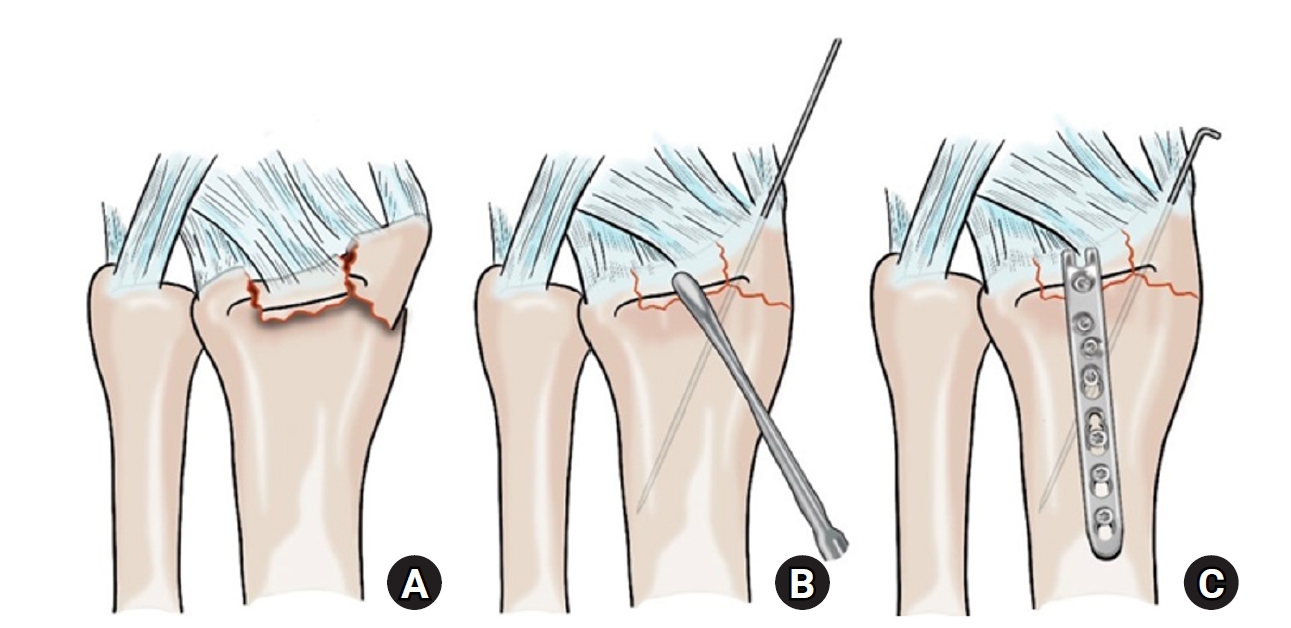
PDF - Background
This study investigated the clinical and radiographic outcomes of hook plate (HP) fixation for volar lunate facet fractures, comparing them with periarticular-type volar locking plates (PVLPs).
Methods
A retrospective review was conducted on 24 patients with distal radius fractures involving volar lunate facet fragments who underwent surgery between January 2016 and April 2021. Patients were divided into two groups: HP (n=12) and PVLP (n=12). Radiographic union, wrist range of motion, Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH) scores, and implant-related complications were compared. Statistical analyses included the Mann-Whitney U test and Fisher exact test.
Results
Radiographic union was achieved in all patients (100%), without secondary displacement or hardware failure. No significant differences were observed between the two groups in wrist flexion (P=0.152), extension (P=0.832), pronation (P=0.792), or supination (P=0.328). The mean DASH scores were 12.8±5.5 in the HP group and 14.6±6.0 in the volar plate group (P=0.449). One patient in the HP group experienced mild flexor tendinopathy that resolved with conservative management. No cases of tendon rupture or early reoperation were reported.
Conclusions
Fixation of volar lunate facet fractures using a HP yielded clinical and radiographic outcomes comparable to those of PVLPs, with a low rate of complications and reliable bony union. Due to its mechanical stability, compatibility with standard surgical approaches, and low risk of flexor tendon irritation, the HP may serve as a valuable alternative for managing volar lunate facet fractures. Level of evidence: IV.
- 381 View
- 11 Download

- Relationship of lateral malleolar fracture patterns to posterior malleolar fracture morphology in supination-external rotation ankle fractures in Korea: a retrospective cohort stduy
- Jong-Eun Kim, Chan-Jin Park, Jun-Young Lee, Keun-Bae Lee, Gun-Woo Lee
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):212-220. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00234
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
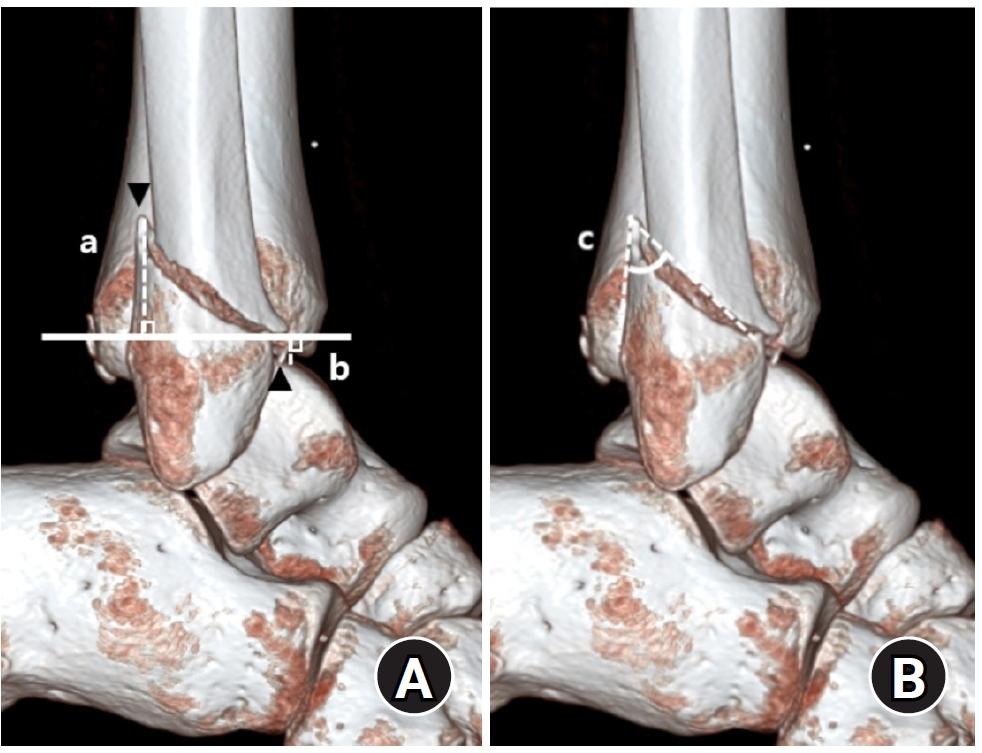
PDF - Background
Posterior malleolar fractures frequently accompany rotational ankle fractures. However, the morphological relationship between lateral and posterior malleolar fractures in supination-external rotation (SER) ankle fractures remains unclear. This study aimed to classify lateral malleolar fracture patterns in SER type 3 and 4 ankle fractures and investigated their associations with posterior malleolar fracture morphology.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 132 patients with SER type 3 or 4 ankle fractures and concurrent posterior malleolar fractures between January 2016 and December 2021. Lateral malleolar fractures were categorized as fibular fractures extending <4.5 cm proximal to the ankle joint (102 ankles) or fibular fractures extending ≥4.5 cm proximal to the ankle joint (30 ankles) based on posterior cortex height measured using three-dimensional computed tomography (3D-CT). Posterior malleolar fracture morphology was assessed using the Haraguchi and Bartonicek classifications. Quantitative parameters—including fracture height, angle, and articular involvement—were analyzed using 3D-CT imaging.
Results
Fibular fractures extending ≥4.5 cm proximal to the ankle joint were associated with a significantly higher frequency of Haraguchi type II and Bartonicek types 3 and 4 posterior malleolar fractures. This group also exhibited greater articular involvement (19.2% vs. 12.0%) and posterior cortical height (55.4 mm vs. 24.8 mm) compared to the <4.5 cm group (all P<0.001).
Conclusions
In SER type 3 and 4 ankle fractures, a fibular fracture extending ≥4.5 cm proximal to the ankle joint may be associated with posterior malleolar fractures exhibiting greater articular involvement and medial extension. Preoperative evaluation of the lateral malleolar fracture pattern may provide useful insights into posterior malleolar morphology and assist in surgical planning. However, these findings should be interpreted with caution due to inherent study limitations. Level of evidence: IV
- 981 View
- 20 Download

- Correlation of bone mineral density with ankle fractures in older adults in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
- Seung Hyun Lee, Chae Hun Lee, Seo Jin Park, Jun Young Lee
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):186-192. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00150
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Bone mineral density (BMD) is well-documented in relation to fractures of the spine, hip, distal radius, and proximal humerus; however, its correlations with other fracture types are less established. This study aimed to analyze BMD and associated risk factors in older adults (≥65 years of age) with osteoporotic ankle fractures. These fractures involve low-energy trauma, resulting from falls from a standing height or lower, and occur from impacts which typically do not cause fractures in individuals with normal bone.
Methods
This retrospective study analyzed data from 1,411 patients diagnosed with ankle fractures admitted to Chosun University Hospital between February 2012 and April 2023. After applying inclusion criteria (age ≥65 years; low energy ankle fracture) and exclusion criteria (high energy trauma, open/multiple fractures, missing dual X-ray absorptiometry [DXA]), 73 of 1,411 patients were analyzed. Lumbar spine, femoral neck, and total hip T scores were obtained with a Horizon Wi DXA scanner, and associations with age, sex, mechanism of injury, comorbidities, smoking status, alcohol consumption, body mass index (BMI), and history of fractures were tested by ANOVA with Scheffe post hoc and Fisher exact tests.
Results
Lower BMD correlated significantly with older age, female sex, and lower BMI (P<0.05) in older adults with ankle fractures. No significant associations were observed for comorbidities (diabetes, hypertension, dementia), smoking, alcohol consumption, injury mechanism, or prior fractures.
Conclusion
These results indicate that older age, female, and lower BMI are linked to reduced BMD in ankle fracture patients over 65 years of age. Focused osteoporosis screening and management may therefore be most beneficial for older, low BMI women presenting with ankle fractures. Level of evidence: IV.
- 896 View
- 2,147,483,670 Download

- Risk factors for ankle fractures in older adults based on clinical components of the Fracture Risk Assessment (FRAX) tool and comorbidities in Korea: a retrospective case-control study
- Myeong Jun Song, Se Woong Jang, Jun Young Lee, Seojin Park
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):193-202. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Ankle fractures are common in older adults; however, their relationship with osteoporotic fractures remains unclear. This study aimed to evaluate potential risk factors for ankle fractures in older adults by analyzing individual clinical components of the Fracture Risk Assessment (FRAX) tool and comorbidities.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective case-control study including 84 patients aged ≥65 years with ankle fractures and 150 controls who underwent bone mineral density (BMD) testing without prior ankle fractures. The variables analyzed included age, sex, body mass index, smoking, alcohol consumption, prior fracture history, and comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and dementia. BMD was measured at the spine, total hip, and femoral neck.
Results
Univariate analysis showed that alcohol consumption, diabetes mellitus, and total hip T-score categories were significantly associated with ankle fractures. In binary logistic regression, alcohol consumption remained significantly associated with higher ankle fracture risk (odds ratio [OR], 5.302; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.778–15.811; P=0.003), and both osteopenia and osteoporosis at the total hip were also associated with increased risk (OR, 3.260, P=0.049; OR, 3.561, P=0.031, respectively). Diabetes mellitus did not reach statistical significance in the adjusted model (P=0.074). Model fit was adequate (Hosmer-Lemeshow P=0.377), and post hoc power analysis confirmed sufficient sample size.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that lower total hip BMD and alcohol-related factors may be associated with ankle fracture risk in older adults. The FRAX score itself was not calculated; instead, this study focused on analyzing selected clinical components. Limitations include the retrospective design, lack of fall and medication data, and cross-sectional BMD assessment. Level of evidence: III.
- 1,164 View
- 22 Download

Review Article
- Atypical ulnar fractures: a narrative review of current concepts and a case of bilateral surgical management
- Chi-Hoon Oh, Hyun Tak Kang, Jun-Ku Lee
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):124-132. Published online July 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00227
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
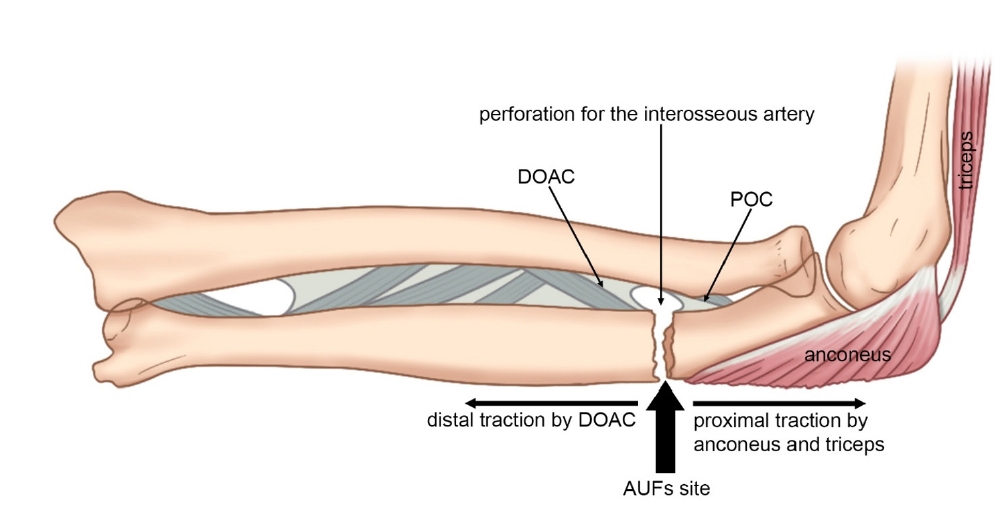
PDF - Atypical ulnar fractures (AUFs) are rare complications that are often linked to long-term antiresorptive therapy. Although atypical femoral fractures are well-studied, AUFs lack standardized diagnostic and treatment protocols. This review summarizes current knowledge on AUFs, including their pathophysiology, diagnostic criteria, and management. A case of bilateral AUFs treated with two distinct osteosynthesis methods is presented, emphasizing the principles of biological healing and mechanical stabilization.
- 1,520 View
- 47 Download

Original Articles
- Risk factors of surgical complications after use of the femoral neck system: a random forest analysis
- Chul-Ho Kim, Hyun-Chul Shon, Han Soul Kim, Ji Wan Kim, Eic Ju Lim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):160-167. Published online July 23, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00157
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The femoral neck system (FNS), a novel fixation device for managing femoral neck fractures (FNFs), has gained popularity in recent years. However, analyses of the surgical complications and reoperation risks associated with the use of FNS remain limited.
Methods
This retrospective observational study analyzed 57 patients who had undergone FNS fixation for FNF at two university hospitals between July 2019 and February 2024. Demographic, perioperative, and outcome variables, including age, sex, fracture classification (Garden, Pauwels, and AO), implant characteristics, tip-apex distance (TAD), neck shortening, and neck-shaft alignment, were analyzed. In addition to univariate analysis, a machine learning analysis was conducted using a random forest classifier with stratified sampling (80% training, 20% testing). The accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and area under the receiver’s operating curve were calculated to assess model performance.
Results
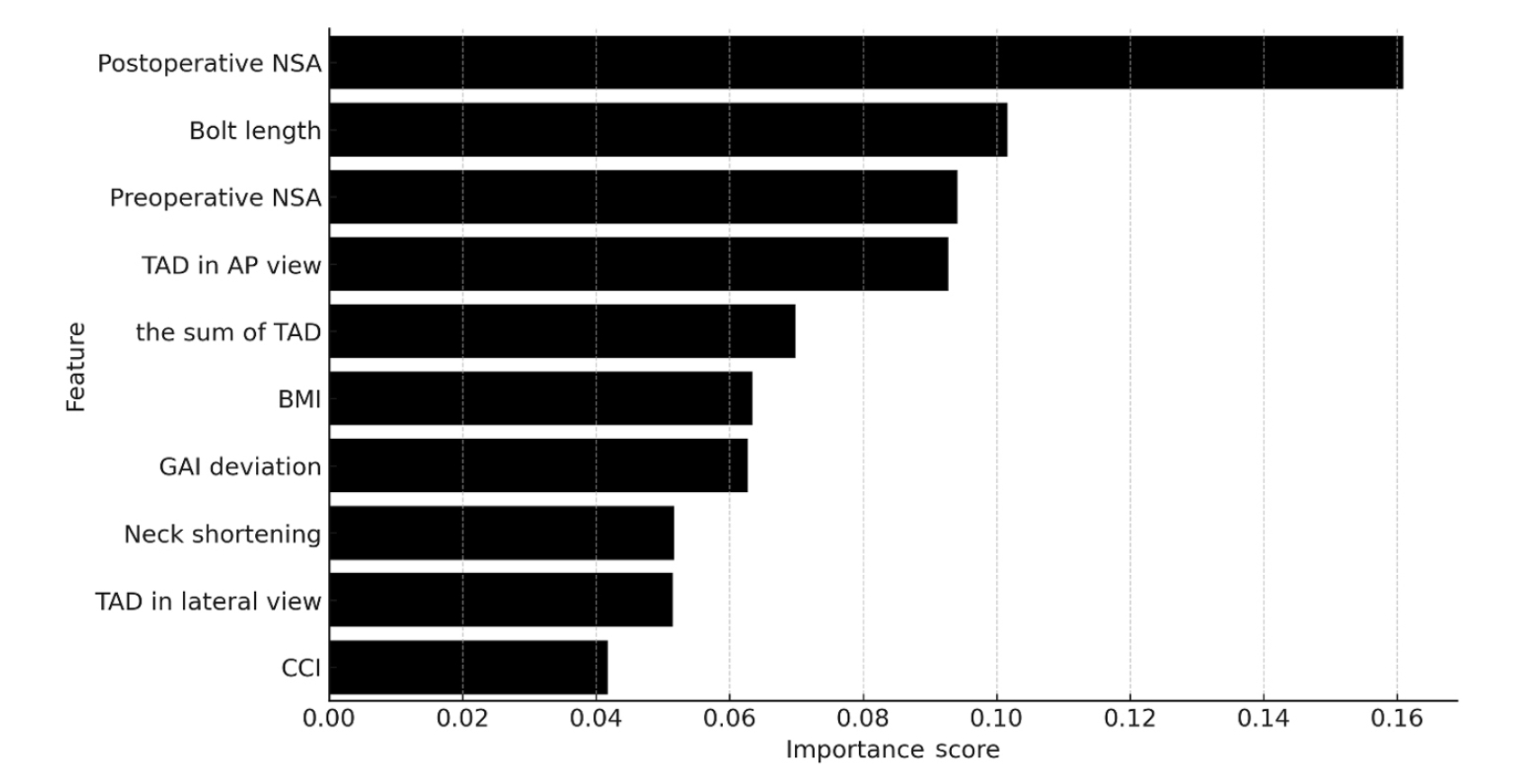
Ten patients experienced osteonecrosis of the femoral head (n=6), implant cut-out or penetration (n=3), and peri-implant fracture (n=1). Univariate analysis revealed that the TAD in the complication group was significantly shorter than that in the control group (12.1 vs. 16.7 mm; P=0.012). Additionally, neck shortening in the complication group was greater than that in the control group (4.9 vs. 2.3 mm; P=0.011). The random forest model achieved an accuracy of 83.3% and identified postoperative neck-shaft angle (NSA) as the most important predictor of complications (feature importance, 0.161), followed by bolt length (0.102) and preoperative NSA (0.094).
Conclusions
Risk factor analysis conducted using a random forest model identified postoperative NSA as the most important feature associated with postoperative complications following FNS. Therefore, care should be taken to normalize the postoperative NSA during FNF surgery. Level of Evidence: III. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Length-stable fixation reduces femoral neck shortening in unstable femoral neck fractures: A retrospective comparative study of length-stable dynamic hip screw versus femoral neck system fixation
Seonghyun Kang, Wonseok Choi, Jeong Seok Choi, Eic Ju Lim, SungJin Ahn, Jong-Keon Oh, William T. Kent, Whee Sung Son, Jae-Woo Cho
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Length-stable fixation reduces femoral neck shortening in unstable femoral neck fractures: A retrospective comparative study of length-stable dynamic hip screw versus femoral neck system fixation
- 1,226 View
- 43 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
- Jae-Ang Sim, Chul-Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):152-159. Published online July 22, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00171
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
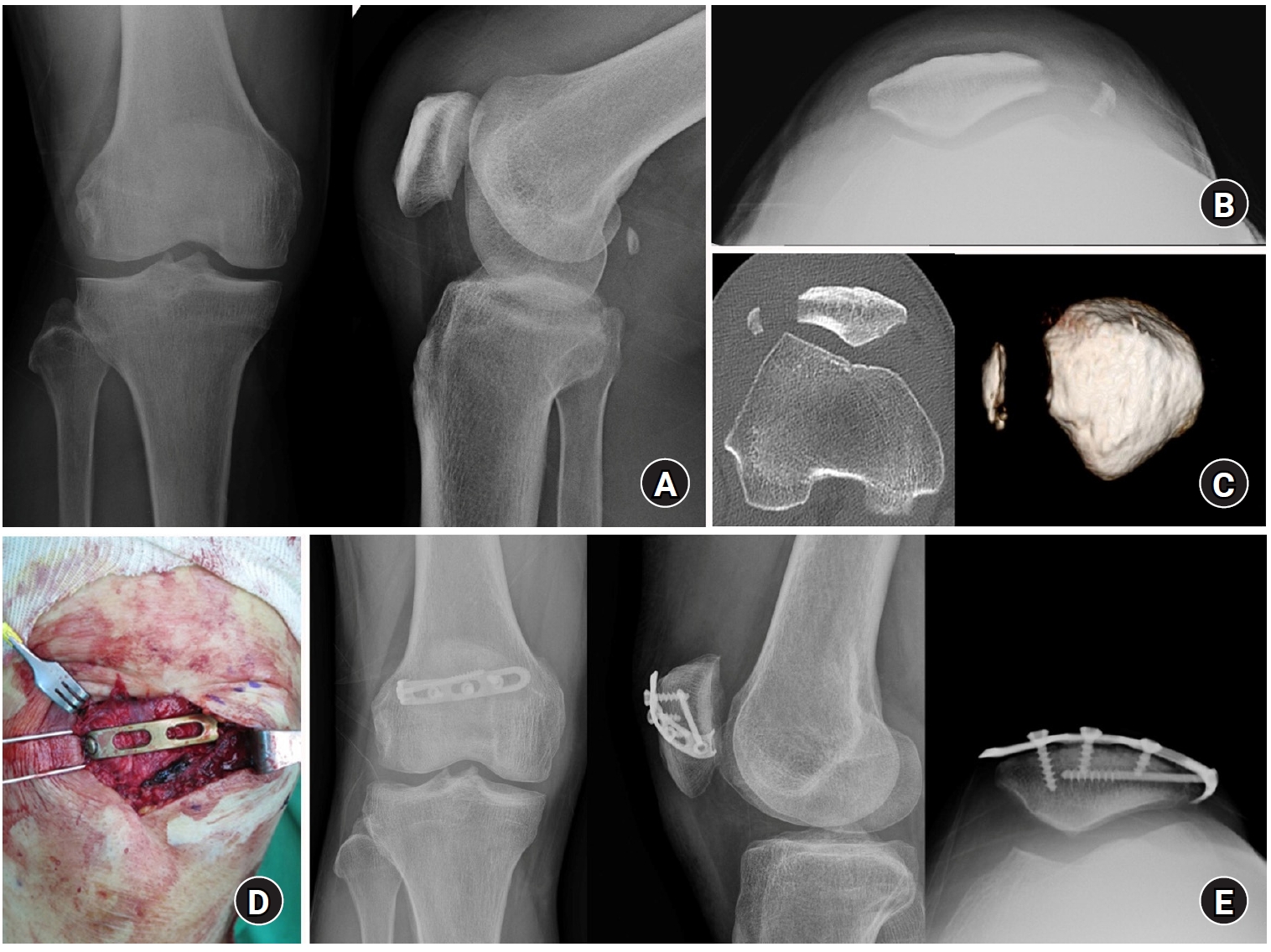
This study investigated the characteristics of lateral marginal fractures of the patella and evaluated the clinical outcomes.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed all patients with lateral marginal fractures of the patella, defined as a vertical fracture line within 15 mm of the lateral patellar border, from 2008 to 2020. In total, 41 patients were included. Patient characteristics, radiologic findings, and clinical outcomes, including the Lysholm score at 1 year postoperation, were evaluated.
Results
The injury mechanisms were direct in 34 cases and indirect in seven. Furthermore, 85% of patients had a skyline view of the patella at the initial visit, and one medial subluxation of the patella was found. Forty of the 41 patients underwent surgery. Anatomical and nonanatomical (>1-mm displacement or excision) reductions were carried out in 36 cases (88%) and five cases (12%), respectively. The average Lysholm score was 89.1 (range, 67–99). The nonanatomical reduction group had a poorer functional score (79.8 vs. 90.4; P=0.010). Lateral patellar compression syndrome occurred in two patients with nonanatomical reduction.
Conclusions
Lateral marginal fractures of the patella affected patellofemoral stability. Anatomical reduction showed good functional outcomes, while nonanatomical reduction was associated with patellofemoral stability and pain. Therefore, surgeons should perform anatomical reduction with any appropriate fixation method. Level of Evidence: IV
- 1,312 View
- 26 Download

Review Article
- Current concepts in the management of phalangeal fractures in the hand
- Hyun Tak Kang, Jun-Ku Lee
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):109-123. Published online July 22, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00136
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
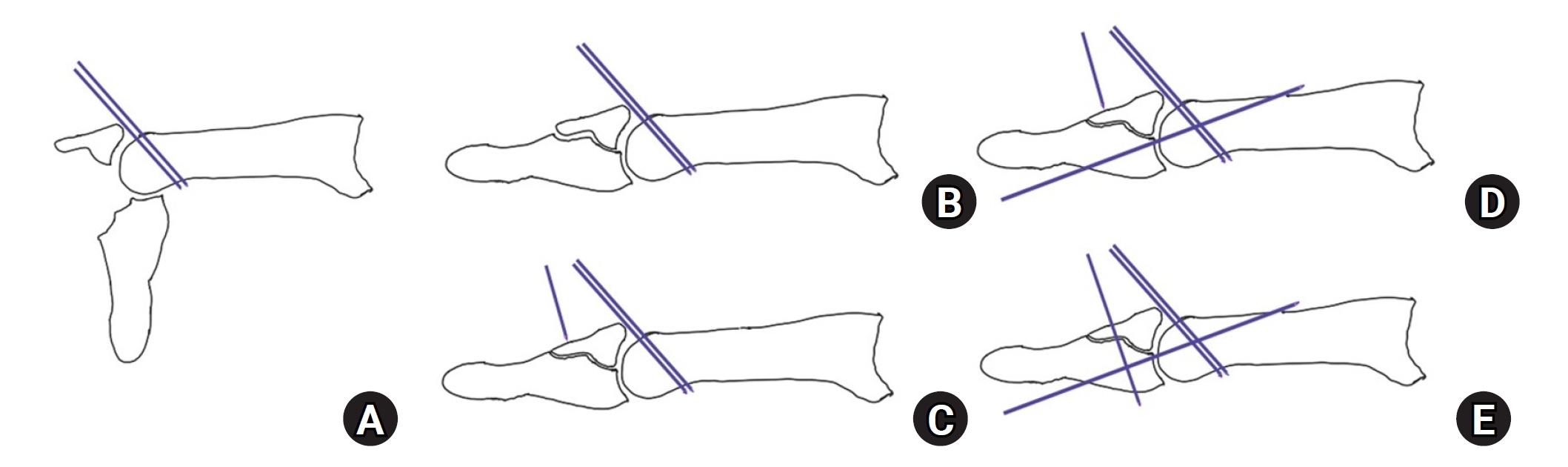
PDF - This review focuses on the treatment of hand fractures based on the anatomical location of the fractured phalanx, excluding the thumb, and examines recent studies on the topic. The main points are as follows: in most cases of hand fractures, conservative treatment should be prioritized over surgical intervention. The three key factors in determining whether surgical treatment is necessary are (1) whether the fracture is intraarticular, (2) the stability of the fracture itself, and (3) the extent of damage to surrounding soft tissues. The primary surgical treatment is closed reduction and Kirschner-wire fixation. The risk of rotational deformity increases with fractures closer to the proximal region. Intra- articular fractures may lead to subsequent stiffness and arthritis; thus, computed tomography is recommended to assess the fracture pattern. Anatomic reduction of intraarticular fragments is required, along with correction of the inherent joint instability. No surgical method has proven to be superior; it is advantageous for the surgeon to choose a surgical approach they are familiar with and confident in, based on the specific fracture and patient factors. Complications in hand fractures are various; the most frequent is stiffness, and nonunion is uncommon. Early joint motion is crucial in minimizing the risk of stiffness.
- 17,306 View
- 378 Download

Original Articles
- Computational simulation of coracoclavicular screw insertion through the superior distal clavicular plate for clinical applications in Korean cadavers
- Hyung-Lae Cho, Ji Han Choi, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):143-151. Published online July 22, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00122
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
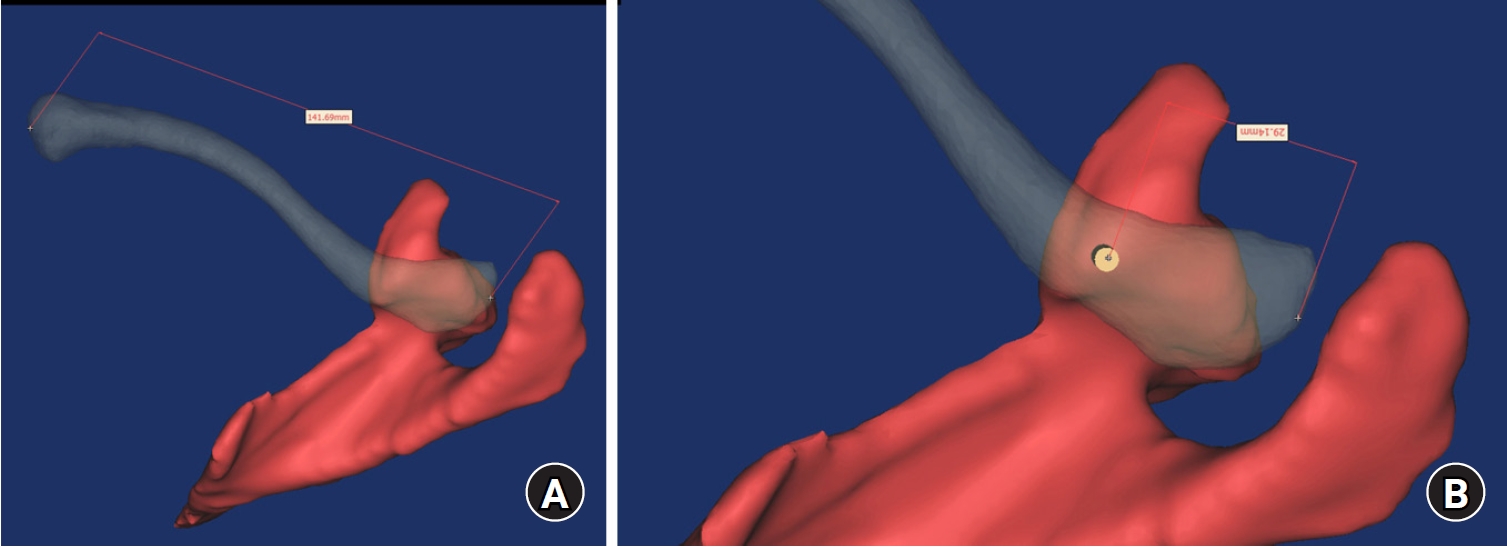
The study was conducted to determine the practical area for inserting the coracoclavicular (CC) screw through the plate by analyzing three-dimensional (3D) shoulder models featuring virtually implanted, actual-size plates and screws.
Methods
Ninety cadaveric shoulders (41 males and 49 females) underwent continuous 1.0-mm slice computed tomography scans. The data were imported into image-processing software to generate a 3D shoulder model, including the scapula and clavicle. The overlapping area between the clavicle and the horizontal portion of the coracoid process (horizontal portion_CP) was analyzed in the cranial view. A curved pelvic recon plate was virtually placed on the upper surface of the distal clavicle, and an actual-size (3.5 mm) CC screw was inserted through the plate.
Results
The distal clavicle directly overlapped with the horizontal portion_CP in the vertical direction. The overlapping area was sufficient to place the 3.5 mm and 4.5 mm-sized screws. In all shoulder models, the CC screw could be inserted through the plate into the vertical direction, with an average length of 35.5 mm (range, 26.2–62.5 mm; standard deviation, 1.2 mm). In 87 models, the CC screw was inserted through the third hole from the lateral end of the plate. Two models were inserted through the second hole, and one model through the fourth hole.
Conclusions
The upper surface of the clavicle has sufficient overlapping area to place CC screws through the plate in the vertical direction in the corresponding hole. Supplemental CC screw fixation through the plate can be performed without additional or special equipment. Level of evidence: IV
- 670 View
- 22 Download

- Biomechanical finite element analysis of a femoral neck system fixation construct for femur neck fractures and clinical implications
- Hoon-Sang Sohn, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):133-142. Published online July 22, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00108
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
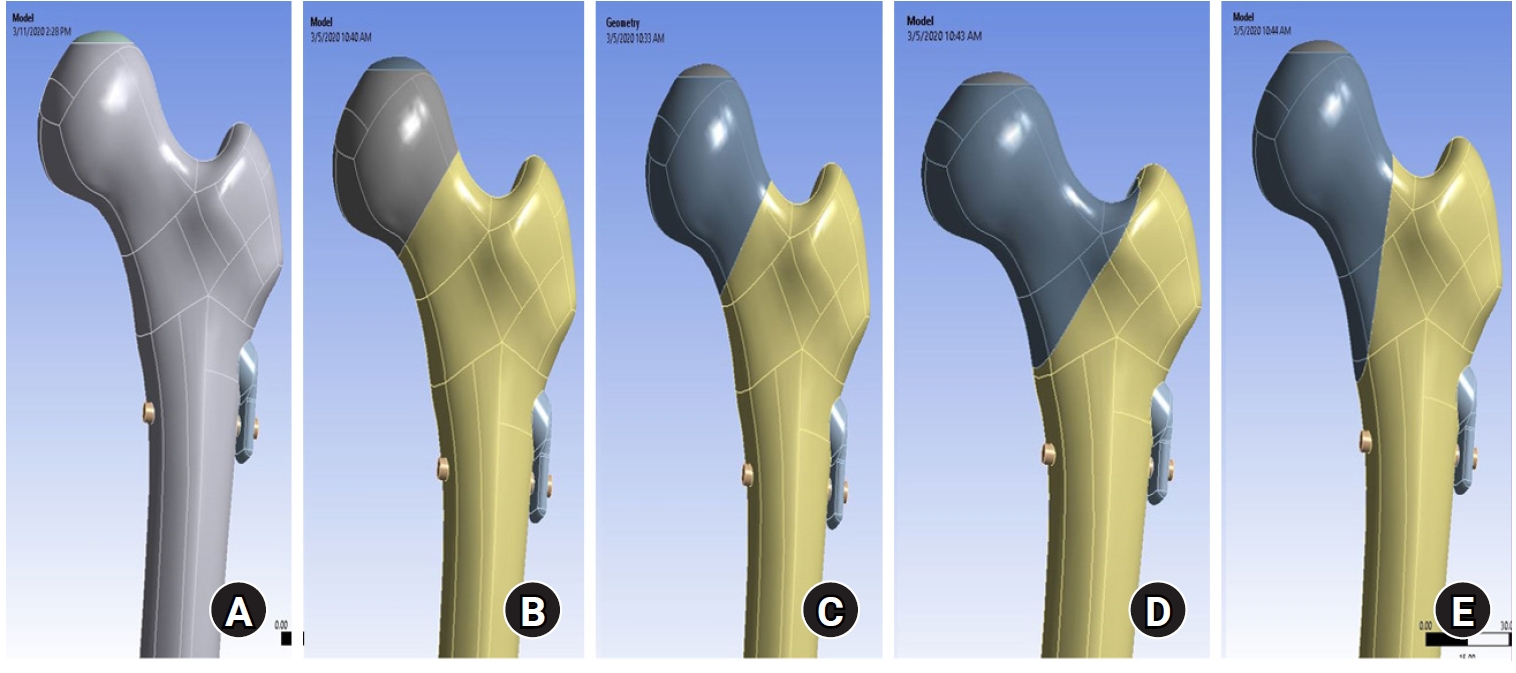
PDF - Background
This study assessed the structural/mechanical stability of fixation constructs with a femoral neck system (FNS) via finite element analysis after simulating femoral neck fractures and explored the clinical implications.
Methods
We simulated subcapital, transcervical, basicervical, and vertical fracture models using a right femur (SAWBONES) and imported the implant model of FNS to Ansys (Ansys 19.0, Ansys Inc.) to place the implant in the optimal position. The distal end of the femur model was completely fixed and was abducted 7°. The force vector was set laterally at an angle of 3° and posteriorly at an angle of 15° in the vertical ground. The analysis was conducted using Ansys software with the von Mises stress (VMS) in megapascals (MPa).
Results
The maximum VMS of the fracture site was 67.01 MPa for a subcapital, 68.56 MPa for a transcervical, 344.54 MPa for a basicervical, and 130.59 MPa for a vertical model. The maximum VMS of FNS was 840.34 MPa for a subcapital, 637.37 MPa for a transcervical, 464.07 MPa for a basicervical, and 421.01 MPa for a vertical model. The stress distribution of basicervical and vertical fractures differed significantly, and the basicervical fracture had higher VMS at the bone, implant, and fracture sites.
Conclusions
FNS fixation should be performed with consideration the osseous anchorage in the femoral head, and this technique might be appropriate for vertical fractures. Regarding the VMS at the fracture site, FNS might be applied cautiously only to basicervical fractures with anatomical reduction without a gap or comminution. Level of evidence: IV. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Finite element analysis of screw thread geometry and titanium plate materials in internal fixation of the human femur
Abdessamed Bachiri, Mustapha Amine Arab, Nadia Kadouri
Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering.2026; : 1. CrossRef
- Finite element analysis of screw thread geometry and titanium plate materials in internal fixation of the human femur
- 1,926 View
- 82 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Articles
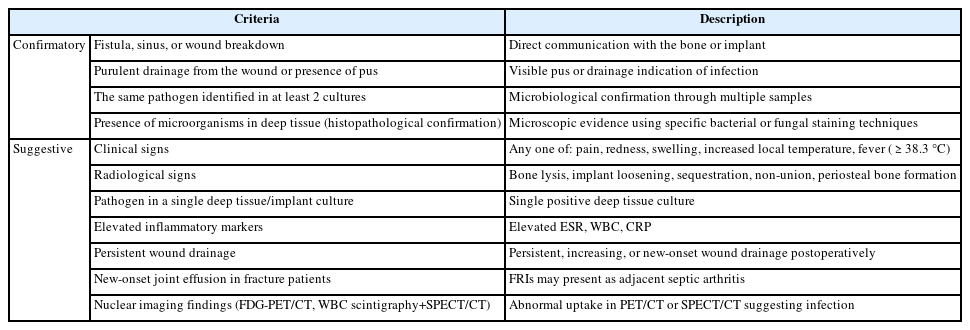
- Fracture-related infections: a comprehensive review of diagnosis and prevention
- HoeJeong Chung, Hoon-Sang Sohn
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):86-95. Published online April 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00164
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fracture-related infections are challenging complications in orthopedic trauma that often require prolonged treatment and impose a significant healthcare burden. Accurate diagnosis and effective prevention strategies are essential for minimizing their occurrence. A recent international consensus has established standardized diagnostic criteria based on clinical, microbiological, radiological, and histopathological findings. Prevention is the top priority and involves a thorough preoperative risk assessment, along with glycemic control, nutritional optimization, and management of comorbidities, as well as intraoperative and postoperative measures such as appropriate antibiotic prophylaxis, surgical site antisepsis, and meticulous wound care. A multidisciplinary approach involving orthopedic surgeons, infectious disease specialists, and microbiologists is crucial for successfully reducing the burden of fracture-related infections.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Personalized Approaches to Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies in Periprosthetic Fracture-Related Infections (PFRIs): Case Series and Literature Review
Marianna Faggiani, Marco Zugnoni, Matteo Olivero, Salvatore Risitano, Giuseppe Malizia, Silvia Scabini, Marcello Capella, Stefano Artiaco, Simone Sanfilippo, Alessandro Massè
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2025; 15(12): 576. CrossRef - Pathogen-Specific Risk for Iterative Surgical Debridement in Orthopedic Infections: A Prospective Multicohort Analysis
Flamur Zendeli, Anna Jędrusik, Raymond O. Schaefer, David Albrecht, Michael Betz, Felix W. A. Waibel, Tanja Gröber, Nathalie Kühne, Sören Könneker, İlker Uçkay
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(24): 8750. CrossRef
- Personalized Approaches to Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies in Periprosthetic Fracture-Related Infections (PFRIs): Case Series and Literature Review
- 6,755 View
- 273 Download
- 2 Crossref

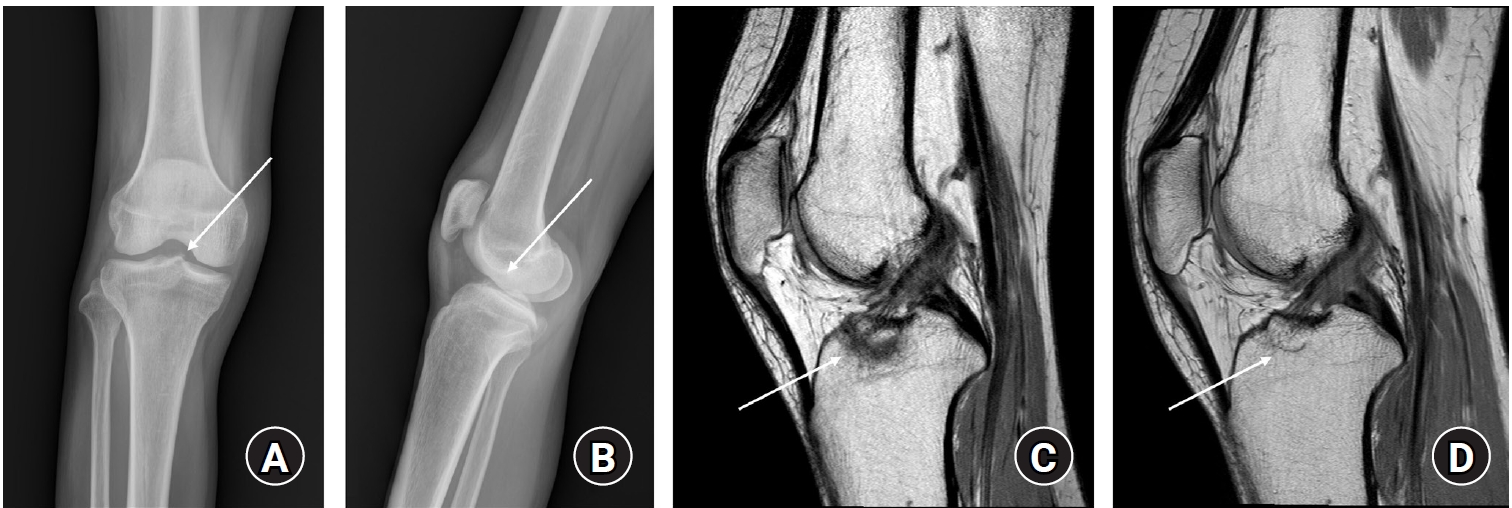
- Treatment of avulsion fractures around the knee
- Jeong-Hyun Koh, Hyung Keun Song, Won-Tae Cho, Seungyeob Sakong, Sumin Lim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):63-73. Published online March 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00073
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fractures of the knee occur when tensile forces cause a bone fragment to separate at the site of soft tissue attachment. These injuries, which frequently affect adolescent athletes, can involve the cruciate and collateral ligaments, arcuate complex, iliotibial band, and patellar and quadriceps tendons. Radiographs aid in the initial diagnosis, while computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging facilitate a comprehensive evaluation of injury severity and concomitant damage. Specific avulsion fracture types include: anterior cruciate ligament avulsions (tibial site, Meyers and McKeever classification), posterior cruciate ligament avulsions (tibial attachment, Griffith's classification), Segond fractures (anterolateral complex injury), iliotibial band avulsions, medial collateral ligament avulsions (reverse Segond, Stieda fractures), arcuate complex avulsions ("arcuate sign"), medial patellofemoral avulsions (patellar dislocations), and patellar/quadriceps tendon avulsions. The treatment depends on the fracture location, displacement, and associated injuries. Non-displaced fractures can be managed conservatively, while displaced fractures or those with instability require surgical reduction and fixation. Prompt recognition and appropriate intervention prevent complications such as deformity, nonunion, malunion, and residual instability. This review provides an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management of knee avulsion fractures to guide clinical decision-making.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
Jae-Ang Sim, Chul-Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(3): 152. CrossRef
- Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
- 18,938 View
- 205 Download
- 1 Crossref

- How to obtain the desired results from distal tibial nailing based on anatomy, biomechanics, and reduction techniques
- Jungtae Ahn, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):74-85. Published online March 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00024

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Distal tibial metaphyseal fractures are commonly caused by high-energy injuries in young men and osteoporosis in older women. These fractures should be clearly distinguished from high-energy pilon fractures. Although the optimal surgical intervention methods for distal tibial metaphyseal fractures remain uncertain and challenging, surgical treatments for nonarticular distal tibia fractures can be broadly divided into two types: plate fixation and intramedullary nail (IMN) fixation. Once functional reduction is achieved using an appropriate technique, distal tibial nailing might be slightly superior to plate fixation in reducing postoperative complications. Thus, the surgical strategy should focus on functional realignment and proceed in the following sequence: (1) restoring the original tibial length, regardless of whether fibular fixation is to be done; (2) making the optimal entry point through an anteroposterior (AP) projection based on the overlapping point between the fibular tip and lateral plateau margin; (3) placing Kirschner wires (Ø2.4 mm) as blocking pins (in the AP orientation for coronal control and in the mediolateral [ML] orientation for sagittal control) as close to the upper locking hole as possible without causing further comminution on the concave aspect of the short fragment; and (4) making the the distal fixation construct with at least two ML and one AP interlocking screw or two ML interlocking screws and blocking screws. After the IMN is adequately locked, blocking pins (Ø2.4 mm) need to be replaced by a 3.5 mm screw.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Rigid intramedullary nailing with suprapatellar approach for tibial shaft fractures in adolescents with open physes
Jong Wha Lee, Jae Ho Cho, Tae Hun Kim, Hyung Keun Song, Won-Tae Cho, Seungyeob Sakong, Hyunil Choi, Sumin Lim
Injury.2026; : 113130. CrossRef - Impact of Foot Width on Patient-Reported Outcomes Assessed by 3-Dimensional Foot Morphometry in Hallux Valgus
Jungtae Ahn, Dae-Cheol Nam, Gu-Hee Jung
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.2025; 17(6): 1062. CrossRef
- Rigid intramedullary nailing with suprapatellar approach for tibial shaft fractures in adolescents with open physes
- 2,951 View
- 56 Download
- 2 Crossref

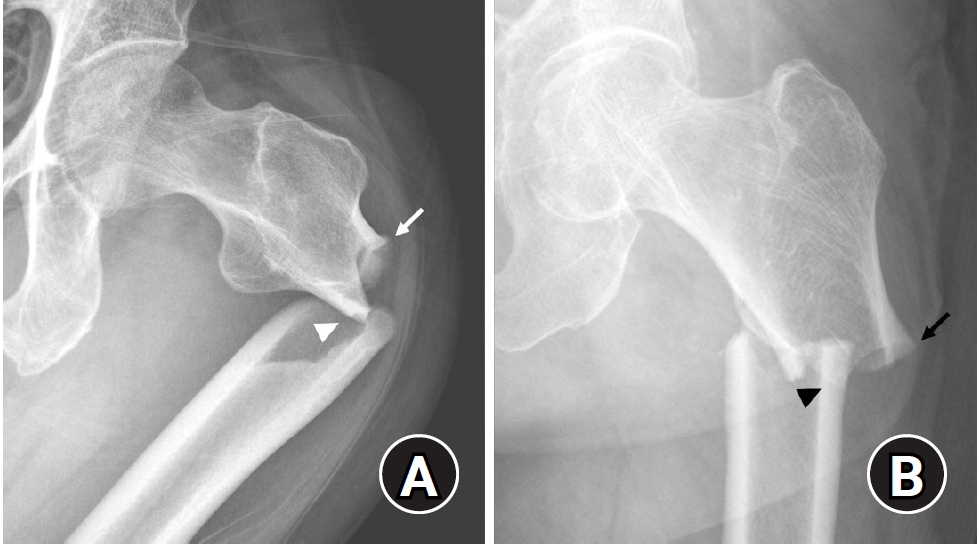
- Atypical femoral fractures: an update
- Won-Tae Cho, Jeong-Hyun Koh, Seungyeob Sakong, Jung-Taek Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):41-52. Published online March 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00031
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This narrative review provides an up-to-date overview of atypical femoral fractures (AFFs), emphasizing diagnostic criteria, epidemiology, pathophysiology, risk factors, and evaluation with screening strategies. AFFs are rare but significant complications associated with prolonged bisphosphonate (BP) therapy for osteoporosis. Although the pathogenesis of AFFs has not been fully elucidated, its primary mechanism is thought to involve impaired bone remodeling, leading to unhealed microfractures that progress to stress fractures under repetitive loading. AFFs can occur in various regions of the femur, influenced by femoral geometry and the lower limb axis. Other risk factors include prolonged steroid use, arthroplasty, genetic predispositions, and metabolic bone disorders. The diagnosis of AFFs is based on criteria established by the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. Key radiographic features include lateral cortical transverse fracture lines and localized cortical thickening, typically with minimal or no comminution on the medial cortex. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for screening tests and magnetic resonance imaging as an advanced imaging modality enable the early detection of incomplete fractures. This multi-modal approach facilitates the prompt identification of prodromal cortical changes, reducing the risk of complete fractures in high-risk populations, particularly patients undergoing prolonged BP therapy. Level of Evidence: V
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Atypical Femur Fractures Without Bisphosphonate Exposure (AFFwB): A Retrospective Report of 21 Cases
Lorenzo Lucchetta, Carmelinda Ruggiero, Samuele Berardi, Alice Franceschi, Michele Bisaccia, Giuseppe Rinonapoli
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 15(1): 25. CrossRef
- Atypical Femur Fractures Without Bisphosphonate Exposure (AFFwB): A Retrospective Report of 21 Cases
- 15,021 View
- 410 Download
- 1 Crossref

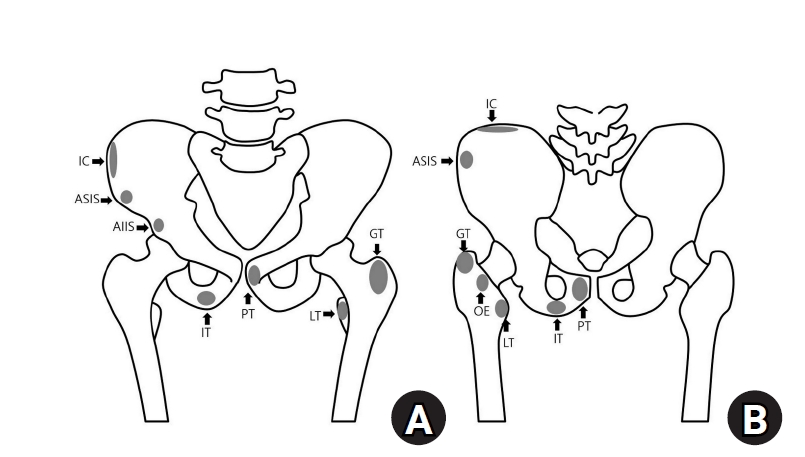
- Avulsion fractures around the hip joint and pelvis
- Won-Sik Choy, Yonghan Cha, Jung-Taek Kim, Jun-Il Yoo, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):53-62. Published online March 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fractures occur when tendons or ligaments are subjected to forces greater than they can withstand at the apophysis or enthesis, regardless of fusion status. The pelvis and hip joint are vulnerable to these injuries due to the diverse muscular structures in these structures, which serve as origins for multiple muscles leading to the lower extremities. Pelvic avulsion fractures commonly affect young athletes, but can also occur in adults. The diagnosis typically involves assessing trauma history, a clinical examination, and radiographic imaging. If the diagnosis is unclear, additional tests such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging may assist in the diagnosis and provide useful information for treatment decisions. While most avulsion fractures respond well to conservative treatment, surgical intervention may be preferred in severe displacements, cases of significant retraction in active athletes, or when a faster recovery is necessary. Chronic or neglected injuries may lead to excessive osseous formation around the pelvis, causing impingement syndromes. Recognizing characteristic radiological findings based on pelvic anatomy helps to make an accurate diagnosis, as chronic injuries can mimic tumors or infectious conditions, necessitating a careful differential diagnosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Avulsion Fracture of the Lesser Trochanter and the Use of Conservative Treatment
Dawid Bartosik, Bartlomiej Cwikla, Anna Kowalczyk, Michalina Loson-Kawalec, Anna Palka-Szymaniec, Bartosz Starzynski, Alina Keska, Jakub Szkuta, Klaudia Wojcik
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Avulsion Fracture of the Lesser Trochanter and the Use of Conservative Treatment
- 9,157 View
- 137 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Article
- Comparison of outcomes of reinforced tension band wiring and precontoured plate and screw fixation in the management of Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures
- Hyun Goo Kang, Tong Joo Lee, Samuel Jaeyoon Won
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):96-101. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00059
- Correction in: J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):168

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures are characterized by significant displacement and comminution, presenting a challenge in selecting the appropriate fixation technique. This study compared the clinical and radiographic outcomes, complications, and reoperation rates of reinforced tension band wiring (TBW) and precontoured plate and screw fixation (PF) in the surgical treatment of Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures.
Methods
This retrospective review analyzed 24 patients diagnosed with Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures, who were treated between 2005 and 2023. Of these, 11 patients underwent reinforced TBW, and 13 received precontoured PF. Clinical outcomes were assessed using Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) scores and the Mayo Elbow Performance Score (MEPS). Radiographic outcomes focused on fracture union. Operative times, complication rates, and reoperation rates were compared between the groups.
Results
Both the reinforced TBW and PF groups achieved satisfactory clinical outcomes, with no significant between-group differences in DASH and MEPS scores (P>0.05). Radiographic union was achieved in all patients. The reinforced TBW group demonstrated a significantly shorter operative time than the PF group (93.6±7.4 min vs. 132.3±13.7 min; P<0.001). Complication rates were similar between the two groups (reinforced TBW, 38.4%; PF, 36.3%), but hardware-related irritation occurred more frequently in the reinforced TBW group. Reoperations were required in 15.8% of the reinforced TBW group due to hardware irritation, whereas no reoperations were necessary in the PF group.
Conclusions
Reinforced TBW and PF are both effective surgical options for managing Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures, yielding comparable clinical and radiographic outcomes. While reinforced TBW offers shorter operative times and lower costs, PF is associated with fewer hardware-related complications. Further prospective studies are needed to optimize treatment strategies for these complex fractures. Level of Evidence: Level III. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Are posterior olecranon locking plates a problem for patients after fracture healing because of prominence?
Reva Qiu, Mallika Makkar, Richard Buckley
Injury.2025; 56(11): 112769. CrossRef
- Are posterior olecranon locking plates a problem for patients after fracture healing because of prominence?
- 2,290 View
- 51 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Article
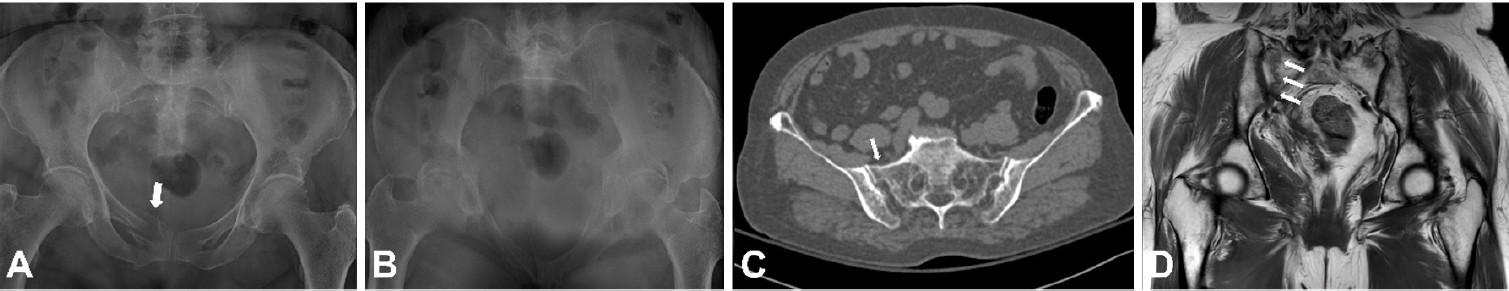
- Easily missed nondisplaced fractures accompanying complete fractures in the lower extremity and pelvis: a narrative review
- Young-Chang Park
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(1):5-12. Published online January 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Nondisplaced fractures accompanying complete fractures are often difficult to detect on plain radiographs or computed tomography scans, posing a diagnostic challenge. The diagnosis of these frequently overlooked injuries can be delayed, potentially leading to suboptimal patient outcomes. This review discusses four commonly missed fracture patterns in the lower extremity and pelvis, including posterior involvement in fragility fractures of the pelvis, intertrochanteric extensions in isolated greater trochanter fractures, ipsilateral femoral neck fractures in high energy femoral shaft fractures, and posterior malleolar fractures in distal spiral tibial shaft fractures. An accurate diagnosis of these accompanying nondisplaced fractures is critical for optimizing surgical outcomes. Surgeons should incorporate thorough preoperative evaluations into their clinical practice to facilitate early detection and appropriate treatment strategies. Prompt identification and comprehensive management remain essential for improving patient outcomes.
- 1,375 View
- 47 Download

Original Articles
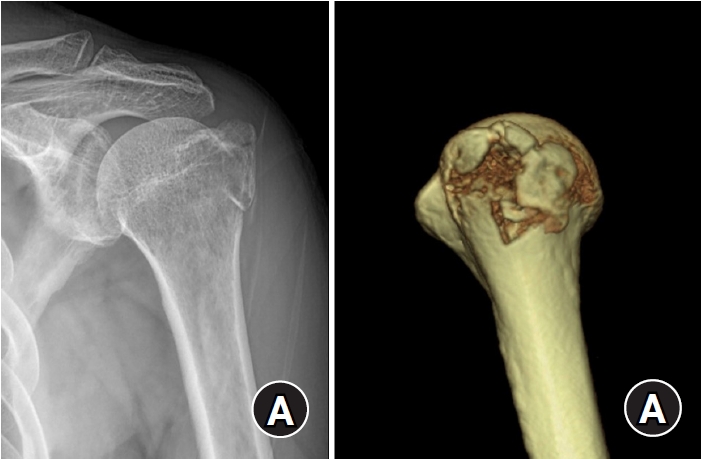
- Outcomes of open reduction and internal fixation using 2.0/2.4 mm locking compression plate in isolated greater tuberosity fractures of humerus
- Sung Choi, Dongju Shin, Sangwoo Kim, Byung Hoon Kwack
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(1):32-39. Published online January 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The purpose of this study was to retrospectively evaluate the radiographic and clinical results of a small single or double low-profile plate fixation of 2.0/2.4 mm locking compression plate (LCP) in treating isolated greater tuberosity (GT) fractures of the humerus. Methods: From June 2015 to October 2022, patients who underwent LCP in treating isolated GT fractures of the humerus were included in this study. The radiological and clinical results were analyzed in 15 patients who underwent open reduction and internal fixation used 2.0/2.4 mm LCP. Results: Bone union was achieved in 14 patients (93.3%) and one failed case was treated with a 2.4 mm single LCP fixation. Radiological union was achieved within 10–20 weeks. Complications occurred in two patients (13.3%), including the reduction failure and shoulder stiffness. At the final follow-up, the average clinical scores were as follows: a visual analog scale for pain of 2.1 (range, 0–5) and a University of California, Los Angeles score of 27.2 (range, 18–31). Regarding range of motion (ROM), the average active ROMs were 142° for forward flexion (range, 120°–150°), 147.1° for abduction (range, 120°– 180°), and 59.3° for external rotation (range, 45°–80°). For internal rotation, the average was observed to reach the 10th thoracic vertebra (range, 1st lumbar vertebra–7th thoracic vertebra). Conclusions: The clinical and radiologic outcomes of treating isolated GT fracture using 2.0/2.4 mm LCP were favorable, and double low-profile plate fixation may be beneficial for sufficient fracture stability if possible. Level of evidence: Level IV, case series.
- 2,045 View
- 59 Download

- Interpositional tricortical iliac bone graft in nonunion of midshaft clavicular fractures
- Eun-Seok Son, Bum-Soon Park, Chang-Jin Yon, Chul-Hyun Cho
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(1):23-31. Published online January 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The purpose of this study was to investigate the radiological and clinical outcomes after interpositional tricortical iliac bone graft with plate fixation for the nonunion of clavicle midshaft fractures. Methods: Between 2007 and 2020, 17 cases who were treated by interpositional tricortical iliac bone graft with plate fixation for the clavicle midshaft nonunion combined with bone defect were investigated. The mean age was 53 years (range, 22–70 years). The mean follow-up period was 102.2 months (range, 18–193 months). Serial plain radiographs were used to evaluate radiological outcomes. The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) score, American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons (ASES) score, and Quick-disabilities of the arm, shoulder, and hand (DASH) score were used to evaluate clinical outcomes. Complications were also evaluated. Results: All cases achieved complete bony union with mean healing time of 17.6 weeks (range, 14–22 weeks). The mean clavicle length difference was significantly decreased from 9.1 mm preoperatively to 2.6 mm postoperatively (P<0.001). The mean UCLA and ASES scores were significantly improved from 18.1 and 52.2 before surgery to 30.6 and 88.6 after surgery (both P<0.001), respectively. The mean final Quick-DASH score was 18.0. Three cases (17.6%) developed postoperative complications including two cases of shoulder stiffness and one case of screw irritation. Conclusions: Interpositional tricortical iliac bone graft with plate fixation for the clavicle midshaft nonunion demonstrated excellent radiological and clinical outcomes. In cases of atrophic nonunion combined with bone defect, this technique is an effective option that can provide structural support and restore clavicle length. Level of evidence: Level IV, case series.
- 2,025 View
- 44 Download

Case Report
- Acute on Chronic Stress Fracture of a Varus Deformed Distal Tibia - A Case Report -
- Seong Kee Shin, Ki Chun Kim, Eli Schmidt, Seung Yeon Cho, Ki Chul Park
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2024;37(4):184-189. Published online October 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2024.37.4.184

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A severe post-traumatic distal tibia vara deformity is an uncommon condition in orthopedics. Typical symptoms include intractable recurrent pain, fragility related to stress fractures over the tensile area, and a limping gait caused by leg length discrepancy. Surgical management should be performed on acute fractures extending from a stress fracture gap. For successful surgical results, deformity correction is important for sustaining axial load bearing for standing and walking. Procedures to manage this condition have been proposed, but there is a high risk of complications, including metal failure, nonunion, and weakness caused by a long period of rehabilitation. In this case, the authors report a successful result using a modified clamshell osteotomy combined with a proximal and distal wedge bone resection in a single stage.
- 1,149 View
- 34 Download

Original Article
- Does the Operator’s Experience Affect the Occurrence of Complications after Distal Radius Fracture Volar Locking Plate Fixation? A Comparative Study of the First Four Years and Thereafter
- Kee-Bum Hong, Chi-Hoon Oh, Chae Kwang Lim, Sungwoo Lee, Soo-Hong Han, Jun-Ku Lee
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2024;37(4):175-183. Published online October 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2024.37.4.175
- Correction in: J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(1):40
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The management of distal radius fractures (DRFs) has evolved with the introduction of volar locking plate (VLP) fixation, offering stable fixation and better outcomes. Nevertheless, the impact of the surgeon’s experience on the complication rates in VLP fixation remains to be determined, particularly for less-experienced surgeons. This study compared the complication rates during the initial four years and subsequent two years of a hand surgeon’s practice of VLP fixation for DRFs.
Materials and Methods
The data between March 2016 and December 2022 were analyzed retrospectively under the Institutional Review Board approval. A single surgeon performed all VLP fixation surgeries after finishing regular hand surgery training, with the first four years representing the less experienced phase (Group 1) and the following two years indicating the experienced phase (Group 2). The patients’ characteristics, operation-related factors, and postoperative complications, including tendon injuries, nerve-related complications, fixation and instrument-related issues, osteosynthesis-related problems, and infections, were compared. In addition, the authors compared the data with a large multicenter study conducted by experienced hand surgeons.
Results
Three hundred and nineteen patients (321 wrists) were included. The mean age was 63.3 years, and 26.3% were male and 73.7% were female. The operation time was 53.7±14.5 minutes and 74.4±26.5 minutes in groups 1 and 2, respectively, which was statistically significantly shorter (p<0.001). The complication rates between the two groups were similar, except for the higher implant removal rates in Group 1. A comparison with a previous multicenter study revealed higher reduction losses and carpal tunnel syndrome in this study, but the overall complication rate was low.
Conclusion
In DRF management, when the operating surgeon has completed an accredited training course, VLP fixation is a good treatment method that can be performed effectively even by less experienced surgeons with low complication rates. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Epidemiological changes and surgical trends of distal radius fractures in adults over 50 years during the COVID-19 pandemic in Korea: a nationwide repeated cross-sectional study
Han-Kook Yoon, So Ra Yoon, Kee-Bum Hong, Youngsu Jung, SeongJu Choi, Jun-Ku Lee
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2026; 39(1): 12. CrossRef - Author correction: “Does the operator's experience affect the occurrence of complications after distal radius fracture volar locking plate fixation? A comparative study of the first four years and thereafter”
Kee-Bum Hong, Chi-Hoon Oh, Chae Kwang Lim, Sungwoo Lee, Soo-Hong Han, Jun-Ku Lee
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(1): 40. CrossRef - Characteristics of patients with distal radius fracture requiring arthroscopic foveal repair after bone union
Min Jung Park, Cheungsoo Ha, Hyun Tak Kang, Yong Hyun Yoon, Jun-Ku Lee, Soo-Hong Han
Arthroscopy and Orthopedic Sports Medicine.2025; 12(2): 70. CrossRef
- Epidemiological changes and surgical trends of distal radius fractures in adults over 50 years during the COVID-19 pandemic in Korea: a nationwide repeated cross-sectional study
- 2,756 View
- 53 Download
- 3 Crossref

Review Articles
- Avulsion Fractures of around the Hand
- Dong Whan Kim, Jung Il Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(3):158-168. Published online July 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.3.158
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An avulsion fracture occurs when soft tissues, including the tendons and ligaments, are forcibly detached from the main bone by an external force. The hand contains numerous anatomical structures, such as ligaments, tendons, and volar plates, which are essential for maintaining multidirectional motion and joint stability. Excessive force applied in a specific direction can damage these structures, leading to avulsion fractures around the joint. These fractures can result in severe complications if left untreated or improperly managed, including joint deformity, contracture, nonunion or malunion of the fracture, secondary osteoarthritis, and limited range of motion. Therefore, an accurate examination, diagnosis, and appropriate treatment are crucial for preventing these adverse outcomes. An avulsion fracture can be managed conservatively when the avulsed fragment does not compromise joint stability or motion. Nevertheless, surgical intervention is required to stabilize the fragment if it affects joint stability or motion. The use of internal fixation has become more prevalent because of recent advances in small implants for fixation.
- 1,077 View
- 18 Download

- Avulsion Fractures around the Hip Joint and Pelvis
- Ha-Yong Kim, Hajun Jang, Jung-Taek Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Jun-Il Yoo, Won-Sik Choy, Yonghan Cha
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(3):150-157. Published online July 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.3.150
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fractures occur when tendons or ligaments are subjected to forces greater than they can withstand at the apophysis or enthesis, regardless of the fusion status. Given the diverse muscular structures around the pelvis and hip joint, which serve as origins for multiple muscles leading to the lower extremities, these areas are vulnerable to such injuries. Pelvic avulsion fractures commonly af-fect young athletes, but they can also occur in adults. Diagnosis typically involves assessing the trauma history, clinical examination, and radiographic imaging. In cases of unclear diagnosis, additional tests, such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, may assist in treatment decisions and diagnosis. Although most avulsion fractures respond well to conservative treatment, surgical interven-tion may be preferred in severe displacements, significant retraction in active athletes, or when a faster recovery is necessary. Chronic or neglected injuries may lead to excessive osseous formation around the pelvis, causing impingement syndromes. Recognizing the characteristic radiological findings based on the pelvic anatomy aids in accurate diagnosis because chronic injuries might mimic tumors or infectious conditions, necessitating a careful differential diagnosis.
- 1,532 View
- 45 Download

Original Articles
- Analysis of Missed Fractures by Bone Scan in Elderly Hip Fracture Patients with Osteoporosis
- Tae Hun Lee, Yeong Hyun Lee, Seo Won Kang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(3):144-149. Published online July 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.3.144
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The incidence of hip fractures is increasing due to an increase in elderly populations because elderly patients often have accompanying diseases, such as cognitive impairment or dementia, which may lead to missed fractures. Therefore, this study assessed the utility of bone scans in detecting missed fractures in elderly patients.
Materials and Methods
This study analyzed the data from 178 patients treated from January 2014 to March 2023. The inclusion criteria were patients who had hip fractures with osteoporosis over 70 years old. Bone scans were performed on average 10 days after injury. The rate and trend of missed fractures not detected in the initial diagnosis were determined based on sex, age, dementia status, and the presence of osteoporosis.
Results
Among the 178 hip fracture patients over 70 years old, 37 patients had a history of being diagnosed with dementia, and 141 patients had never been diagnosed. Missed fractures were confirmed in 49 cases (42 patients) (23.6%). The dementia group had 13 missed fractures, and the non-dementia group had 36 missed fractures, but there was no significant difference. Rib fractures were most common, followed by vertebral fractures.
Conclusion
Missed diagnoses of fractures were common among elderly hip fracture patients. A whole body bone scan appeared to be effective in detecting missed fractures. Therefore, identifying accompanying fractures through bone scans and delivering appropriate treatment can play an important role in postoperative rehabilitation.
- 679 View
- 9 Download

- Effect of Coincident Hip Fracture on Distal Radius Fracture in Patients Treated with a Volar Locking Plate: A Matched-Pair Analysis of Elderly Patients
- Hyoung-Seok Jung, Min-Su Chu, Jae-Sung Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(3):137-143. Published online July 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.3.137
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Although the incidence of simultaneous distal radius and hip fractures in older patients is minimal, patients with these coincident types of fractures exhibit unique features. This study analyzed the outcomes associated with operative treatment involving volar-locking plates in patients who sustained distal radius fractures and hip fractures and compared them with those in matched control patients who had undergone treatment for isolated distal radius fractures.
Materials and Methods
Between 2010 and 2015, 34 patients, who met the criteria for hip and distal radius fractures, were retrospectively reviewed. Thirty-four matched patients who underwent volarlocking plate fixation for isolated distal radius fractures during the same period were also reviewed. The clinical outcomes between the groups were compared using postoperative radiological parameters.
Results
The radiological assessment revealed a better radial length and inclination in the control group than in the study group at the final follow-up. In other words, patients with coincident hip fractures showed a higher tendency for loss of reduction. Despite the differences in radiological parameters, no significant differences in clinical outcomes were observed, except for grip strength.
Conclusion
Although volar-locking plating provides greater stabilization, a loss of reduction occurred in patients with coincident hip fractures.
- 898 View
- 9 Download

- Restoration of Lateral Tibial Plateau Widening and Articular Depression Is Necessary to Prevent Valgus Deformities after Arthroscopic Reduction and Internal Fixation in AO/OTA 41.B2 or B3 Fractures
- Jun-Ho Kim, Kang-Il Kim, Sang-Hak Lee, Gwankyu Son, Myung-Seo Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(3):125-136. Published online July 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.3.125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the factors affecting valgus deformities after arthroscopic reduction and internal fixation (ARIF) in lateral joint-depression tibial plateau fractures.
Materials and Methods
Patients with lateral joint-depression tibial plateau fractures treated with ARIF were assessed retrospectively. The radiological evaluations included the articular depression distance (ADD) and the lateral plateau widening distance (LPWD) on preoperative and postoperative computed tomography. A postoperative valgus deformity was defined as valgus malalignment (mechanical axis ≥3°) and valgus deviation (Δmechanical axis of the operated knee from the healthy knee of ≥5°). Subgroup analyses based on a postoperative valgus deformity were performed to compare the clinical outcomes, including the range of motion, patient-reported outcomes measures, and failure and osteoarthritis progression. Furthermore, factors affecting the postoperative mechanical and Δmechanical axes were assessed.
Results
Thirty-nine patients were included with a mean follow-up of 44.6 months (range, 24-106 months). Valgus malalignment and valgus deviation were observed after ARIF in 10 patients (25.6%) and five patients (12.8%), respectively. The clinical outcomes were similar in patients with and without a postoperative valgus deformity. On the other hand, lateral compartment osteoarthritis progression was significantly higher in the valgus deformity group than in the non-valgus deformity group (valgus malalignment group: 50.0% vs 6.9%, p=0.007; valgus deviation group: 60.0% vs 11.8%, p=0.032). One patient with valgus deformity underwent realignment surgery at postoperative five years. The preoperative ADD and postoperative LPWD were significantly associated with the postoperative mechanical (both, p<0.001) and Δmechanical (ADD, p=0.001; LPWD, p=0.025) axes. Moreover, the lateral meniscectomized status during ARIF was significantly associated with the Δmechanical axis (p=0.019).
Conclusion
Osteoarthritis progression was highly prevalent in patients with postoperative valgus deformity. Thus, the restoration of lateral plateau widening and articular depression and preservation of the meniscus are necessary to prevent a valgus deformity after ARIF in lateral joint-depression tibial plateau fractures.
- 2,861 View
- 43 Download

- Comparison of the Radiological Outcomes of an Anatomical Quadrilateral Surface Plate with a Pelvic Reconstruction Plate in Acetabulum Fractures
- Sung Hyun Yoon, Hee Gon Park, Dong Uk Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(2):95-101. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.2.95
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study compared the radiological outcomes of fixation using an anatomical quadrilateral surface plate with those using a traditional pelvic reconstruction plate for fractures involving the quadrilateral surface or superomedial wall of the acetabulum.
Materials and Methods
From 2015 to 2022, 47 patients who met the inclusion and exclusion criteria were analyzed retrospectively. Internal fixation of an acetabular fracture was achieved with a pelvic reconstruction plate (n=28) or an anatomical quadrilateral surface plate (n=19). The ability to achieve immediate postoperative anatomical reduction and the long-term outcomes were assessed by confirming the arthritic changes. Immediate postoperative reduction quality and long-term radiological outcomes for post-traumatic arthritis were assessed using the Matta scoring system on standard radiographs.
Results
The assessment of immediate postoperative reduction in the pelvic reconstruction plate group was satisfactory in 16 patients (57.1%) and unsatisfactory in 12 patients (42.9%). In the anatomical quadrilateral surface plate group, the results were satisfactory in 16 patients (84.2%) and unsatisfactory in 3 patients (15.8%). When evaluating over an extended follow-up period in the pelvic reconstruction plate group, 19 patients (67.9%) demonstrated satisfactory, while 9 patients (32.1%) had unsatisfactory outcomes. In the anatomical quadrilateral surface plate group, 12 patients (63.2%) achieved satisfactory, and 7 patients (36.8%) had unsatisfactory outcomes. The immediate postoperative reduction quality was superior in the anatomical quadrilateral surface plate group (p=0.03). Comparing longterm results, the anatomical quadrilateral surface plate group did not have statistically more favorable outcomes (p=0.49).
Conclusion
In this study, the anatomical quadrilateral surface plate achieved sufficiently good radiological results without significant difference from the existing pelvic reconstruction plate. It was concluded that it is a useful option that can replace the existing metal plate in the selection of surgery for acetabular fractures.
- 919 View
- 10 Download

- Comparison of Results between Minimally Invasive Plate Fixation and Antegrade Intramedullary Nailing of Recon-Type in Low-Energy Injury Distal Femoral Shaft Fractures
- Hong Moon Sohn, Gwangchul Lee, Ba Rom Kim, Jung Soo Oh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(2):87-94. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.2.87
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study compared the outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis and antegrade intramedullary nailing for low-energy fracture of the distal femoral shaft.
Materials and Methods
A study was conducted on 30 patients who underwent surgery for low-energy fractures of the distal femoral shaft between January 2016 and April 2022. The study compared 15patients who underwent minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (Group P) with 15 patients who underwent recon-type antegrade intramedullary nailing (Group N). We evaluated intraoperative blood loss, operative time, C-arm exposure time, bone density, final union status, anatomical reduction, and clinical evaluation. The complications were also examined, and statistical analysis was conducted to compare the two groups.
Results
The blood loss, surgery time, and C-arm time were similar in the two groups. The radiographic assessments and clinical evaluations were also similar in the two groups. The clinical results showed no difference between the groups. Group N had one case of nonunion and one case of delayed union, while Group P had one case of nonunion and one case of peri-prosthetic fracture.
Conclusion
Antegrade intramedullary nailing of the recon-type demonstrated comparable results to minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Hence, antegrade intramedullary nailing of the recon-type, which enhances stability by fixing the entire femur and providing additional fixation in the distal portion, is deemed appropriate for treating distal femoral shaft fractures.
- 787 View
- 17 Download

- Clinical Outcomes of Triple Tension Band Wirings in Comminuted Patellar Fracture: A Comparison with Conventional Tension Band Wiring
- Hyun-Cheol Oh, Han-Kook Yoon, Joong-Won Ha, Sang Hoon Park, Sungwoo Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(2):82-86. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.2.82
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study devised triple tension band wirings (TTBW) fixation in patients with comminuted patella fractures to compare the clinical result of TTBW with that of tension band wiring (TBW).
Materials and Methods
This study was conducted on 91 patients who had undergone surgery diagnosed with acute patella fracture from January 2011 to December 2016. The study included 51 double TBW patients (Group 1) and 40 patients with TTBW (Group 2).
Results
Five out of 51 cases had a loss of reduction and fixation failure in Group 1, and no failure of fracture formation healing occurred in Group 2. Nonunion was noted in one case in Group 1 and no case in Group 2. Eight K-wire migration cases were observed in Group 1, which was not observed in Group 2. Six patients in Group 1 underwent revisional surgery. No patients in Group 2 had a reoperation. As a result of a one-year follow-up after the operation, the mean range of motion of the knee joint in groups 1 and 2 was 128.3°±11.3° and 127.9°±10.8°, respectively. The Lysholm’s scores for groups 1 and 2 were 90.8±4.2 and 90.3±3.8 points, respectively, which was not statistically significant.
Conclusion
TTBW is a helpful technique for the surgical treatment of comminuted patella fractures. The TTBW method has less reoperation due to nonunion and fixation failure. After a one-year followup, the clinical results were similar to the conventional TBW method. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
Jae-Ang Sim, Chul-Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(3): 152. CrossRef
- Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
- 844 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Biomechanical Investigation to Establish Stable Fixation Strategies for Distal Tibial Fractures in Various Situations: Finite Element Analysis Studies
- Sung Hun Yang, Jun Young Lee, Gu-Hee Jung, Hyoung Tae Kim, Ba Woo Ko
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(2):71-81. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.2.71
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the structural and mechanical stability as well as the clinical significance of various fixation constructs for distal tibial fractures using finite element analysis.
Materials and Methods
Fracture models with 20 mm and 120 mm defects were produced, and implants of an intramedullary nail and anatomical plate model were applied. An axial load of 800 N with 60% distribution in the medial compartment and 40% in the lateral compartment was applied and analyzed using Ansys ® software.
Results
In the intramedullary nail model, the maximum von Mises stress occurred at the primary lag screw hole and adjacent medial cortex, while in the plate model, it occurred at the locking holes around the fracture. The maximum shear stress on the bone and metal implant in the fracture model with a 20 mm defect was highest in the plate assembly model, and in the fracture model with a 120 mm defect, it was highest in the two-lag screw assembly model.
Conclusion
Based on an analysis of the maximum shear stress distribution, securing the fixation strength of the primary lag screw hole is crucial, and the assembly model of the intramedullary nail with two lag screws and a blocking screw applied was the model that best withstood the optimal load. Securing the locking hole directly above the fracture is believed to provide the maximum fixation strength because the maximum pressure in the plate model is concentrated in the proximal locking hole and the surrounding cortex. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How to obtain the desired results from distal tibial nailing based on anatomy, biomechanics, and reduction techniques
Jungtae Ahn, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(2): 74. CrossRef
- How to obtain the desired results from distal tibial nailing based on anatomy, biomechanics, and reduction techniques
- 952 View
- 19 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Articles
- Treatment of Avulsion Fractures around the Knee
- Sumin Lim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(2):117-124. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.2.117
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fractures are common in athletes and result from high-impact or sudden, forceful movements involving the separation of a bone fragment at the ligament or tendon attachment site. The key focus areas include the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments, medial collateral ligament, anterolateral complex, arcuate complex, medial patellofemoral ligament, patellar tendon, and quadriceps tendon. Diagnostic approaches combine radiography with advanced imaging techniques, such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, to elucidate the extent of injury and guide treatment decisions. Treatment ranges from conservative management for non-displaced fractures to surgical intervention for displaced fractures, with strategies customized based on the specific ligament involved and the nature of the fracture.
- 1,316 View
- 10 Download

- Avulsion Fractures in the Ankle and Foot
- Gyeong Hoon Lim, Jae Won Kim, Sung Hyun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(2):102-116. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.2.102
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An avulsion fracture occurs when a muscle-tendon unit attached to a bone produces sufficient force to tear a fragment of the bone. If not treated properly, this injury can lead to deformity, nonunion, malunion, pain, and disability. Although avulsion fractures around the foot and ankle can occur anywhere there are tendon and ligament attachments, they are common in the anterior talofibular ligament, anterior-inferior tibiotalar ligament, calcaneal tuberosity, the base of the fifth metatarsal, and navicular bone. The optimal treatment for each fracture depends on the location and severity of the fracture. Conservative treatment involves limiting weight bearing for a period, splint immobilization, and using various orthoses. Surgical treatment is usually reserved for cases of severe displacement or when nonsurgical treatment has failed. The goals of surgery include reduction of the fracture fragment, prevention of nonunion or malunion and soft tissue injury, and early return to function. The decision for each treatment modality may depend on the patient demographics or preferences and the surgeon experience. This review summarizes previous and current views on the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of common avulsion fractures to guide the treatment and diagnosis.
- 2,094 View
- 48 Download

Original Article
- The Results of Intramedullary Nailing with Sliding Restriction and Dynamization Method in Treating Intertrochanteric Fractures
- Hyun Cheol Oh, Sang Hoon Park, Jae Seok Chae, Han Kook Yoon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):8-14. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.8
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
To evaluate the results of intramedullary nailing with sliding restriction and dynamization methods in treating intertrochanteric fractures.
Materials and Methods
From August 2016 to March 2019, patients aged 65 years and older who underwent intramedullary nailing in treating intertrochanteric fractures were enrolled in this study. The radiological and clinical results were analyzed in 49 patients who had undergone lag screw sliding re-striction and dynamization of the distal interlocking screw method.
Results
Forty-seven patients achieved union without complications (95.9%). The mean union period was 6.5 weeks (range, 6-9 weeks). Complications occurred in two patients (4.1%), including the cut through of the lag screw in one patient and varus deformity of more than 10° in the other. The preinjury mean Koval grade was 2.8 (range, 1-7). The mean was 3.3 (range, 1-7) at the final follow-up, and the mean difference was 0.5 (range, 0-2).
Conclusion
Intramedullary nailing with a sliding restriction and dynamization method for treating in-tertrochanteric fractures achieved union. The reduction achieved during surgery was maintained with good clinical results. This method is a safe and effective treatment technique for femoral intertrochanteric fractures.
- 645 View
- 12 Download

Review Articles
- Osteoporotic Hip Fracture: How We Make Better Results?
- Byung-Chan Choi, Kyung-Jae Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):52-59. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.52
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The prevalence of osteoporosis and incidence of osteoporotic fractures is increasing gradually as life expectancy is prolonged and the aged population increases. Osteoporotic hip fractures (femoral neck fractures and femoral intertrochanteric fractures) have high mortality because the patients with these fractures are elderly and have several comorbidities. Thorough preparation and a multidisciplinary approach in the preoperative period are critical, and early surgery is recommended. There are also several principles to treat osteoporotic hip fractures and prevent fixation failures. Many studies have suggested various treatment methods for femoral neck fractures and femoral intertrochanteric fractures. Functional recovery treatment is essential based on the patient’s health and activity levels. Finally, aggressive management of osteoporosis and the prevention of falling is needed to treat osteoporotic hip fractures successfully.
- 642 View
- 24 Download

- Complications of Hand Fractures and Its Prevention
- Jong Woo Kang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):46-51. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.46
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Complications of hand fractures occur regardless of the methods used for their treatment. The treatment is also challenging. The most common and troublesome complications of hand fractures are malunion, finger stiffness, and consequent functional impairment. Early recognition and meticulous treatment of these complications is essential for improvement in hand function and satisfaction. Most of all, surgeons should clearly understand that prevention of complications is the easiest way to ensure a satisfactory outcome in hand fractures.
- 685 View
- 19 Download

Original Articles
- Prediction of Syndesmotic Instability according to the Lateral Malleolus Fracture Pattern in Supination-External Rotation Type Ankle Fractures: Short Oblique versus Long Oblique Fracture
- Chan-Jin Park, Min-Su Lee, Keun-Bae Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):39-45. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined whether preoperative radiological evaluations can predict syndesmotic instability according to the lateral malleolus fracture pattern in supination-external rotation-type ankle fractures.
Materials and Methods
This study enrolled 132 patients (132 ankles) with supination-external rotation stage 3 and 4 ankle fractures. Three-dimensional computed tomography was used for the morphological classification of the lateral malleolus fractures. A long oblique fracture was defined when the posterior cortical bone height of the fracture was 4.5 cm or more from the plafond of the distal tibial articular surface. A short oblique fracture was defined when the height was less than 4.5 cm. The demographic characteristics and syndesmotic instability of the two groups were evaluated.
Results
Short oblique fractures were confirmed in 102 cases, and long oblique fractures were confirmed in 30 cases. Long oblique fractures occurred at a statistically significantly higher incidence in younger ages and among males compared to short oblique fractures. Syndesmotic instability was more common in long oblique fractures.
Conclusion
In supination-external rotation-type ankle fractures, syndesmotic instability was observed in approximately 13%. Specifically, when the fracture pattern of the lateral malleolus is long oblique, the incidence of syndesmotic instability is approximately three times higher than in short oblique fractures. Therefore, meticulous evaluations of the lateral malleolus fracture pattern and establishing an appropriate treatment plan before surgery are crucial. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship of lateral malleolar fracture patterns to posterior malleolar fracture morphology in supination-external rotation ankle fractures in Korea: a retrospective cohort stduy
Jong-Eun Kim, Chan-Jin Park, Jun-Young Lee, Keun-Bae Lee, Gun-Woo Lee
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(4): 212. CrossRef
- Relationship of lateral malleolar fracture patterns to posterior malleolar fracture morphology in supination-external rotation ankle fractures in Korea: a retrospective cohort stduy
- 638 View
- 10 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Effect of Additional Medial Locking Plate Fixation and Autogenous Bone Graft for Distal Femur Nonunion after Lateral Locking Plate Fixation
- Ho Min Lee, Jong Pil Kim, In Hwa Baek, Han Sol Moon, Sun Kyo Nam
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):30-38. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.30
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the outcomes of additional medial locking plate fixation and autogenous bone grafting in the treatment of nonunions that occurred after initial fixation for distal femoral fractures using lateral locking plates.
Materials and Methods
The study involved eleven patients who initially underwent minimally invasive lateral locking plate fixation for distal femoral fractures between January 2008 and December 2020. The initial procedure was followed by additional medial locking plate fixation and autogenous bone grafting for clinically and radiographically confirmed nonunions, while leaving the stable lateral locking plate in situ. A clinical evaluation of the bone union time, knee joint range of motion, visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores, presence of postoperative complications, and functional evaluations using the lower extremity functional scale (LEFS) were performed.
Results
In all cases, bone union was achieved in an average of 6.1 months after the secondary surgery. The range of knee joint motion, weight-bearing ability, and VAS and LEFS scores improved at the final follow-up compared to the preoperative conditions. All patients could walk without walking assistive devices and did not experience pain at the fracture site. On the other hand, three patients complained of pain in the lateral knee joint caused by irritation by the lateral locking plate; hence, lateral hardware removal was performed. One patient complained of mild paresthesia at the anteromedial incision site. Severe complications, such as deep infection or metal failure, were not observed.
Conclusion
For nonunion with stable lateral locking plates after minimally invasive lateral locking plate fixation of distal femur fractures, additional medial locking plate fixation and autogenous bone grafting, while leaving the lateral locking plate intact, can achieve successful bone union.
- 392 View
- 5 Download

- Cephalomedullary Nailing with an Additional Cannulated Screw Fixation in Basicervical Femur Fractures
- Keong-Hwan Kim, Woo Dong Nam, Yeon Sik Heo, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):22-29. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study is to analyze the clinical results of patients with basicervical fracture undergoing cephalomedullary nailing (CMN) with an additional cannulated screw fixation compared to only performing CMN. We hypothesized that a difference may exist in the clinical outcomes if an ad-ditional screw is fixed with CMN compared to only performing CMN in basicervical fracture.
Materials and Methods
A total of 28 consecutive patients who underwent CMN for basicervical fracture were included. In 9 cases, only CMN was conducted, and in 19 cases, an additional cannulated screw fixation was performed with CMN. Bone union, sliding distance, reduction status, and fixation failure were evaluated by postoperative radiography, and ambulatory ability was evaluated by functional results. These findings were compared between a group of CMN and a group of CMN with an additional cannulated screw.
Results
There were 4 males and 24 females with a mean age of 84 years (range, 69–100 years). No significant difference was found in postoperative reduction, tip-apex distance, bone union, and walking function recovery after surgery between the two groups, but in the sliding distance of the lag screw, the CMN group demonstrated more sliding (6.2 mm [range, 2.5–13.4 mm] vs 3.5 mm [range, 0.1– 9.2 mm]; p=0.045). Among the two groups, only one case of fixation failure at the postoperative four months was observed in the CMN group (p=0.321), and hemiarthroplasty with nail construct removal was performed.
Conclusion
CMN with additional cannulated screw fixation is a safe and reliable surgical option in basicervical fracture. It provided favorable clinical outcomes and may be a good alternative for treating basicervical fracture.
- 1,272 View
- 14 Download

- Short-term Treatment Comparison of Teriparatide and Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in Patients with Acute Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures
- Joonoh Seo, Ki Youn Kwon, Bumseok Lee, Hoon-Sang Sohn
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):15-21. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.15
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study compared the 3-month treatment effects of teriparatide and percutaneous vertebroplasty for acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.
Materials and Methods
A retrospective study was conducted on 76 patients diagnosed with acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures from January 1, 2020 to December 31, 2022. The patients were divided into the teriparatide group and the percutaneous vertebroplasty+alendronate group. The visual analog scale (VAS), Oswestry disability index (ODI), and height of the vertebrae anterior wall were measured before treatment and at 1 and 3 months after treatment.
Results
Of the 76 patients, 42 were treated with teriparatide, and 34 were treated with percutaneous vertebroplasty. The symptoms improved in both groups, with a decrease in the VAS and ODI scores at 1 and 3 months after treatment, respectively. On the other hand, there was no significant difference in the VAS, ODI score, and anterior vertebral body height between the two groups before treatment and at 1 and 3 months after treatment.
Conclusion
In the treatment of acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures, conservative treatment using teriparatide showed similar short-term (3 months) treatment results to percutaneous vertebroplasty in terms of improvement in back pain and function and degree of reduction in anterior vertebral body height.
- 990 View
- 32 Download

- Triplane Fracture Management: Prediction of Periosteal Entrapment and the Need for Open Reduction by Measurements of the Physeal Fracture Gap in Preoperative Computed Tomography Scans
- Dae Hee Lee, Joo Han Kwon, Jae Uk Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):1-7. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study measured the physeal fracture gap on preoperative ankle computed tomography (CT) to predict the periosteal entrapment that requires an open reduction in distal tibia triplane fractures.
Materials and Methods
This study retrospectively reviewed patients who had undergone internal fixation for a triplane fracture from April 2004 to September 2022. The demographic data, including age,body mass index, and past medical history, were analyzed. In the radiographic evaluations, ankle CT and ankle simple radiographs, including anteroposterior (AP), lateral, and mortise views, were taken preoperatively. Postoperatively, simple ankle radiographs were obtained periodically, including AP, mortise, and lateral views. The physeal fracture gap was measured on ankle CT, and the larger gap between the coronal and sagittal view of CT was selected. The residual physeal gap <2 mm was considered an adequate reduction.
Results
Of 17 cases, three demonstrated successful reduction using closed reduction techniques. Periosteal entrapment was observed in 14 cases open reduction cases. In all three closed reduction cases, the physeal gap estimated on preoperative ankle CT was under 3 mm with a mean gap of 2.4±0.2 mm (range, 2.1-2.5 mm). In the remaining 14 open reduction cases, the measured physeal gap was over 3 mm, averaging 5.0±2.7 mm (range, 3.1-12.2 mm). There was a significant difference in the preoperative physeal gap between the two groups (p<0.01). Overall, good reduction was achieved in all 17 cases; the postoperative physeal gap was under 2 mm with a mean of 1.0±0.5 mm (closed reduction group, 0.5±0.2 mm; open reduction group, 1.1±0.5 mm).
Conclusion
Open reduction is strongly recommended for triplane fractures with a physeal fracture gap of 3 mm or more in preoperative ankle CT, suggesting the possibility of an entrapped periosteum in the fracture gap. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnostic values of radiographic indices for predicting periosteal entrapment in pediatric proximal phalangeal base physeal fractures of toes
Ho Young Park, Jeong-Seok Moon, Kiwook Kim
Skeletal Radiology.2026; 55(1): 97. CrossRef
- Diagnostic values of radiographic indices for predicting periosteal entrapment in pediatric proximal phalangeal base physeal fractures of toes
- 1,384 View
- 20 Download
- 1 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


