Most cited articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse articles > Most cited articles
Most-cited are based on citations from 2023 ~ 2025.
Review Article
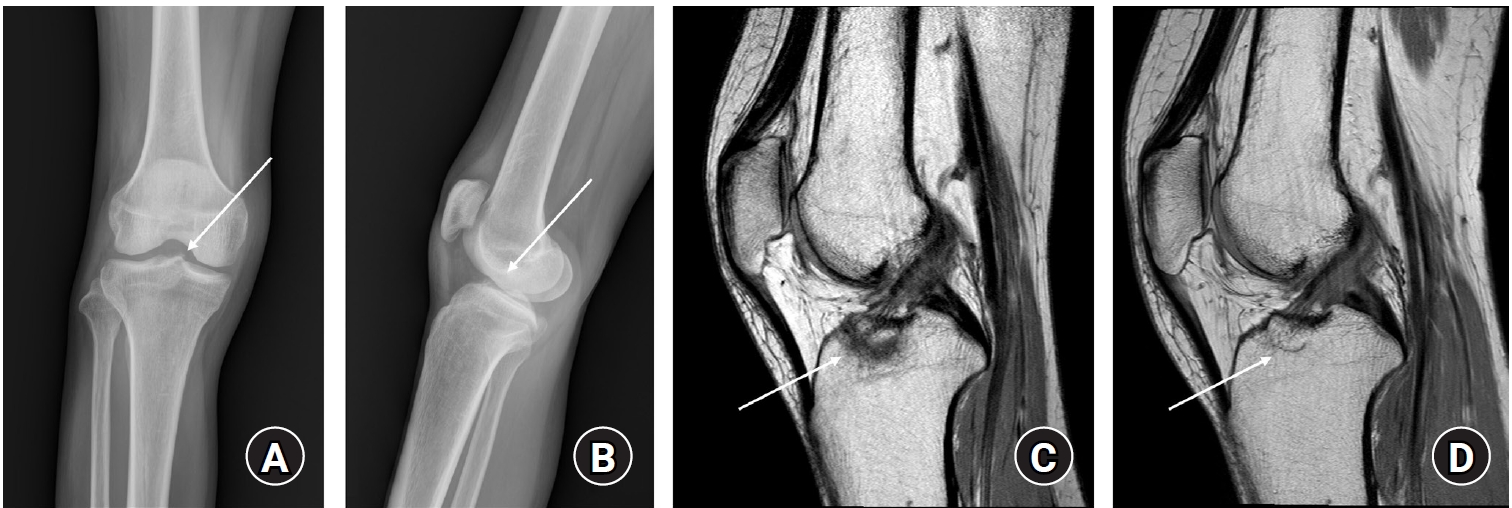
- Treatment of avulsion fractures around the knee
- Jeong-Hyun Koh, Hyung Keun Song, Won-Tae Cho, Seungyeob Sakong, Sumin Lim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):63-73. Published online March 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00073
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fractures of the knee occur when tensile forces cause a bone fragment to separate at the site of soft tissue attachment. These injuries, which frequently affect adolescent athletes, can involve the cruciate and collateral ligaments, arcuate complex, iliotibial band, and patellar and quadriceps tendons. Radiographs aid in the initial diagnosis, while computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging facilitate a comprehensive evaluation of injury severity and concomitant damage. Specific avulsion fracture types include: anterior cruciate ligament avulsions (tibial site, Meyers and McKeever classification), posterior cruciate ligament avulsions (tibial attachment, Griffith's classification), Segond fractures (anterolateral complex injury), iliotibial band avulsions, medial collateral ligament avulsions (reverse Segond, Stieda fractures), arcuate complex avulsions ("arcuate sign"), medial patellofemoral avulsions (patellar dislocations), and patellar/quadriceps tendon avulsions. The treatment depends on the fracture location, displacement, and associated injuries. Non-displaced fractures can be managed conservatively, while displaced fractures or those with instability require surgical reduction and fixation. Prompt recognition and appropriate intervention prevent complications such as deformity, nonunion, malunion, and residual instability. This review provides an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management of knee avulsion fractures to guide clinical decision-making.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
Jae-Ang Sim, Chul-Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(3): 152. CrossRef
- Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
- 5,156 View
- 79 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- Does the Operator’s Experience Affect the Occurrence of Complications after Distal Radius Fracture Volar Locking Plate Fixation? A Comparative Study of the First Four Years and Thereafter
- Kee-Bum Hong, Chi-Hoon Oh, Chae Kwang Lim, Sungwoo Lee, Soo-Hong Han, Jun-Ku Lee
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2024;37(4):175-183. Published online October 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2024.37.4.175
- Correction in: J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(1):40
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The management of distal radius fractures (DRFs) has evolved with the introduction of volar locking plate (VLP) fixation, offering stable fixation and better outcomes. Nevertheless, the impact of the surgeon’s experience on the complication rates in VLP fixation remains to be determined, particularly for less-experienced surgeons. This study compared the complication rates during the initial four years and subsequent two years of a hand surgeon’s practice of VLP fixation for DRFs.
Materials and Methods
The data between March 2016 and December 2022 were analyzed retrospectively under the Institutional Review Board approval. A single surgeon performed all VLP fixation surgeries after finishing regular hand surgery training, with the first four years representing the less experienced phase (Group 1) and the following two years indicating the experienced phase (Group 2). The patients’ characteristics, operation-related factors, and postoperative complications, including tendon injuries, nerve-related complications, fixation and instrument-related issues, osteosynthesis-related problems, and infections, were compared. In addition, the authors compared the data with a large multicenter study conducted by experienced hand surgeons.
Results
Three hundred and nineteen patients (321 wrists) were included. The mean age was 63.3 years, and 26.3% were male and 73.7% were female. The operation time was 53.7±14.5 minutes and 74.4±26.5 minutes in groups 1 and 2, respectively, which was statistically significantly shorter (p<0.001). The complication rates between the two groups were similar, except for the higher implant removal rates in Group 1. A comparison with a previous multicenter study revealed higher reduction losses and carpal tunnel syndrome in this study, but the overall complication rate was low.
Conclusion
In DRF management, when the operating surgeon has completed an accredited training course, VLP fixation is a good treatment method that can be performed effectively even by less experienced surgeons with low complication rates. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Author correction: “Does the operator's experience affect the occurrence of complications after distal radius fracture volar locking plate fixation? A comparative study of the first four years and thereafter”
Kee-Bum Hong, Chi-Hoon Oh, Chae Kwang Lim, Sungwoo Lee, Soo-Hong Han, Jun-Ku Lee
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(1): 40. CrossRef
- Author correction: “Does the operator's experience affect the occurrence of complications after distal radius fracture volar locking plate fixation? A comparative study of the first four years and thereafter”
- 1,068 View
- 46 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Clinical Outcomes of Triple Tension Band Wirings in Comminuted Patellar Fracture: A Comparison with Conventional Tension Band Wiring
- Hyun-Cheol Oh, Han-Kook Yoon, Joong-Won Ha, Sang Hoon Park, Sungwoo Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(2):82-86. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.2.82
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study devised triple tension band wirings (TTBW) fixation in patients with comminuted patella fractures to compare the clinical result of TTBW with that of tension band wiring (TBW).
Materials and Methods
This study was conducted on 91 patients who had undergone surgery diagnosed with acute patella fracture from January 2011 to December 2016. The study included 51 double TBW patients (Group 1) and 40 patients with TTBW (Group 2).
Results
Five out of 51 cases had a loss of reduction and fixation failure in Group 1, and no failure of fracture formation healing occurred in Group 2. Nonunion was noted in one case in Group 1 and no case in Group 2. Eight K-wire migration cases were observed in Group 1, which was not observed in Group 2. Six patients in Group 1 underwent revisional surgery. No patients in Group 2 had a reoperation. As a result of a one-year follow-up after the operation, the mean range of motion of the knee joint in groups 1 and 2 was 128.3°±11.3° and 127.9°±10.8°, respectively. The Lysholm’s scores for groups 1 and 2 were 90.8±4.2 and 90.3±3.8 points, respectively, which was not statistically significant.
Conclusion
TTBW is a helpful technique for the surgical treatment of comminuted patella fractures. The TTBW method has less reoperation due to nonunion and fixation failure. After a one-year followup, the clinical results were similar to the conventional TBW method. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
Jae-Ang Sim, Chul-Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(3): 152. CrossRef
- Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
- 300 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Biomechanical Investigation to Establish Stable Fixation Strategies for Distal Tibial Fractures in Various Situations: Finite Element Analysis Studies
- Sung Hun Yang, Jun Young Lee, Gu-Hee Jung, Hyoung Tae Kim, Ba Woo Ko
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(2):71-81. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.2.71
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the structural and mechanical stability as well as the clinical significance of various fixation constructs for distal tibial fractures using finite element analysis.
Materials and Methods
Fracture models with 20 mm and 120 mm defects were produced, and implants of an intramedullary nail and anatomical plate model were applied. An axial load of 800 N with 60% distribution in the medial compartment and 40% in the lateral compartment was applied and analyzed using Ansys ® software.
Results
In the intramedullary nail model, the maximum von Mises stress occurred at the primary lag screw hole and adjacent medial cortex, while in the plate model, it occurred at the locking holes around the fracture. The maximum shear stress on the bone and metal implant in the fracture model with a 20 mm defect was highest in the plate assembly model, and in the fracture model with a 120 mm defect, it was highest in the two-lag screw assembly model.
Conclusion
Based on an analysis of the maximum shear stress distribution, securing the fixation strength of the primary lag screw hole is crucial, and the assembly model of the intramedullary nail with two lag screws and a blocking screw applied was the model that best withstood the optimal load. Securing the locking hole directly above the fracture is believed to provide the maximum fixation strength because the maximum pressure in the plate model is concentrated in the proximal locking hole and the surrounding cortex. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How to obtain the desired results from distal tibial nailing based on anatomy, biomechanics, and reduction techniques
Jungtae Ahn, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(2): 74. CrossRef
- How to obtain the desired results from distal tibial nailing based on anatomy, biomechanics, and reduction techniques
- 514 View
- 15 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Triplane Fracture Management: Prediction of Periosteal Entrapment and the Need for Open Reduction by Measurements of the Physeal Fracture Gap in Preoperative Computed Tomography Scans
- Dae Hee Lee, Joo Han Kwon, Jae Uk Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):1-7. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study measured the physeal fracture gap on preoperative ankle computed tomography (CT) to predict the periosteal entrapment that requires an open reduction in distal tibia triplane fractures.
Materials and Methods
This study retrospectively reviewed patients who had undergone internal fixation for a triplane fracture from April 2004 to September 2022. The demographic data, including age,body mass index, and past medical history, were analyzed. In the radiographic evaluations, ankle CT and ankle simple radiographs, including anteroposterior (AP), lateral, and mortise views, were taken preoperatively. Postoperatively, simple ankle radiographs were obtained periodically, including AP, mortise, and lateral views. The physeal fracture gap was measured on ankle CT, and the larger gap between the coronal and sagittal view of CT was selected. The residual physeal gap <2 mm was considered an adequate reduction.
Results
Of 17 cases, three demonstrated successful reduction using closed reduction techniques. Periosteal entrapment was observed in 14 cases open reduction cases. In all three closed reduction cases, the physeal gap estimated on preoperative ankle CT was under 3 mm with a mean gap of 2.4±0.2 mm (range, 2.1-2.5 mm). In the remaining 14 open reduction cases, the measured physeal gap was over 3 mm, averaging 5.0±2.7 mm (range, 3.1-12.2 mm). There was a significant difference in the preoperative physeal gap between the two groups (p<0.01). Overall, good reduction was achieved in all 17 cases; the postoperative physeal gap was under 2 mm with a mean of 1.0±0.5 mm (closed reduction group, 0.5±0.2 mm; open reduction group, 1.1±0.5 mm).
Conclusion
Open reduction is strongly recommended for triplane fractures with a physeal fracture gap of 3 mm or more in preoperative ankle CT, suggesting the possibility of an entrapped periosteum in the fracture gap. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnostic values of radiographic indices for predicting periosteal entrapment in pediatric proximal phalangeal base physeal fractures of toes
Ho Young Park, Jeong-Seok Moon, Kiwook Kim
Skeletal Radiology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Diagnostic values of radiographic indices for predicting periosteal entrapment in pediatric proximal phalangeal base physeal fractures of toes
- 507 View
- 11 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Articles
- Fluid Management of Trauma Patients
- Yo Huh, Jaeri Yoo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(2):69-76. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.2.69
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fluid therapy is one of the fundamental treatments for the management of trauma patients. Apart from supplementary hydration, fluid therapy is also applied for resuscitation. Especially in cases of hypovolemic shock due to bleeding, fluid therapy needs to be carefully adjusted to correct the shock. The importance of fluid therapy is increasing not only in resuscitation and treatment after hospitalization but also in pre-hospital care. Fluid therapy needs to be adjusted based depending each patient’s volume status. The various classifications of fluids include crystalloid solutions, glucose solutions, and colloid solutions. Although not included as a fluid therapy, blood transfusion is increasingly gaining more importance than fluid therapy in unstable trauma patients. Early appropriate fluid therapy is crucial in the treatment of hemodynamically unstable patients such as multiple trauma and massive bleeding, whereas comprehensive fluid therapy should be applied by considering the characteristics of specific injuries such as fractures, vascular damage, and cerebral hemorrhage, as well as the age groups (children, the elderly, and pregnant women).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of the Eye Care Protocol in the Intensive Care Unit Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Kyu Won Lim, Shin Young Ha, In Soon Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(3): 432. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of the Eye Care Protocol in the Intensive Care Unit Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- 1,019 View
- 53 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Hip Fractures in the Elderly: Perioperative Management and Prevention of Medical Complications
- Keong-Hwan Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(1):39-44. Published online January 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.1.39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Elderly patients with hip fractures are at an increased risk of developing medical complications with higher mortality rates. Most patients require surgical treatment, and an early surgical intervention can reduce complications and lower mortality risk. A restrictive red blood cell transfusion strategy is usually applied, and the amount of transfusion can be reduced through medications such as tranexamic acid. Delirium can be prevented using non-pharmacological methods. In addition, it is necessary to prevent venous thromboembolism through mechanical or chemical prophylaxis. A multidisciplinary approach using the ERAS (Enhanced Recovery After Surgery) protocol and orthogeriatric care can help to reduce medical complications and mortality.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treatment of Incompletely Displaced Femoral Neck Fractures Using Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced in Patients Older Than 50 Years of Age
Jee Young Lee, Gyu Min Kong
Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma.2025; 39(7): 352. CrossRef
- Treatment of Incompletely Displaced Femoral Neck Fractures Using Trochanteric Fixation Nail-Advanced in Patients Older Than 50 Years of Age
- 587 View
- 19 Download
- 1 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA

 First
First Prev
Prev


