Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Comparative results of the femoral neck system versus the dynamic hip screw for stable femoral neck fractures in older adults in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
- Byung-Chan Choi, Byung-Woo Min, Kyung-Jae Lee, Jun-Sik Hong
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):203-211. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00276
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
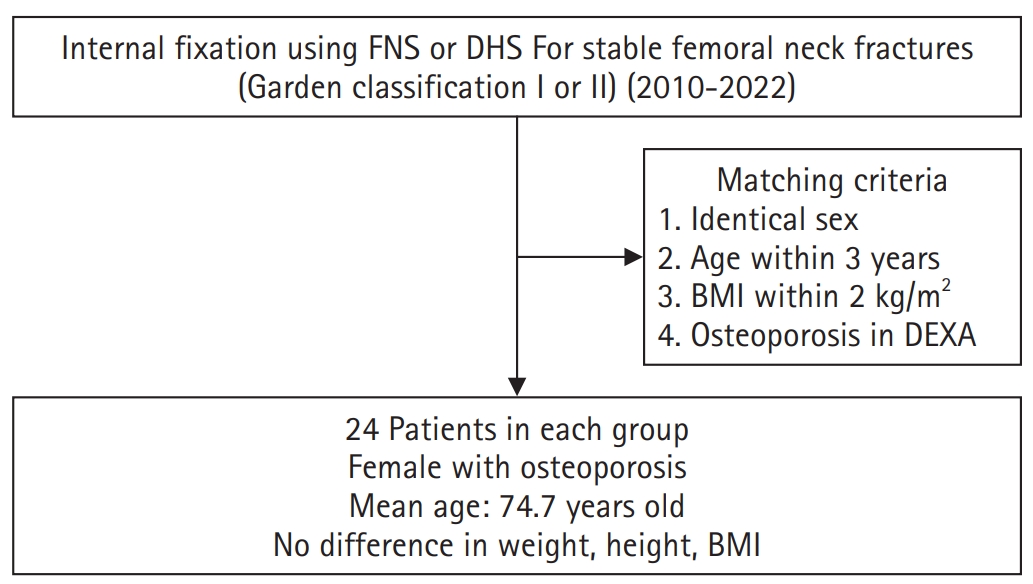
This study aimed to compare the clinical and radiological outcomes of the femoral neck system (FNS) and the dynamic hip screw (DHS) for the internal fixation of stable femoral neck fractures in older adults.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study included 48 matched older adult patients based on sex, age, BMI, and osteoporosis status, who had undergone internal fixation with either FNS or DHS for stable femoral neck fractures between January 2010 and December 2022. To minimize selection bias, a 1:1 case-control matching was performed based on sex, age, body mass index (BMI), and the presence of osteoporosis. A total of 48 patients (24 in each group) were included. We compared perioperative data (operation time, hemoglobin change, transfusion rate), functional outcomes using the Koval score, and radiological outcomes, including union rate, femoral neck shortening, and complication rates.
Results
The mean operation time was significantly shorter in the FNS group than in the DHS group (60.9 minutes vs. 70.8 minutes; P=0.007). There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in the union rate (87.5% in FNS vs. 95.8% in DHS), femoral neck shortening, final Koval score distribution, or overall complication rates (12.5% in both groups).
Conclusions
For treating stable femoral neck fractures in older adults, the FNS demonstrated comparable clinical and radiological outcomes to the DHS, with the distinct advantage of a shorter operation time. While these findings suggest that the FNS is a promising and safe alternative that may reduce the surgical burden, definitive conclusions are precluded by the small sample size, warranting further research to corroborate these results. Level of evidence: IV.
- 1,682 View
- 21 Download

- Computational simulation of coracoclavicular screw insertion through the superior distal clavicular plate for clinical applications in Korean cadavers
- Hyung-Lae Cho, Ji Han Choi, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):143-151. Published online July 22, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00122
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
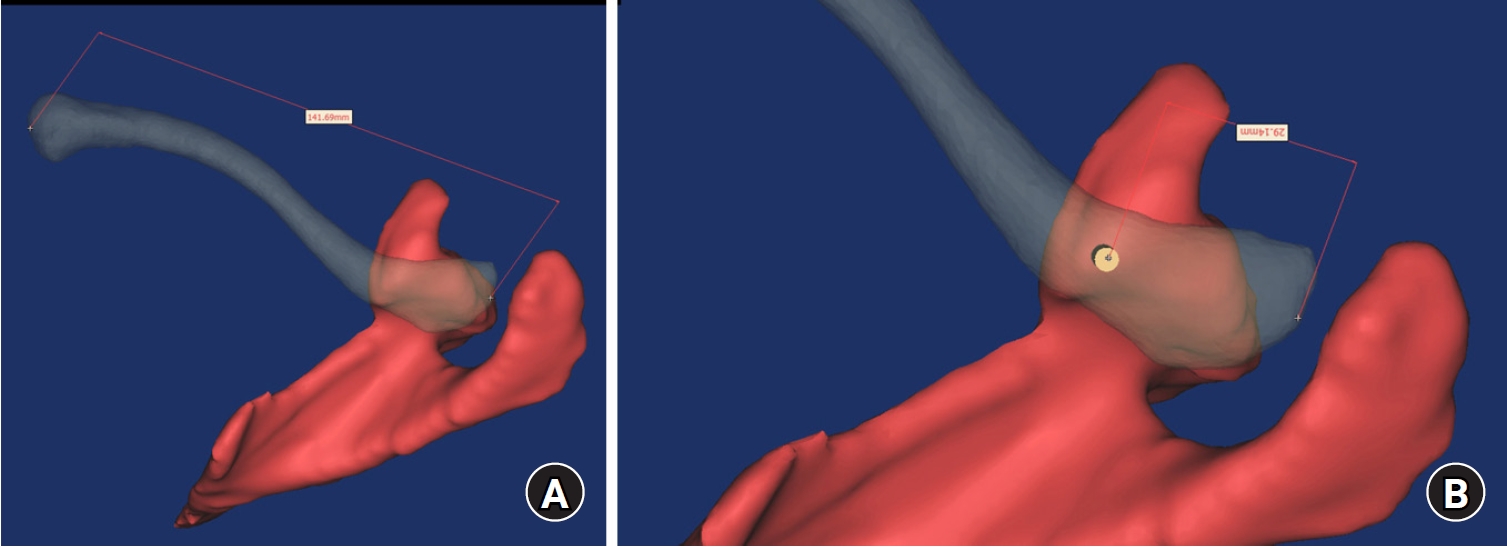
The study was conducted to determine the practical area for inserting the coracoclavicular (CC) screw through the plate by analyzing three-dimensional (3D) shoulder models featuring virtually implanted, actual-size plates and screws.
Methods
Ninety cadaveric shoulders (41 males and 49 females) underwent continuous 1.0-mm slice computed tomography scans. The data were imported into image-processing software to generate a 3D shoulder model, including the scapula and clavicle. The overlapping area between the clavicle and the horizontal portion of the coracoid process (horizontal portion_CP) was analyzed in the cranial view. A curved pelvic recon plate was virtually placed on the upper surface of the distal clavicle, and an actual-size (3.5 mm) CC screw was inserted through the plate.
Results
The distal clavicle directly overlapped with the horizontal portion_CP in the vertical direction. The overlapping area was sufficient to place the 3.5 mm and 4.5 mm-sized screws. In all shoulder models, the CC screw could be inserted through the plate into the vertical direction, with an average length of 35.5 mm (range, 26.2–62.5 mm; standard deviation, 1.2 mm). In 87 models, the CC screw was inserted through the third hole from the lateral end of the plate. Two models were inserted through the second hole, and one model through the fourth hole.
Conclusions
The upper surface of the clavicle has sufficient overlapping area to place CC screws through the plate in the vertical direction in the corresponding hole. Supplemental CC screw fixation through the plate can be performed without additional or special equipment. Level of evidence: IV
- 671 View
- 22 Download

Review Article
- How to obtain the desired results from distal tibial nailing based on anatomy, biomechanics, and reduction techniques
- Jungtae Ahn, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):74-85. Published online March 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00024

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Distal tibial metaphyseal fractures are commonly caused by high-energy injuries in young men and osteoporosis in older women. These fractures should be clearly distinguished from high-energy pilon fractures. Although the optimal surgical intervention methods for distal tibial metaphyseal fractures remain uncertain and challenging, surgical treatments for nonarticular distal tibia fractures can be broadly divided into two types: plate fixation and intramedullary nail (IMN) fixation. Once functional reduction is achieved using an appropriate technique, distal tibial nailing might be slightly superior to plate fixation in reducing postoperative complications. Thus, the surgical strategy should focus on functional realignment and proceed in the following sequence: (1) restoring the original tibial length, regardless of whether fibular fixation is to be done; (2) making the optimal entry point through an anteroposterior (AP) projection based on the overlapping point between the fibular tip and lateral plateau margin; (3) placing Kirschner wires (Ø2.4 mm) as blocking pins (in the AP orientation for coronal control and in the mediolateral [ML] orientation for sagittal control) as close to the upper locking hole as possible without causing further comminution on the concave aspect of the short fragment; and (4) making the the distal fixation construct with at least two ML and one AP interlocking screw or two ML interlocking screws and blocking screws. After the IMN is adequately locked, blocking pins (Ø2.4 mm) need to be replaced by a 3.5 mm screw.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Rigid intramedullary nailing with suprapatellar approach for tibial shaft fractures in adolescents with open physes
Jong Wha Lee, Jae Ho Cho, Tae Hun Kim, Hyung Keun Song, Won-Tae Cho, Seungyeob Sakong, Hyunil Choi, Sumin Lim
Injury.2026; : 113130. CrossRef - Impact of Foot Width on Patient-Reported Outcomes Assessed by 3-Dimensional Foot Morphometry in Hallux Valgus
Jungtae Ahn, Dae-Cheol Nam, Gu-Hee Jung
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.2025; 17(6): 1062. CrossRef
- Rigid intramedullary nailing with suprapatellar approach for tibial shaft fractures in adolescents with open physes
- 2,954 View
- 56 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Articles
- Cephalomedullary Nailing with an Additional Cannulated Screw Fixation in Basicervical Femur Fractures
- Keong-Hwan Kim, Woo Dong Nam, Yeon Sik Heo, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(1):22-29. Published online January 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.1.22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
The purpose of this study is to analyze the clinical results of patients with basicervical fracture undergoing cephalomedullary nailing (CMN) with an additional cannulated screw fixation compared to only performing CMN. We hypothesized that a difference may exist in the clinical outcomes if an ad-ditional screw is fixed with CMN compared to only performing CMN in basicervical fracture.
Materials and Methods
A total of 28 consecutive patients who underwent CMN for basicervical fracture were included. In 9 cases, only CMN was conducted, and in 19 cases, an additional cannulated screw fixation was performed with CMN. Bone union, sliding distance, reduction status, and fixation failure were evaluated by postoperative radiography, and ambulatory ability was evaluated by functional results. These findings were compared between a group of CMN and a group of CMN with an additional cannulated screw.
Results
There were 4 males and 24 females with a mean age of 84 years (range, 69–100 years). No significant difference was found in postoperative reduction, tip-apex distance, bone union, and walking function recovery after surgery between the two groups, but in the sliding distance of the lag screw, the CMN group demonstrated more sliding (6.2 mm [range, 2.5–13.4 mm] vs 3.5 mm [range, 0.1– 9.2 mm]; p=0.045). Among the two groups, only one case of fixation failure at the postoperative four months was observed in the CMN group (p=0.321), and hemiarthroplasty with nail construct removal was performed.
Conclusion
CMN with additional cannulated screw fixation is a safe and reliable surgical option in basicervical fracture. It provided favorable clinical outcomes and may be a good alternative for treating basicervical fracture.
- 1,273 View
- 14 Download

- Comparison of Clinical Outcomes for Femoral Neck System and Cannulated Compression Screws in the Treatment of Femoral Neck Fracture
- Jae Kwang Hwang, KiWon Lee, Dong-Kyo Seo, Joo-Yul Bae, Myeong-Geun Song, Hansuk Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(3):77-84. Published online July 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.3.77
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study compared the clinical and radiological results of the femoral neck system (FNS) and cannulated compression screws (CCS) for the fixation of femoral neck fractures.
Materials and Methods
Patients who underwent FNS or CCS internal fixation for femoral neck fractures between January 2016 and January 2022 were analyzed retrospectively. The hip joint function using the Harris hip score (HHS) was evaluated three months and one year after surgery. The operation time, fracture healing time, and associated surgical complications in the two groups were compared and analyzed statistically.
Results
Seventy-nine patients were categorized into 38 FNS and 41 CCS groups. The FNS group had a longer operation time and higher postoperative HHS at three months (p<0.01). Femoral neck shortening was lower in the FNS group (p=0.022). There were no significant differences in the fracture healing time and other complications.
Conclusion
There were no differences in most clinical outcomes and complications between the two groups except for the three-month HHS and femoral neck shortening. This study suggests that FNS could be an alternative to CCS for treating femoral neck fractures.
- 1,001 View
- 19 Download

Case Report
- Single Percutaneous Retrograde Anterior Column Screw Fixation in a Minimally Displaced Transverse Acetabular Fracture - A Case Report -
- Seungyup Shin, Jinkyu Park, Sungho Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(2):57-61. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.2.57
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - According to the Letournel classification, a transverse fracture is the only elementary fracture pattern that breaks both the anterior and posterior border of the innominate bone. A transverse acetabular fracture separates the innominate bone into two segments: the iliac segment and the ischiopubic segment. Therefore, minimally displaced transverse fractures can be stabilized by purchasing both segments with a large-diameter single screw. Although it is not a stable internal fixation construct compared with plates and screws, it provides sufficient stability to promote early mobilization and early weight-bearing while minimizing the risk of secondary displacement and preventing secondary complications associated with prolonged bed rest and immobilization. The authors successfully treated a case of minimally displaced transverse acetabular fracture with percutaneous column fixation using a retrograde fashion of a single anterior column screw. This report discusses the case with a literature review and deliberates the usefulness of the procedure.
- 505 View
- 11 Download

Original Articles
- Computational Simulation of Femoral Neck System and Additional Cannulated Screws Fixation for Unstable Femoral Neck Fractures and the Biomechanical Features for Clinical Applications
- Ju-Yeong Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(1):1-9. Published online January 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
To identify the biomechanical features for clinical applications through a computational simulation of the fixation of the Femoral Neck System (FNS) with additional cannulated screws for a Pauwels type III femoral neck fractures.
Materials and Methods
Thirty cadaveric femurs underwent computed tomography, and the images were transferred to the Mimics ® program, resulting in three-dimensional proximal femur models. A three-dimensional scan of the FNS and 6.5 mm and 7.0 mm cannulated screws was performed to enable computerized virtual fixation of FNS with additional cannulated screws for unstable femoral neck fractures. Furthermore, the cannulated screw used for additional fixation was modeled and used as a cylinder within the Ansys program. The biomechanical characteristics of these models were investigated by applying a physiological load virtually.
Results
The maximum von Mises stress value at bone was 380.14 MPa in FNS and 297.87 MPa in FNS+7.0 mm full-thread cannulated screw. The maximum von Mises stress value at FNS was 786.83 MPa in FNS and 435.62 MPa in FNS+7.0 mm full-thread cannulated screw. The FNS group showed the highest maximum von Mises stress values at bone and FNS. For total deformation, the maximum deformation value was 10.0420 mm in FNS and 9.2769 mm in FNS+7.0 mm full-thread cannulated screws. The FNS group represented the highest maximum deformation compared to the other groups.
Conclusion
Considering the anatomical spatiality and biomechanical characteristics of the FNS in unstable femoral neck fractures, when one 7.0 mm full thread cannulated screw was also fixed to the anterosuperior portion of the FNS, significant biomechanical stability was demonstrated.
- 751 View
- 10 Download

- Usefulness of Percutaneous Cannulated Screws with Tension Band Wiring for Minimally Displaced Fractures of the Patella
- Ho Min Lee, Jong Pil Kim, Phil Hyun Chung, Eun Woo Bae
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(4):142-150. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.4.142
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
To evaluate the usefulness of percutaneous cannulated screws with tension band wiring (PC-STBW), a minimally invasive surgical technique, compared to conservative treatment for a minimally displaced patella transverse fracture.
Materials and Methods
The subjects included patients from 2010 to 2019 with transverse patella fractures, who were diagnosed as minimally displaced fractures, and were followed up for at least 1 year. Of these, 61 patients who were treated with cylinder casts were classified as Group A, and 53 patients who were treated with PCSTBW were classified as Group B. The clinical evaluation was carried out by evaluation of the radiographic bone union and calculation of the Bostman knee score. Any complications observed were investigated.
Results
All patients in both groups showed no further displacement of the fracture gap, and the bone union was achieved in all cases. The functional evaluation of the knee joint measured at the 8- and 12-week follow-up showed superior results in Group B wherein subjects were treated with surgery, and similar results were seen in both groups during the 6 months and 1-year follow-up. One case in Group A suffered the complication of knee stiffness.
Conclusion
For the treatment of minimally displaced transverse patellar fractures, both conservative treatment and PCSTBW showed similar good results at the 6-month and one-year follow-up. However, the PCSTBW technique showed superior clinical results in the early stage follow-up within 12 weeks.
- 470 View
- 6 Download

- Minimal Invasive Fixation Methods for the Metacarpal Fracture
- Ki Youn Kwon, Jin Rok Oh, Ji Woong Kwak
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(1):9-15. Published online January 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.1.9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study compared the radiologic and clinical outcomes of metacarpal fractures treated with two minimally invasive surgical techniques: Kirschner wire (K-wire) fixation and headless screw fixation.
Materials and Methods
This study included 52 patients (46 males and 6 females; age 18-55 years) with distal metacarpal fractures (middle and distal shaft, including the neck) who had undergone K-wire fixation or headless screw fixation. All subjects were followed up for at least six months. The radiologic assessments were performed to evaluate the angular deformity and shortenings. The total active motion (TAM), grip strength, and patients’ subjective functional assessment were measured to evaluate the hand function. The time taken to return to work (RTW) and adverse events were analyzed.
Results
Of the 52 cases, metacarpal fractures treated with headless screw fixation and K-wire fixation showed a significant difference associated with early RTW (p<0.05). There were no significant differences between the subjects treated with K-wire fixation and those with headless screw fixation in terms of the radiologic measurement, hand function examinations, complications, and adverse events (p>0.05).
Conclusion
After a six-month follow-up, minimally invasive K-wire fixation and headless screw fixation produced similar clinical and radiologic outcomes in subjects with metacarpal fractures. Compared to K-wire fixation, however, headless screw fixation led to earlier functional recovery and might be a better option for treating metacarpal fractures in this regard.
- 560 View
- 5 Download

- Comparison of Reductions of Left and Right Proximal Portions of Intertrochanteric Fractures Treated by Intramedullary Nailing
- Hyun Cheol Oh, Joong Won Ha, Yung Park, Sang Hoon Park, Han Kook Yoon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(2):64-70. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.2.64
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the effect of lag screw insertion on proximal fragments by separating the right and left sides of intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients that underwent intramedullary nailing.
Materials and Methods
Patients aged ≥65 years that underwent intramedullary nailing after a diag-nosis of intertrochanteric fractures during the period February 2012 to May 2016 were included in the study. The subjects were divided into right and left side groups. The effect of the clockwise rotational force generated when a lag screw was inserted on the proximal fragment was evaluated in both groups.
Results
In the right and left groups, most proximal fragments were located in the intramedullary canal after surgery (45 cases [75.0%] and 67 cases [73.6%], respectively). Clockwise rotation due to lag screw placement in the right group occurred in two cases (3.3%), which both showed internal rotation, and in four cases (4.4%) in the left group, all of which showed external rotation.
Conclusion
After intramedullary nailing of intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients, proximal fragments were mostly located in the intramedullary cavity. The results obtained confirmed that the clockwise rotational force generated by lag screw insertion did not affect left or right sides. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Which side should be taken care of when positioning a lag screw in intertrochanteric femoral fracture: right or left?
Min Uk Do, Kyeong Baek Kim, Sang-Min Lee, Hyun Tae Koo, Won Chul Shin
European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Midterm Outcomes of Intramedullary Fixation of Intertrochanteric Femoral Fractures Using Compression Hip Nails: Radiologic and Clinical Results
You-Sung Suh, Jae-Hwi Nho, Min Gon Song, Dong Woo Lee, Byung-Woong Jang
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.2023; 15(3): 373. CrossRef
- Which side should be taken care of when positioning a lag screw in intertrochanteric femoral fracture: right or left?
- 693 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Comparing Outcomes of Screw Fixation and Non-Fixation for Small-Sized Posterior Malleolar Fragment in Ankle Trimalleolar Fractures
- Jee-Wook Ko, Gun-Woo Lee, Keun-Bae Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(1):8-15. Published online January 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.1.8
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study was undertaken to compare outcomes of screw fixation and non-fixation of a small-sized posterior malleolar fragment involving less than 25% articular surface in ankle trimalleolar fractures. Materials and Methods: A total of 32 consecutive ankles (32 patients), with posterior malleolar fragment involving 15%-25% of the joint surface, were enrolled in the study. Patients were divided into 2 groups according to whether the fragment was fixed or not (fixed: 20 ankles, non-fixed: 12 ankles). The minimum follow-up period was 12 months. Median size of the posterior malleolar fragment in the fixed and non-fixed groups were 24.6% (range, 22.3%-25.0%) and 22.1% (range, 17.4%-24.3%), respectively. Complications as well as clinical and radiographic outcomes were compared and analyzed between the two groups. Results: Clinical outcomes, including American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society (p=0.501), visual analogue scale (p=0.578), and ankle range of motion (p=0.552), showed no difference between groups at the final follow-up. No differences were obtained in the radiographic outcomes, including joint stepoff (p=0.289) and fragment gap (p=0.289). Complications, including 1 case of delayed union and 1 case of wound infection, were reported in the fixed group. Conclusion: Clinical outcomes and radiographic outcomes of the non-fixation group were satisfactory and comparable to the fixation group. Our results indicate that anatomical reduction with small-sized posterior malleolar fragment in ankle trimalleolar fractures is sufficient for satisfactory outcomes, without the need for additional internal fixation.
- 800 View
- 11 Download

- Comparison of Percutaneous versus Open Pedicle Screw Fixation for Treating Unstable Thoracolumbar Fractures
- Jin Young Han, Ki Youn Kwon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(1):1-8. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study compared the clinical and radiological results between two groups of patients with percutaneous fixation or conventional fixation after hardware removal.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study analyzed 68 patients (43 open fixation and 43 percutaneous screw fixation [PSF] 25) who had undergone fixation for unstable thoracolumbar fractures. The radiologic results were obtained using the lateral radiographs taken before and after the fixation and at the time of hardware removal. The clinical results included the time of operation, blood loss, time to ambulation, duration of the hospital stay and the visual analogue scale.
RESULTS
The percutaneous pedicle screw fixation (PPSF) group showed better results than did the conventional posterior fixation (CPF) group (p<0.05) in regard to the perioperative data such as operation time, blood loss, and duration of the hospital stay. There were no significant differences in wedge angle, local kyphotic angle, and the ΔKyphotic angle on the postoperative plane radiographs between the two groups (p>0.05). There were no significant differences in the wedge angle and local kyphotic angle after implant removal (p>0.05) between the two groups as well. However, there were significant differences in the segmental montion angle (p<0.001), and the PPSF group showed a larger segmental motion angle than did the CPF group (CPF 1.7°±1.2° vs PPSF 5.9°±3.2°, respectively).
CONCLUSION
For the treatment of unstable thoracolumbar fractures, the PPSF technique could achieve better clinical results and an improved segmental motion angle after implant removal within a year than that of the conventional fixation method. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comparison of 2 Surgical Treatments for Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures: Temporary Osteosynthesis and Arthrodesis
Halil Ibrahim Süner, Rafael Luque Pérez, Daniel Garríguez-Pérez, Marta Echevarría Marín, Jose Luis Pérez, Ignacio Domínguez
World Neurosurgery.2022; 166: e419. CrossRef
- A Comparison of 2 Surgical Treatments for Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures: Temporary Osteosynthesis and Arthrodesis
- 1,517 View
- 22 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Reports
- Subtrochanteric Fracture Reduction during Intramedullary Nailing: Technical Note
- Gyu Min Kong
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(2):107-111. Published online April 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.2.107
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The subtrochanteric area is the place where mechanical stress is most concentrated in the femur. When a fracture happens, bone union is delayed and nonunion often occurs. The recommended treatment for atypical fractures is an anatomical reduction of the fracture site as the frequency of nonunion is higher than that of ordinary fractures. Various reduction methods have been suggested, and good results have been obtained. On the other hand, the occurrence of posterior displacement of the distal fragment during the insertion of an intramedullary nail is often overlooked. This is probably because the bone marrow of the femur tends to form an elliptical shape in the anteroposterior direction. The author attempted to insert a blocking screw into the distal part of the fracture to prevent posterior displacement of the distal fragment while performing intramedullary nailing of the femur fracture and achieved a good reduction state easily.
- 713 View
- 7 Download

- Avulsion Fracture of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament from Femoral Insertion Occurred in a Patient with Residual Poliomyelitis: A Case Report
- Wonchul Choi, Taesup Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(4):149-153. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.4.149
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fracture of the posterior cruciate ligament from its femoral insertion is quite rare, particularly in adults, and the treatment guidelines have not been established. A 68-year-old female patient with residual poliomyelitis presented with an avulsion fracture of the femoral insertion of the posterior cruciate ligament after a falling accident and was treated with arthroscopic headless compression screw fixation and pull-out suture of the avulsed ligament. We report this case with a relevant discussion of this type of injury.
- 399 View
- 0 Download

- Spino-Pelvic Fixation in Unstable Sacral Fracture: A Case Report
- Jung Hwan Choi, Kyu Tae Hwang, Seung Gun Lee, Chang Nam Kang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(4):145-148. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.4.145
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 22-year-old female patient visited the emergency room (ER) after a pedestrian traffic accident in a drunken state. An examination at the ER revealed fractures at the right side of the sacral ala, sacral foramina, left anterior acetabulum, right inferior ramus, and right superior articular process of S1. She underwent spino-pelvic fixation and iliosacral (IS) screw fixation. One year later, bone union was completed and implant removal was performed and the treatment was completed without complications. The authors recommend spino-pelvic fixation and IS screw fixation for unstable sacral fractures as one of the excellent methods for obtaining posterior stability of the pelvis among the various treatments of unstable sacral fractures.
- 346 View
- 1 Download

Original Articles
- Computational Simulation of Multiple Cannulated Screw Fixation for Femoral Neck Fractures and the Anatomic Features for Clinical Applications
- Jin Hoon Jeong, Gu Hee Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(2):37-44. Published online April 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.2.37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To identify the anatomic features for clinical applications through a computational simulation of the fixation of three cannulated screws for a femoral neck fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty cadaveric femurs underwent computed tomography and the images were transferred to the Mimics® program, resulting in three-dimensional proximal femur models. A three-dimensional scan of the 7.0 mm cannulated screw was performed to enable computerized virtual fixation of multiple cannulated screws for femoral neck fractures. After positioning the screws definitively for cortical support, the intraosseous position of the cannulated screws was evaluated in the anteroposterior image and axial image direction.
RESULTS
Three cannulated screws located at the each ideal site showed an array of tilted triangles with anterior screw attachment and the shortest spacing between posterior and central screws. The central screw located at the lower side was placed in the mid-height of the lesser trochanter and slightly posterior, and directed toward the junction of femoral head and neck to achieve medial cortical support. All the posterior screws were limited in height by the trochanteric fossa and were located below the vastus ridge, but the anterior screws were located higher than the vastus ridge in 10 cases. To obtain the maximum spacing of the anterior and posterior screws on the axial plane, they should be positioned parallel to the cervical region nearest the cortical bone at a height not exceeding the vastus ridge.
CONCLUSION
The position of cannulated screws for cortical support were irregular triangular arrangements with the anterosuperior apex. The position of the ideal central screw in the anteroposterior view was at the mid-height of the lesser trochanter toward the junction of the femoral head and neck, and the anterior and posterior screws were parallel to the neck with a maximal spread just inferior to the vastus ridge. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Computational Simulation of Femoral Neck System and Additional Cannulated Screws Fixation for Unstable Femoral Neck Fractures and the Biomechanical Features for Clinical Applications
Ju-Yeong Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2023; 36(1): 1. CrossRef
- Computational Simulation of Femoral Neck System and Additional Cannulated Screws Fixation for Unstable Femoral Neck Fractures and the Biomechanical Features for Clinical Applications
- 687 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Surgical Outcome of Posterior Pelvic Fixation Using S1, S2 Screws in Vertically Unstable Pelvic Ring Injury
- Kwang Hee Yeo, Nam Hoon Moon, Jae Min Ahn, Jae Yoon Jeong, Jae Hoon Jang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(1):9-17. Published online January 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.1.9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Iliosacral screw fixation is an effective and less invasive method that is used widely for the definitive treatment of unstable pelvic ring injuries. On the other hand, fixation failures after iliosacral screw fixation have been reported in vertically unstable pelvic ring injuries. This study examined the surgical outcomes of posterior pelvic fixation using S1 and S2 screws in vertically unstable pelvic ring injuries.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between January 2011 and April 2016, 17 patients with vertically unstable pelvic ring injuries who met the minimum 1 year follow-up criteria were treated with internal fixation using posterior pelvic S1 and S2 screws. Their mean age was 43.9 years. According to the AO/OTA classification, 10 patients had C1, 6 had C2, and 1 had C3 injuries. Surgical treatments of single or multiple steps, where necessary, were performed by two surgeons. The clinical and radiologic outcomes were assessed retrospectively using radiographs and medical records.
RESULTS
Overall, 16 patients had bone healing without screw loosening; however, one patient could not maintain anterior pelvic fixation because of an open fracture and deep infection in the anterior pelvic ring. Of five patients who complained of neurological symptoms after injury, three had partially recovered from their neurological deficit. At the last follow-up, the clinical outcomes according to the Majeed score were excellent in 5, good in 6, fair in 4, and poor in 2 patients. The postoperative radiologic outcomes by Matta and Tornetta's method were excellent in 5, good in 8, and fair in 4 patients. Malposition of the S2 screw was identified in one case. The mean time to union was 14.6 weeks after surgery.
CONCLUSION
S1 and S2 screw fixation can be an effective treatment option for posterior pelvic stabilization in vertically unstable pelvic ring injuries when considering the surgical outcomes, such as screw loosening and loss of reduction. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fixation Options of Unstable Posterior Pelvic Ring Disruption: Ilio-Sacral Screw Fixation, S2AI Fixation, Posterior Tension Band Plate Fixation, and Spino-Pelvic Fixation
Dong-Hee Kim, Jae Hoon Jang, Myungji Shin, Gu-Hee Jung
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2019; 32(4): 240. CrossRef
- Fixation Options of Unstable Posterior Pelvic Ring Disruption: Ilio-Sacral Screw Fixation, S2AI Fixation, Posterior Tension Band Plate Fixation, and Spino-Pelvic Fixation
- 560 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Reports
- Intrapelvic Penetration of Lag Screw in Proximal Femoral Nailing: A Case Report
- Jung Woo Lee, Hong Man Cho, Jae Woong Seo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(4):203-208. Published online October 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.4.203
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hip fractures are common among elderly individuals. Internal fixation with the intramedullary system has been widely used to treat intertrochanteric femur fractures. The Gamma 3 nail is a useful device for fixating trochanteric fractures of the proximal femur. We report a rare complication of medial pelvic penetration of the lag screw of a Gamma 3 nail two months after surgery. There was a complete separation between the nail body and lag screw, and the lag screw penetrated through the acetabulum into the pelvis. We report a case of unstable intertrochanteric fracture with intrapelvic penetration after surgical treatment with proximal femoral nailing and a case followed by fatal results.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Medial lag screw migration in an intramedullary nail combination
Zac Dragan, Ryan J Campbell, Terence R Moopanar
BMJ Case Reports.2025; 18(3): e262436. CrossRef - Slipped hip acetabular cortical screw: Laparoscopy to the rescue
Nidhi Paswan, Lovenish Bains, Soukat Ali Khan, Anubhav Vindal, Lalit Maini
Journal of Minimal Access Surgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endovascular assisted removal of intrapelvic lag screw after intramedullary proximal femoral nail: A case report and literature review
Zakaria Mousati, Mathias Van Den Broek, Joren Callaert, Jan Gielis, Kris Govaers
Trauma Case Reports.2023; 46: 100873. CrossRef - Intrapelvic migration of the lag screw in intramedullary nailing after intertrochanteric fracture fixation: A case report
Aymen Ben Fredj, Hedi Rbai, Fourat Farhat, Marouen Berriri
Clinical Case Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Intramedullary nailing confers an increased risk of medial migration compared to dynamic hip screw fixation in unstable intertrochanteric hip fractures
Gin Way LAW, Yoke Rung WONG, Antony GARDNER, Yau Hong NG
Injury.2021; 52(11): 3440. CrossRef - Medial migration in cephalomedullary nail fixation of pertrochanteric hip fractures
G. W. Law, Y. R. Wong, A. K-S. Yew, A. C. T. Choh, J. S. B. Koh, T. S. Howe
Bone & Joint Research.2019; 8(7): 313. CrossRef - Intrapelvic Migration of the Lag Screw with Wedge Wing from Dyna Locking Trochanteric Nail: A Case Report and Literature Review
Yong-Woo Kim, Weon-Yoo Kim, Kyong-Jun Kim, Se-Won Lee
Hip & Pelvis.2019; 31(2): 110. CrossRef
- Medial lag screw migration in an intramedullary nail combination
- 1,461 View
- 16 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Arthroscopic Assisted Bioabsorbable Screw Fixation for Radial Head Fractures: A Report of Two Cases
- Bong Ju Park, Ki Yong An, Yong Suk Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(1):35-39. Published online January 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.1.35
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Most radial head fractures occur as the result of low-energy mechanisms, such as a trip or fall on the outstretched hand. These fractures typically occur when an axial load is applied to the forearm, causing the radial head to hit the capitellum of the humerus. Good results are shown with nonsurgical treatments for Mason type 2 fractures. However, if there is a limitation of elbow joint exercise or displacement of more than 2 mm, an operative treatment should be considered. We treated two patients with arthroscopic assisted bioabsorbable screw (K-METâ„¢; U&I Corporation, Uijeongbu, Korea) fixation for radial head fractures to prevent complications of open reduction and minimize radiation exposure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bioabsorbable Screws Used in Hallux Valgus Treatment Using Proximal Chevron Osteotomy
Woo-Jin Shin, Young-Woo Chung, Ki-Yong An, Jae-Woong Seo
Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society.2018; 22(4): 181. CrossRef
- Bioabsorbable Screws Used in Hallux Valgus Treatment Using Proximal Chevron Osteotomy
- 690 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Pediatric Cartilaginous Tibia Eminence Fracture Overlooked on Plain Radiograph: A Report of Two Cases
- Seong Eun Byun, Yunseong Choi, Wonchul Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(1):29-34. Published online January 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.1.29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In children with open physis, avulsion fracture of the tibia eminence, as an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury, is more commonly observed than an ACL rupture. Pure cartilaginous avulsions of the ACL tibia insertion seldom occurs. In such case, cartilaginous lesion is frequently overlooked or misdiagnosed on plain radiograph and may result in a less favorable treatment outcome. We report two cases of cartilaginous tibia eminence fractures of the children that were initially overlooked from plain radiographs, and then diagnosed by magnetic resonance imaging, which was ultimately treated by arthroscopyassisted headless compression screw fixation.
- 495 View
- 4 Download

Original Articles
- The Role of Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate Graft in the Dynamic Hip Screw Fixation of Unstable Intertrochanter Fracture
- Chul Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim, Eic Ju Lim, Jae Suk Chang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(4):250-257. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.4.250
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to introduce our method of stabilizing unstable intertrochanteric fractures by using the dynamic hip screw (DHS) with a beta-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP) graft and to compare the outcomes of this procedure with those of the conventional DHS without β-TCP.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients who underwent surgery by using DHS between March 2002 and January 2016 were retrospectively reviewed for analysis of the outcomes. The inclusion criteria were: 1) age of 60 years and older; 2) low-energy fracture resulting from a fall from no greater than the standing height; 3) multifragmentary pertrochanteric fracture (AO classification 31-A2.2, 2.3); and 4) follow-up of over 3 months. We compared 29 patients (29 hips) who underwent surgery, using DHS without β-TCP, with 29 age-sex matched patients (29 hips) who underwent surgery using DHS with grafted β-TCP granules to empty the trochanter area after reaming. We investigated the fracture union rate, union time, and length of lag screw sliding.
RESULTS
Bone union was achieved in all cases. The mean union time was 7.0 weeks in the β-TCP group and 8 .8 weeks in the non-β-TCP group. The length of lag screw sliding was 3.6 mm in the β-TCP group and 5 .5 mm in the non-β-TCP group. There were no implant failure cases in both groups.
CONCLUSION
The β-TCP graft for reinforcement DHS acquired satisfactory clinical outcomes for treating unstable intertrochanteric fractures.
- 437 View
- 3 Download

- Surgical Treatment for Stable 2-Part Intertrochanteric Femur Fracture Using Dynamic Hip Screw with 2-Hole Side Plate in Elderly Patients
- Kyung Hoon Lee, Suk Ku Han, Seung Jae Chung, Jongho Noh, Kee Haeng Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(3):192-199. Published online July 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.3.192
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the postoperative outcomes of elderly patients with stable 2-part intertrochanteric femur fractures surgically treated using dynamic hip screw with 2-hole side plate.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From February 2008 to January 2014, 50 patients older than the age of 65 years, who had been followed-up for more than 6 months after the operation at The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital were enrolled. A clinical evaluation of the skin incision length, operating time, and ambulatory status, using Clawson's Ambulation Capacity Classification, was performed, and a radiologic evaluation of Fogagnolo reduction quality, tip-apex distance (TAD), Cleveland index, sliding extent of lag screws, time duration till bony union, and complications was also done.
RESULTS
The mean skin incision length was 9.8 cm (range, 8-13 cm), the mean operating time was 41.4 minutes (range, 30-60 minutes), and 32 patients recovered their ambulatory function. Forty-eight patients gained bony union, and the time lapsed till union was average 10.6 weeks (range, 8-16 weeks). The evaluation of postoperative radiologic images showed the following reduction statuses by the Fogagnolo classification: 46 cases of "Good", 3 cases of "Acceptable," and 1 case of "Poor." Moreover, the mean TAD was 18.9 mm (range, 9.0-24.9 mm). While 45 cases fit into the zone 5 of the Cleveland index, other 3 were within zone 8 and the other 2 were within zone 6. The mean sliding length of the lag screws were 4.9 mm (range, 0.1-19.4 mm). There were a case of nonunion and a case of periprosthetic infection with nonunion as complications.
CONCLUSION
Using dynamic hip screws with 2-hole side plate for stable 2-part intertrochanteric femur fractures in elderly patients showed satisfactory results with respect to the recovery of ambulatory functions and bony union.
- 466 View
- 0 Download

- The Usefulness of Poller Screw with Antegrade Nailing in the Initial Treatment of Infraisthmal Femur Shaft Fracture
- Jeong Hyun Yoo, Hyoung Soo Kim, Chang Geun Kim, Ho Il Kwak, Sang Heon Song
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(4):230-236. Published online October 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.4.230
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the radiologic and clinical outcomes after intramedullary nailing with Poller screw insertion at initial stage in infraisthmal femur shaft fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Seven consecutive patients (7 femurs) treated with antegrade intramedullary nailing with Poller screw insertion for the infraisthmal femur shaft fracture were reviewed retrospectively. There were 4 male and 3 female patients. Mean age was 46.1 years (20-72 years). Operative time including Poller screw insertion, time for union, malalignment, and range of motion were evaluated.
RESULTS
All 7 cases had primarily healed successfully. Mean time for radiologic union was 19.1 weeks (16-24 weeks) postoperatively. One case had 5 degree valgus malalignment. One case of 15 mm shortening was reported and he required shoe lift orthosis. All cases had a full range of motion in hip and knee joint.
CONCLUSION
Antegrade intramedullary nailing with Poller screw insertion is useful in the initial treatment of infraisthmal femur shaft fracture, because it could provide additional stability. An additional 20 minutes were required but a Poller screw should be considered according to the anatomic location of a femur shaft fracture.
- 514 View
- 4 Download

- Results of Use of Compression Hip Screw with Trochanter Stabilizing Plate for Reverse Oblique Intertrochanteric Fracture
- Byung Woo Min, Kyung Jae Lee, Gyo Wook Kim, Ki Cheor Bae, Si Wook Lee, Du Han Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(2):120-126. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.2.120
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to analyze the use of a compression hip screw with a trochanter stabilizing plate for treatment of reverse oblique intertrochanteric fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed the results of 33 cases of reverse oblique intertrochanteric fracture treated with a compression hip screw with a trochanter stabilizing plate from January 2000 to December 2012 which were followed-up for more than one year. We evaluated postoperative bone union period, change of neck-shaft angle, sliding of hip screw, and other complications.
RESULTS
Of 33 patients, satisfactory reduction was achieved in 28 patients. Five patients had an unsatisfactory reduction, with two cases of excessive screw sliding, one of broken metal, one of varus deformity, and one of internal rotation deformity. We performed corrective osteotomy in varus and internal rotation deformity and partial hip replacement in a case of excessive screw sliding. Bone union was achieved in 29 patients, and the average bone union period was 19.2 weeks.
CONCLUSION
We consider that a compression hip screw with a trochanteric stabilized plate is a good option for treatment of reverse oblique intertrochanteric femoral fractures. However, adequate fracture reduction and ideal implant placement are a basic necessity for successful treatment.
- 785 View
- 6 Download

Case Report
- Rupture of the Extensor Pollicis Longus Tendon at the Proximal Screw of Volar Plate Fixation for Distal Radius Fracture: A Case Report
- Dong Ju Shin, Seung Oh Nam, Hun Sik Cho
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(4):338-342. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.338
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - As volar plate fixation of distal radius fracture becomes more common, reports of ruptured extensor pollicis longus tendon by a protruding distal screw tip are also increasing steadily. Authors have experienced a rare case of ruptured extensor pollicis longus tendon at the prominent proximal screw of fixed volar plate for distal radius fracture, and we report it herein with a review of the literature.
- 533 View
- 1 Download

Original Article
- Treatment of Unstable Sacral Fractures Related to Spino-Pelvic Dissociations
- Hong Sik Kim, Jung Hwan Lee, Ki Chul Park, Ye Soo Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(3):178-183. Published online July 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.3.178
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the outcomes of surgical treatment modality in unstable sacral fractures combined with spinal and pelvic ring injury depending on the presence of spino-pelvic dissociations.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The subjects were 16 patients, with unstable sacral fractures combined with spinal and pelvic ring injuries, were operated from July 2004 to January 2011. The patients were divided into 2 groups depending on the presence of spino-pelvic dissociations: those with dissociations were group 1, and those without dissociations were group 2. Group 1 was treated with spino-pelvic fixations using iliac screw, while group 2 was treated with percutaneous iliosacral screw fixations. The availability of the radiological bony union with its application periods, and clinical results using visual analogue scale (VAS) and oswestry disability index (ODI) were evaluated, retrospectively.
RESULTS
Out of 16 patients, 8 patients in group 1 were treated with spino-pelvic fixation using iliac screw, and 8 patients in group 2 were treated with percutaneous iliosacral screw fixation. The mean bony union period was 17.4 weeks in group 1, and 19.6 weeks in group 2. The Mean VAS and ODI scores on the last follow-up were 2.5 points and 15.6 points in group 1, 2 points and 18.8 points in group 2, respectively. Both groups had favorable clinical results at the last follow-up.
CONCLUSION
For surgical treatments of unstable sacral fractures, spino-pelvic fixation using iliac screws is advised for cases with combined spino-pelvic dissociation, while percutaneous iliosacral screw fixation is advised for cases without combined dissociation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Integrative Korean Medicine Treatment for Sacral Fracture: Two Clinical Cases
Yeon Soo Kang, Pil Je Park, So Jeong Kim, Hyun Jin Jang, Min Ju Kim, Hyeon Kyu Choi, Jeong Kyo Jeong, Ju Hyun Jeon, Young Il Kim
Journal of Acupuncture Research.2023; 40(3): 281. CrossRef - Spino-Pelvic Fixation in Unstable Sacral Fracture: A Case Report
Jung-Hwan Choi, Kyu-Tae Hwang, Seung Gun Lee, Chang-Nam Kang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2018; 31(4): 145. CrossRef
- Integrative Korean Medicine Treatment for Sacral Fracture: Two Clinical Cases
- 700 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

Case Report
- Extensive Metallosis Caused by Plate and Screw Construct for Distal Fibular Fracture - A Case Report -
- Ki Tae Park, Kwang Bok Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(2):147-150. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.2.147
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Metallosis has been reported in the setting of weight-bearing joint arthroplasties, like the hip and knee joints. However, the prevalence of metallosis in non-articular portions is very uncommon. We report a rare case of a patient who had metallosis secondary by fibular nonunion after fixation with plate and screw. In addition, we discuss the clinical and the operative findings, as well as the outcome of this uncommon complication.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Plate on Plate Osteosynthesis for the Treatment of Nonhealed Periplate Fractures
Georgios Arealis, Vassilios S. Nikolaou, Andrew Lacon, Neil Ashwood, Mark Hamlet
ISRN Orthopedics.2014; 2014: 1. CrossRef
- Plate on Plate Osteosynthesis for the Treatment of Nonhealed Periplate Fractures
- 599 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- A Comparison between Compression Hip Screw and Intramedullary Nail for the Treatment of AO/OTA A2.2 Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture
- Phil Hyun Chung, Suk Kang, Jong Pil Kim, Young Sung Kim, Ho Min Lee, Jong Hyun Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(1):44-49. Published online January 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.1.44
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To compare the result between the compression hip screw (CHS) and intramedullary (IM) nail for the treatment of AO/OTA A2.2 intertrochanteric fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed 95 cases of AO/OTA A2.2 intertrochanteric fracture, which were treated with CHS or IM nail by one surgeon from March 1994 to December 2009. One group was treated with CHS (Group I, 28 cases) and the other was treated with IM nail (Group II, 67 cases). We evaluated the mean operation time, the amount of bleeding and transfusion, hospital duration, radiological results and the clinical outcome with the mobility score of Parker and Palmer.
RESULTS
Radiologically, the tip-apex distance, change of neck-shaft angle, and union time were not significantly different between both groups (p>0.05). Clinically, the mean operation time, the amount of bleeding and transfusion, hospital duration and the mobility score were not significantly different (p>0.05). The post-operative complications were lag screw slippage over 25 mm (1 case) and loosening of device (1 case) in group I. In group II, there were perforation of the femoral head (1 case), nail breakage (1 case) and deep infection (1 case).
CONCLUSION
There was no significant differences that are clinical and radiological results in the treatment of AO/OTA A2.2 intertrochanteric fracture, using CHS and IM nail. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comparison of Clinical Results between Compression Hip Screw and Proximal Femoral Nail as the Treatment of AO/OTA 31-A2.2 Intertrochanteric Femoral Fractures
Phil Hyun Chung, Suk Kang, Jong Pil Kim, Young Sung Kim, Ho Min Lee, In Hwa Back, Kyeong Soo Eom
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2016; 51(6): 493. CrossRef
- A Comparison of Clinical Results between Compression Hip Screw and Proximal Femoral Nail as the Treatment of AO/OTA 31-A2.2 Intertrochanteric Femoral Fractures
- 1,659 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Anatomical Study of Symphysis Pubis Using 3 Dimensional Computed Tomography in Koreans
- Ji Wan Kim, Jung Min Park, Jae Suk Chang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(1):32-36. Published online January 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.1.32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To acquire anatomical data for the normal pelvic bone structure using three-dimensional computed tomography (3D CT) and to propose the most appropriate angle and screw length for safe screw insertion during symphysis pubis plating.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We performed 3D CT analysis in 52 patients who required plating and selected a medial and lateral insertion point between the symphysis pubis and the pubic tubercle. Using a three-dimensional medical image analysis program, we evaluated the appropriate screw length, sagittal angle, and oblique angle at each point in this cohort.
RESULTS
At the medial point, the sagittal angle was determined to be 49.1degrees with an average screw length of 49.4 mm. At the lateral point, we calculated an average screw length of 49.1 mm, oblique angle of 23.2degrees, and sagittal angle of 45.7degrees. The screw length was longer in men than in women (4.6 mm and 7.3 mm, respectively) at the medial and lateral point.
CONCLUSION
At the symphysis pubis diastasis, we can insert the screw caudally at 49degrees with a minimal length of 37 mm at the medial point. We can insert the screw caudally at 46degrees, medially at 23degrees, with a minimal 34 mm length at the lateral point.
- 555 View
- 3 Download

- Anatomical Reduction of All Fracture Fragments and Fixation Using Inter-Fragmentary Screw and Plate in Comminuted and Displaced Clavicle Mid-Shaft Fracture
- Kyoung Hwan Koh, Min Soo Shon, Seung Won Lee, Jong Ho Kim, Jae Chul Yoo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(4):300-304. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.300
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To report the treatment results of anatomical reduction of all fracture fragments and internal fixation using an inter-fragmentary screw and plate in displaced mid-shaft clavicle fracture with comminution.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between June 2005 and August 2011, 13 consecutive displaced clavicle fractures with comminution (Edinburgh classification IIB2) treated by anatomic reduction and internal fixation using inter-fragmentary screw and plate were retrospectively evaluated. There were 11 male and 2 female patients with a mean age of 37.4 years (15~55 years). The right clavicle was injured in 4 patients and the dominant arm was involved in 46%. The mean duration from trauma to surgery was 7.0 days. The cause of injury was a traffic accident in three, a fall in two, and sports activity or direct injury in eight patients. All of the fracture pieces were anatomically reduced and fixed with inter-fragmentary screws. An additional plate was applied to maintain and reinforce the reduction of the fracture. Radiographic assessments for the numbers of fragments and the amount of shortening and displacement were performed. To verify the fracture healing and determine the time from fracture surgery to union and complications, all of the radiographs taken after surgery were evaluated.
RESULTS
The number of fragments was 2 in 7 cases, 3 in 5 cases, and 6 in one case. The mean shortening of the clavicle was 1.1 cm (0.3~2.1 cm) and mean displacement between the main fragments was 2.6 cm (1.3~4.5 cm). The mean duration of follow-up was 16.5 months (8~26 months). Radiographic union was achieved in all patients with a mean time to union of 10.8 weeks (8~14 weeks). There were no complications including metal failure, nonunion, or infection.
CONCLUSION
Anatomical reduction of all the fracture fragments and fixation using inter-fragmentary screws in addition to the usual plate fixation showed good fracture healing in displaced clavicle fracture with comminution. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Additional fixation using a metal plate with bioresorbable screws and wires for robinson type 2B clavicle fracture
Woo Jin shin, Young Woo Chung, Seon Do Kim, Ki-Yong An
Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow.2020; 23(4): 205. CrossRef - Use of Composite Wiring on Surgical Treatments of Clavicle Shaft Fractures
Kyung Chul Kim, In Hyeok Rhyou, Ji Ho Lee, Kee Baek Ahn, Sung Chul Moon
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2016; 29(3): 185. CrossRef
- Additional fixation using a metal plate with bioresorbable screws and wires for robinson type 2B clavicle fracture
- 843 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Operative Treatment of Unstable Pelvic Ring Injury
- Sang Hong Lee, Sang Ho Ha, Young Kwan Lee, Sung Won Cho, Sang Soo Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(4):243-249. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.243
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyze the clinical and radiological results of the different fixation methods according to the type and displacement of unstable pelvic ring injuries.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty-three patients with unstable pelvic ring injuries from January 2005 to December 2009 were classified according to the AO/OTA classification system. When patients had been diagnosed with unstable pelvic ring injuries with partial instability, they were treated by anterior fixation with a plate and posterior percutaneous iliosacral screw fixation. When patients had been diagnosed with unstable pelvic ring injuries with complete instability, they were treated by open reduction and anterior to posterior fixation with a plate through the ilioinguinal approach. The radiological results were evaluated using Matta and Saucedo's method, and the clinical results were evaluated using Rommens and Hessmann's method.
RESULTS
The outcomes from the radiological evaluation were that the displacement of the posterior pelvic ring were improved by about 6.65 mm in unstable pelvic ring injuries with partial instability. The displacement of the posterior pelvic ring were improved by about 7.8 mm in unstable pelvic ring injuries with complete instability. The clinical results were excellent in 13 cases and good in 6 cases on latest follow-up.
CONCLUSION
Good results can be achieved by selecting the treatment method according to the type of unstable pelvic ring injurie and displacement. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Displacement of an anterior pelvic ring fracture after L5, S1, and iliac screw fixation: a case report
Euijin Cho, Joonghyuk Kim, Hyeongyu Lim, Kyeol Han, Yonghun Pee, Junhong Min, Il-Tae Jang, Jeesoo Jang
Journal of Korean Society of Geriatric Neurosurgery.2025; 21(1): 24. CrossRef - Functional outcomes in pelvic fractures and the factors affecting them– A short term, prospective observational study at a tertiary care hospital
Subhajit Ghosh, Sameer Aggarwal, Prasoon Kumar, Vishal Kumar
Journal of Clinical Orthopaedics and Trauma.2019; 10(5): 896. CrossRef - Outcome of Surgical Treatment of AO Type C Pelvic Ring Injury
Do Hyeon Moon, Nam Ki Kim, Jun Sung Won, Jang Seok Choi, Dong Hyun Kim
Hip & Pelvis.2014; 26(4): 269. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Humeral Proximal or Distal Shaft Fractures Using a 3.5/5.0 Metaphyseal Locking Plate
Hyoung Keun Oh, Suk Kyu Choo, Jung Il Lee, Dong Hyun Seo
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(4): 305. CrossRef
- Displacement of an anterior pelvic ring fracture after L5, S1, and iliac screw fixation: a case report
- 849 View
- 6 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Surgical Treatment of Femoral Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures in Elderly Patients: Comparative Study between Compressive Hip Screws and Additional Trochanteric Stabilizing Plates
- Kap Jung Kim, Dae Suk Yang, Sang Ki Lee, Won Sik Choy, Kyoung Wan Bae
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(4):295-300. Published online October 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.4.295
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the radiologic results between compressive hip screw and compressive hip screw with additional trochanteric stabilizing plate in patients with femoral unstable intertrochanteric fractures in patients with more 65 years old.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From 2006 to May 2009, 121 cases were included. Group I (compressive hip screw only) was 54 cases and group II (compressive hip screw with trochanteric stabilizing plate) was 67 cases. We checked the lag screw sliding, lateral translation of greater trochanter, changes of neck-shaft angle and complications through periodic follow up of radiographs.
RESULTS
Mean lag screw sliding was 7.6 mm in group I and 3.9 mm in group II (p=0.001). Mean lateral translation of greater trochanter was 3.86 mm in group I and 0.59 mm in group II (p=0.01). Mean changes of neck-shaft angle was nearly the same, 3.57degrees in group I and 3.66degrees in group II. Complications were 15 cases in group I and 10 cases in group II.
CONCLUSION
Compressive hip screw with additional trochanteric stabilizing plate was effective surgical option in patients with femoral unstable intertrochanteric fractures in patients with more than 65 years old. It decreased lag screw sliding, lateral translation of greater trochanter and complication rates. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Role of Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate Graft in the Dynamic Hip Screw Fixation of Unstable Intertrochanter Fracture
Chul-Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim, Eic Ju Lim, Jae Suk Chang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2016; 29(4): 250. CrossRef
- The Role of Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate Graft in the Dynamic Hip Screw Fixation of Unstable Intertrochanter Fracture
- 715 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Failure of Removal of Stripped Locking Screw after Locking Compression Plating
- Sung Jin Kim, Kyung Jae Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(2):169-173. Published online April 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.2.169
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the incidence and possible causes of stripped locking screws that make difficult to remove the locking compression plate. We also tried to find the useful methods to remove the stripped locking screws.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between May 2005 and January 2009, 84 patients who underwent operations for removal of locking compression plate were included in this study. We removed 298 3.5-mm locking screws and 289 5.0-mm locking screws in these patients. We retrospectively investigated the incidence and possible causes of stripped locking screws and evaluated the pros and cons of the methods that we have used to remove the stripped locking screws.
RESULTS
17 out of 298 3.5-mm locking screws (5.7%) and 2 out of 289 5.0-mm locking screws (0.7%) were encountered with difficulties by hexagonal driver during removal because of the stripping of the hexagonal recess. First we used the conical extraction screw for all the stripped locking screws and only 3 screws were removed successfully. We removed 3 screws by cutting the plate around the stripped locking screw and twisting the plate with the screw and we removed 1 screw by the use of hallow reamer after cutting the plate. Twelve screw shafts were left except grinding of screw head by metal-cutting burr. There was one iatrogenic re-fracture in whom we have used with hallow reamer.
CONCLUSION
At the time of locking compression plate removal, difficulties of locking screw removal due to the stripping of the hexagonal recess should be expected and surgeon must prepare several methods to solve this problem. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An inexpensive and rapid method for removal of multiple stripped locking screws following locking plating
Won Ro Park, Jae Hoon Jang
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2019; 57(C): 134. CrossRef
- An inexpensive and rapid method for removal of multiple stripped locking screws following locking plating
- 794 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Comparison of the Compression Hip Screw (CHS) and the Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA) for Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture
- Jong Min Lim, Jeung Il Kim, Jong Seok Oh, Kuen Tak Suh, Jae Min Ahn, Dong Joon Kang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(4):360-366. Published online October 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.4.360
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the radiologic, clinical results between who had intertrochanteric fracture, treated with Compression Hip Screw (CHS) and Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed each 36 and 48 patients of intertrochanteric fracture which were treated with CHS or PFNA by one surgeon from January 2005 to June 2009. We evaluated mean operation time, amount of bleeding, radiologic results, and the clinical outcomes with the mobility score of Parker and Palmer, social function scoring system.
RESULTS
The mean operation time, amount of bleeding were less in the PFNA group, there were 116.7 min, 486.1 ml for the CHS group versus 87.7 min, 289.6 ml for the PFNA group. The radiologic results were not significantly different. Decrease of mobility score of Parker and Palmer, social function score were similar. Proximal migration of leg screw and perforation of femoral head was 2 case and deep infection was 1 cases in CHS group.
CONCLUSION
There were no significant differences that are clinical and radiological results in treatment of intertrochanteric fracture using the CHS and PFNA. But PFNA is less invasive device than CHS, therefore it may be useful device in elderly patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Chronic kidney disease patients with intertrochanteric fracture have a high mortality rate
Tae Woo Kim, Sang-Min Lee, Nam Hoon Moon, Won Chul Shin
Injury.2021; 52(8): 2350. CrossRef - Comparison between the Results of Internal Fixation Using Proximal Femur Nail Anti-rotation and Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty in Treatment of Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures of Elderly Patients
Sung-Hwan Kim, Soo-Won Lee, Gyu-Min Kong, Mid-Um JeaGal
Hip & Pelvis.2012; 24(1): 45. CrossRef - Treatment of Intertrochanteric Fractures Using Targon Proximal Femoral Nails
Il Ho Park, Jong Kyoung Won, Kye Young Han
Hip & Pelvis.2012; 24(2): 117. CrossRef - A Comparison of Intramedullary and Extramedullary Fixations for the Treatment of Reverse Oblique or Transverse Intertrochanteric Femoral Fractures
Yerl-Bo Sung, Jung-Yun Choi, Eui-Yub Jung
Hip & Pelvis.2012; 24(2): 109. CrossRef
- Chronic kidney disease patients with intertrochanteric fracture have a high mortality rate
- 2,158 View
- 5 Download
- 4 Crossref

- Analysis of the Causes for Failed Compression Hip Screws in Femoral Intertrochanteric Fracture and Hip Reconstruction Operation
- Ui Seoung Yoon, Jin Soo Kim, Jae Sung Seo, Jong Pil Yoon, Seung Yub Baek
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(3):270-275. Published online July 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.3.270
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyze the causes of fixation failure of compression hip screw and evaluate outcomes of hip arthroplasty for reconstruction.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed 108 femoral intertrochanteric fractures that underwent compression hip screw between January 1997 and December 2007. Failure group (group I) contained 28 cases who had hip arthroplasty for failed compression hip screw and the control group (group II) contained 80 cases who had successive compression hip screw. We analyzed the causes of failure of compression hip screw and evaluated the results of hip arthroplasty for reconstruction.
RESULTS
In group I, 21 cases (75%) were unstable fractures. Group II, 14 cases (17%) were unstable fractures. Tip-apex distance was 26.5 (18~35) mm in group I and 18.6 (8~22) mm in group II. Lateral wall fracture of greater trochanteric area was combined in 24 cases (85.7%) in group I and 9 cases (11.3%) in group II. Harris Hip Score improved from 33.5 (22~43) points to 84.2 (75~93) points after salvage hip arthroplasty.
CONCLUSION
We considered the causes of failed compression hip screw to be fracture instability, increased tip-apex distance and presence of lateral wall fracture of greater trochanter. Hip arthroplasty was found to be a useful method for failed compression hip screw.
- 486 View
- 1 Download

- Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation versus Compression Hip Screw with Trochanter Stabilizing Plate for Unstable Intertrochanteric Hip Fractures
- Jae Young Rho, Sang Bum Kim, Youn Moo Heo, Seong Jin Cho, Dong Sik Chae, Woo Suk Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(2):161-166. Published online April 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.2.161
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyze and compare the clinical and radiologic results of treatments in unstable intertrochanteric fractures of the femur with proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) and compression hip screw with trochanter stabilizing plate (CHS with TSP).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the results of 66 cases of unstable intertrochanteric fractures of the femur treated with PFNA (Group I) and CHS with TSP (Group II) which could be followed up for minimum a year. We evaluated several comparative factors such as operation time, blood loss, time to bone union, changes in neck-shaft angle, sliding of screw (or blade), complications, postoperative pain, social-function score of Jensen, and mobility score of Parker and Palmer.
RESULTS
Group I showed shorter operation time and less blood loss with significance than group II (p<0.05), but there were no differences between the groups in the mean time to bone union, changes in neck-shaft angle, sliding of screw (or blade), complications, postoperative pain, and social-function score of Jensen (p>0.05). Two cases of cutting out of the blade through the femoral head were found in group I. One case of cutting out of the screw, one case of the breakage of the plate, and loosening of the plate were found in group II as complications.
CONCLUSION
We think that there were no significant differences between PFNA and CHS with TSP in view point of radiologic and clinical outcomes in unstable intertrochanteric fractures of the femur, but PFNA is less invasive device than CHS with TSP, therefore it may be useful device in elderly patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Results of Use of Compression Hip Screw with Trochanter Stabilizing Plate for Reverse Oblique Intertrochanteric Fracture
Byung-Woo Min, Kyung-Jae Lee, Gyo-Wook Kim, Ki-Cheor Bae, Si-Wook Lee, Du-Han Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(2): 120. CrossRef - Effectiveness of the Valgus Reduction Technique in Treatment of Intertrochanteric Fractures Using Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation
Ji-Kang Park, Hyun-Chul Shon, Yong-Min Kim, Eui-Sung Choi, Dong-Soo Kim, Kyoung-Jin Park, Byung-Ki Cho, Jung-Kwon Cha, Sang-Woo Kang
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2013; 48(6): 441. CrossRef - A Comparison of Intramedullary and Extramedullary Fixations for the Treatment of Reverse Oblique or Transverse Intertrochanteric Femoral Fractures
Yerl-Bo Sung, Jung-Yun Choi, Eui-Yub Jung
Hip & Pelvis.2012; 24(2): 109. CrossRef
- Results of Use of Compression Hip Screw with Trochanter Stabilizing Plate for Reverse Oblique Intertrochanteric Fracture
- 912 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Treatment of Ulnar Olecranon Fracture Using Acutrak Screw
- Hyungchun Kim, Kwangryul Kim, Moonsup Lim, Youngil Park, Inhwan Hwang, Jihoon Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(4):270-275. Published online October 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.4.270
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical results of Acutrak screw fixation for ulnar olecranon fractures. MATERIALS AND METHODS: We reviewed 15 cases of ulnar olecranon fractures which were treated with Acutrak screws from February 2003 to September 2007. Follow-up period is from 12 months to 42 months. We used Mayo classification. Radiologic results were analyzed according to step-off, gap, reduction loss, and functional results were analyzed according to pain and ROM. We analyzed union time, operation time, incision size and complications. RESULTS: In functional results, there were 3 good cases out of 3 Mayo type IA, 8 good cases and 2 fair cases out of 10 type IIA, 1 fair case and 1 poor case out of 2 type IIB. In radiologic results, there was 1 case of reduction loss. Average union time was 9.4 weeks, average operation time was 24 minutes and average incision size was 1.8 cm. CONCLUSION: We conclude that Acutrak screw fixation can be a treatment option for olecranon fracture of Mayo type IA and IIA.
- 481 View
- 3 Download

- Treatment of Unstable Intertrochanteric Fracture in Elderly Patients : Comparison between the Results of Internal Fixation Using Compression Hip Screw and Cemented Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty
- Myung Sik Park, Woo Chul Jung, Hyuk Park, Byung Yun Hwang, Young Jin Lim, Myung Guk Jung, Hong Man Cho
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(3):138-144. Published online July 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.3.138
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To perform comparative analysis between the results of internal fixation using compression hip screw and cemented bipolar hemiarthroplasty in unstable intertrochanteric fracture in elderly patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January 2001 to October 2006, we reviewd 73 patients, who were treated surgically for unstable intertrochanteric fractures, with a minimum of 2 years follow up. The patient's age was older than 60 year old. The patients were divided into two groups and evaluated, retrospectively. One group was treated with cemented bipolar hemiarthroplasty (Group A, 34 cases), and the other group was treated with compression hip screw (Group B, 39 cases). We evaluated the amount of intraoperative bleeding, operative time, clinical results and complications between the two groups.
RESULTS
The amount of intraoperative bleeding and operative time were no statistically significant between the two groups. Group A showed a better result than Group B for clinical outcome using Johnson Daily Activity of Life. Complications in the group A were comprised of dislocation (1 case), nonunion of greater trochanter (1 case), infection (1 case) and loosening (1 case), and those in the group B were comprised of loss of fixation (8 cases) and infection (1 case).
CONCLUSION
We found that short-term outcomes of cemented bipolar hemiarthroplasty for unstable intertrochanteric fractures were satisfactory. However, a longer-follow up period is necessary to clarify the efficacy of cemented bipolar hemiarthroplasty. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Early Rehabilitation in Elderly after Arthroplasty versus Internal Fixation for Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures of Femur: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jun-Il Yoo, Yong-Chan Ha, Jae-young Lim, Hyun Kang, Byung-Ho Yoon, Hyunho Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2017; 32(5): 858. CrossRef - The Comparison of Compression Hip Screw and Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty for the Treatment of AO Type A2 Intertrochanteric Fractures
Yee-Suk Kim, Jae-Seung Hur, Kyu-Tae Hwang, Il-Yong Choi, Young-Ho Kim
Hip & Pelvis.2014; 26(2): 99. CrossRef
- Early Rehabilitation in Elderly after Arthroplasty versus Internal Fixation for Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures of Femur: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 736 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The Comparison between ITST(TM) (Intertrochanteric/Subtrochanteric) & DHS (Dynamic Hip Screw) in Unstable Femur Intertrochanteric Fracture
- Ho Seung Jeon, Byung Mun Park, Kyung Sub Song, Hyung Gyu Kim, Jong Ju Yun
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(3):131-137. Published online July 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.3.131
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate between DHS and ITST nail (2nd generation) on the treatment of unstable femur intertrochanteric fracture in patients over 70 years old.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
61 cases of unstable intertrochanteric fracture (grouped 37 patients with DHS and 24 patients with ITST) who were taken the operation from Mar. 2003 to Sep. 2007 were analysed regarding to union time, sliding length of lag screws, operation time, blood loss, postoperative complications and functional recovery score by Skovron.
RESULTS
The mean union time was 14.7 weeks in study group (ITST). The mean union time was 16.2 weeks in control group (DHS). The lag screw slidings were 7.2 mm in study group and 8.7 mm in control group. The operation times were 57.9 min in study group and 76.9 min in control group. The amount of blood loss were 67.7 ml in study group and 227.4 ml in control group. The complications were 4 cases in study group and 4 cases in control group. The Skovron recovery scores were 76.5% in study group and 73.7% in control group.
CONCLUSION
From a practical point of short operation time, less amount of bleeding and less complication, author think that the ITST nail is useful implant for treatment of unstable femur intertrochanteric fracture in patient of old age. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unstable Intertrochanteric Fracture Treated with ITST: A Comparative Study between Groups with and without Comminution of Greater Trochanter
Kyung-Sub Song, Sang-Ho Lee, Seong-Hun Jeong, Su-Keon Lee, Sung-Ha Hong
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(1): 36. CrossRef - Treatment of the Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture with Proximal Femoral Nail: Nailing Using the Provisional K-wire Fixation
Gu-Hee Jung
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(3): 223. CrossRef
- Unstable Intertrochanteric Fracture Treated with ITST: A Comparative Study between Groups with and without Comminution of Greater Trochanter
- 740 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Factors Predicting Complications after Internal Fixation of Femoral Neck Fractures
- Tae Ho Kim, Jong Oh Kim, Sung Sik Kang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(2):79-84. Published online April 30, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.2.79
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the factors predicting complications after internal fixation using multiple cannulated screws in the patients with femoral neck fracture, the authors performed a comparative study of a success group and a failure group and reviewed the literature.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixty-eight patients with intracapsular femoral neck fractures were treated by multiple pinning from January 2000 to July 2007 and followed up more than one year. Relationships between the complications such as failure of union, collapse of femoral head due to osteonecrosis of femoral head and several affecting factors including the degree of displacement by Garden stage, state of reduction, position of screws, patient's age, time interval from injury to operation, anatomical fracture site and two weeks postoperative (99m)Tc-MDP bone scan were analyzed.
RESULTS
Statistically significant factors were the degree of displacement by Garden stage (p<0.001), reduction state (p<0.001) and postoperative two weeks (99m)Tc-MDP bone scan (p<0.001).
CONCLUSION
An accurate anatomical reduction is needed to decrease complications with multiple cannulated screws fixation of femoral neck fracture. Displacement of fracture by Garden stage and (99m)Tc-MDP bone scan are major factors predicting complications.
- 921 View
- 1 Download

- Volar Percutaneous Cannulated Screw Fixation for Subacute Scaphoid Wasit Fracture
- Jae Kwang Kim, Jong Oh Kim, Seung Yup Lee, Nam Hoon Do
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(2):104-109. Published online April 30, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.2.104
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To report the surgical results of volar percutaneous cannulated compression screw fixation in subacute scaphoid fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between January 2004 and January 2007, eight consecutive patients with subacute scaphoid waist fracture, who sought medical attention between 4 weeks to 6 months after injury, were included in this study. All patients were male of an average age 29.2 years (range, 19 to 44). Mean duration of injury was 10.3+/-4.1 weeks. An acutrak cannulated screw (Acumed, Hillsboro, OR) was introduced volarly under image intensifier guidance in all patients. We performed radiological evaluation preoperatively and postoperatively. And we performed 12 months postoperatively using grip strength, range of motion (ROM) of the wrist, Mayo Modified Wrist Score (MMWS) and Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and the Hand (DASH) score for functional evaluation.
RESULTS
Preoperative radiography showed minimal sclerosis line in three patients and a bone resorption around fracture sites in two patients. However, no patient had dorsal intercalated segment instability or more than 35 degrees of lateral intrascaphoid angle. Fractures united successfully at 11.6+/-2.1 weeks postoperatively without any requirement for a further procedure. At 12 months follow-up evaluations, ROM of the injured wrist was 93% of the uninjured wrist and grip strength of the injured wrist was 95% of the injured wrist. The mean MMWS was 93+/-6.6 and the mean DASH score was 4.8+/-1.2.
CONCLUSION
We believe that volar percutaneous cannulated screw fixation is a reliable method in case of subacute scaphoid waist fracture without scaphoid deformity or carpal instability. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgical Outcome of Stable Scaphoid Nonunion without Bone Graft
Eun Sun Moon, Myung Sun Kim, Il Kyu Kong, Min Sun Choi
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(1): 69. CrossRef
- Surgical Outcome of Stable Scaphoid Nonunion without Bone Graft
- 657 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Change of Kyphotic Angle in Posterior Pedicle Screw Fixation for Thoracic and Lumbar Burst Fractures: Comparison Study by the Screw Fixation Level
- Jeong Gook Seo, Jong Ho Park, Jeong Seok Moon, Woo Chun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(1):39-44. Published online January 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.1.39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the relationship between the level of screw fixation and the stability of the segment of endplate fracture after posterior pedicle screw instrumentation for thoracic and lumbar burst fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The 41 patients of burst fractures who had been operated with pedicle screw instrumentation were retrospectively evaluated. The patients were divided into two groups by the levels of screw fixation. One group was treated with screws fixed by one-level to the direction of fractured endplate (One-level group, 16 cases). The other group was treated with screws fixed by two-level to the direction of endplate fracture (Two-level group, 25 cases). The two groups were compared by the radiographic changes of kyphotic angle between the day of surgery and 6 months after surgery.
RESULTS
At the 6 months, one-level group showed the change of kyphotic angle of 17.5+/-2.4 degrees, which was different from two-level group of 5.2+/-0.8 degrees (p=0.000).
CONCLUSION
In posterior pedicle screws fixation for thoracic and lumbar burst fractures, 2 vertebrae to the direction of the endplate fracture should be included to prevent the postoperative kyphotic change. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical and Radiological Efficacy of Short-Segment In Situ Fixation vs. Long-Segment Fixation and Corpectomy in Young Patients With Traumatic Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures
Yoseb Oh, SungHwan Hwang, Shin Won Kwon, Hyung Jin Shin, Sunho Kim
Korean Journal of Neurotrauma.2025; 21(4): 303. CrossRef
- Clinical and Radiological Efficacy of Short-Segment In Situ Fixation vs. Long-Segment Fixation and Corpectomy in Young Patients With Traumatic Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures
- 613 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Treatment of Failed Intertrochanteric Fractures to Maintain the Reduction in Elderly Patients
- Soon Yong Kwon, Hyun Woo Park, Sang Uk Lee, Soo Hwan Kang, Jae Young Kwon, Jung Hoon Do, Seung Koo Rhee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(4):267-273. Published online October 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.4.267
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to evaluate and report the new method with a cement augmented screw fixation again to treat the failed intertrochanteric fracture in elderly which were treated with ordinary compression hip screw initially.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From Mar. 1988 to May 2007, 10 patients (mean age 69 years) with the failed intertrochanteric fracture which were treated with initial hip screw, were treated with a cement augmented compression hip screw again. The mean follow-up after surgery was over 18 months. The cause of failure, the period upto the reoperation, the neck-shaft angle after the reoperation, the position of lag screw in the femoral head, and the degree of union at last follow-up were analyzed. The change in the functional hip capacity were evaluated by the classification of Clawson.
RESULTS
Causes of failure were superior cutting-out in 6 cases, cortical anchorage failure in 3, and nonunion in one case. The period upto the reoperation was average 7.8 months. Valgus reduction of average 5.7degrees was achieved, and the positions of lag screw were postero-inferior in 6 cases, center in 3, infero-center in one case. We obtained complete union in 9 cases. The functional outcome showed moderate in 6 cases, good in 3 and poor degree in one case.
CONCLUSION
Cement augmented compression hip screw treatment will possibly reduce cutting-out of screw and bring more stability in fixation for intertrochanteric fractures in old osteoporotic patients, as well, even in failed cases treated with initial compression hip screw, but proper selection of patients is important. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Safety and Effectiveness of the Anchor Augmentation with Bone Cement on Osteoporotic Femoral Fracture: A Systematic Reviews
So Young Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2019; 32(2): 89. CrossRef
- Safety and Effectiveness of the Anchor Augmentation with Bone Cement on Osteoporotic Femoral Fracture: A Systematic Reviews
- 712 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Treatment of Transverse Patellar Fracture with Cannulated Screws
- Jung Man Kim, Ju Seok Yoo, Yong Jin Kwon, Jang Ok Cheon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(2):149-153. Published online April 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.2.149
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To assess the indication and effect of screw fixation in the transverse patellar fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We analysed the results of 14 transverse patellar fractures fixed with screws from January 1991 to May 2005. Mean follow-up period was 47 months (range, 12~143 months). We analysed the radiologic union, operation time, ROM and postoperative Lysholm score.
RESULTS
All fractures healed uneventfully. The mean displacement was decreased from 2.2 mm preoperatively to 0.3 mm postoperatively (p=0.001, Wilcoxon signed rank test). The mean operation time was 34 minutes (range, 20 to 60 minutes). Normal range of motion was achieved in 13 knees (92.9%). Average Lysholm score was 95.9 at final follow-up.
CONCLUSION
Screw fixation seemed to be useful for treatment of transverse patellar fracture even in comminuted fractures with large fragments. The advantage of this technique was the preservation of extensor mechanism, simplicity, short operation time and good cosmesis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgery of patellar fractures using a medial parapatellar approach
Yong-Cheol Yoon, Jae-Ang Sim, Jin-Hun Hong
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Results of Tension Band Wiring and Additional Circumferential Wiring in Treatment of Comminuted Patella Fracture
Young Min Lee, Kook Jin Chung, Ji Hyo Hwang, Hong Kyun Kim, Yong Hyun Yoon
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(3): 206. CrossRef
- Surgery of patellar fractures using a medial parapatellar approach
- 722 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Upper Sacral Morphology Related to Iliosacral Screw Fixation in Korean
- Jung Jae Kim, Chul Young Jung, Hyoung Keun Oh, Byoung Se Yang, Jae Suck Chang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(2):115-122. Published online April 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.2.115
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate upper sacral morphology and anatomy of safe zone related to iliosacral screw fixation in Korean.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
100 patients performed pelvis 3D CT scan were evaluated. We used 16 channel CT and analyzed reconstructed image (shaded-surface display, transparent image and reformat image).
RESULT
The angle between superior aspect of S1 body and iliac cortical density is 27.3°, between anterior cortical line of S1,2 body and horizontal plane 24.6°, and between superior aspect of S1 body and horizontal plane is 39.7°. The axis of S1, S2 pedicle is 32.5° and 15.6° toward anteromedial. The area of S1 pedicle according to sagittal plane and sagittal-oblique axis is 310.7 mm2 and 384.8 mm2. Also, S2 pedicle area is increased 163.1 mm2 to 188.4 mm2. The average depth of ala indentation is 5.1 mm and the maximal value is 9.5 mm. Distinct upper sacral dysplasia is 22%, transitional form is 32%.
CONCLUSION
We measured Korean upper sacrum with 3D-CT, found out dysplasia come up to 54%. Considering the frequency of dysplasia, the investigation of anatomy and technique is essential to sacroiliac screw insertion. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Percutaneous posterior transiliac plate versus iliosacral screw fixation for posterior fixation of Tile C-type pelvic fractures: a retrospective comparative study
Chul-Ho Kim, Jung Jae Kim, Ji Wan Kim
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Measurement of Optimal Insertion Angle for Iliosacral Screw Fixation Using Three-Dimensional Computed Tomography Scans
Jung-Jae Kim, Chul-Young Jung, Jonathan G. Eastman, Hyoung-Keun Oh
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.2016; 8(2): 133. CrossRef
- Percutaneous posterior transiliac plate versus iliosacral screw fixation for posterior fixation of Tile C-type pelvic fractures: a retrospective comparative study
- 660 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

Case Report
- Old Atlantoaxial Rotary Subluxation Associated with High-riding Vertebral Arteries: Arthrodesis Using C1 Lateral Mass Screws and C2 Laminar Screws: A Case Report
- Kyeong Hwan Kim, Jin Sup Yeom, Kun Woo Park, Soon Woo Hong, Bong Soon Chang, Choon Ki Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(1):90-93. Published online January 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.1.90
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To the best of our knowledge, there has been no domestic report on posterior atlantoaxial fusion with segmental screw fixation using C2 laminar screws and C1 lateral mass screws for atlantoaxial subluxation. We report the result of this operation performed in a patient with old atlantoaxial rotary subluxation who required posterior fusion. We chose this technique in this patient because wire fixation was not suitable due to osteoporosis, and transarticular screw fixation and use of C2 pedicle screws were not feasible due to the peculiar bony anatomy of the axis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Indirect Decompression using Segmental Screw Fixation for Cervical Myelopathy Caused by C1-2 Subluxation - Technical Note -
Yoon Jong Kim, Kyeong Hwan Kim, Jong Hwa Won, Hak Jin Min, Ui Seong Yoon, Jin Sup Yeom
The Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2007; 42(6): 815. CrossRef
- Indirect Decompression using Segmental Screw Fixation for Cervical Myelopathy Caused by C1-2 Subluxation - Technical Note -
- 689 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- Treatment for the Supracondylar Fractures of the Distal Humerus with Cannulated Screw
- Jin Soo Park, Young Khee Chung, Jung Han Yoo, Kyu Cheol Noh, Kook Jin Chung, Dong Nyoung Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(1):58-63. Published online January 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.1.58
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the results of the treatment of the supracondylar fractures of the humerus according to the fixation methods with cannulated screw.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eight patients, aged 49 to 82 years (average, 65 years), were reviewed after a mean follow-up of 16 months (range, 12~24 months). According to AO classification all fractures were classified as type A2 (simple transverse supracondylar fracture). All patients underwent closed reduction. Percutaneous fixation with cannulated screws was performed in 8 patients. Three of 8 patients had associated medical problems and one patient had distal radius fracture. The functional results were assessed by the Mayo Elbow Performance Score.
RESULTS
Mean operation time was 59 minutes (45~75) and all the patients with cannulated screw fixation had bony union and were able to early ROM exercise. Mean ranges of motion was 5~120 degrees with excellent functional results. Functional evaluation of elbow joint by Mayo method showed mean value of 88 (75~95).
CONCLUSION
The cannulated screw fixation of supracondylar fracture of humerus, especially in the elderly aged group with medical disease had excellent functional results (rigid fixation & early ROM exercise) due to shortening of surgery time and anesthesic time, combined with decreased technical difficulties of the surgical procedure
- 773 View
- 12 Download

- Treatment of Acetabular Column Fractures with Limited Open Reduction and Screw Fixation
- Jung Jae Kim, Hyoung Keun Oh, Sung Yoon Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(1):26-32. Published online January 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.1.26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the results of limited open reduction and screw fixation of acetabular fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Six acetabular fractures were treated with fluoroscopic guided screw fixation. The mean age was 46 years old and mean follow-up period was 18 months. There were 3 anterior column fractures, 2 transverse fractures and 1 both column fracture. Anterior column screw fixation was used in 5 cases and posterior column fixation in 1 case. Limited ilioinguinal approach was used in 4 cases and percutaneous screw fixation in 2 cases.
RESULTS
The mean union time was 16.6 weeks. The postoperative radiographic results revealed 2 cases with an anatomic reduction and 4 cases with an imperfect reduction. The clinical results showed 1 case with excellent, 4 cases with good and 1 case with fair. Regarding complication, there was 1 case of SI joint penestration without clinical symptoms.
CONCLUSION
Limited open reduction and screw fixation can be a useful alternative treatment for acetabular fractures in patients with minimally displaced fracture, severe multisystem trauma and soft tissue injury not suitable to traditional treatment.
- 644 View
- 1 Download

- The Operative Treatment of Radial Head or Neck Fracture: The Sub-classification of Mason Type II Fracture
- Hyun Dae Shin, Kyung Cheon Kim, Se Min Woo, Yong Bum Joo, Dong Kyu Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(4):449-453. Published online October 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.4.449
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the results of treatment according to the sub-classification of the Mason type II fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From 1999 to 2003, according to the sub-classification of the Mason type II fracture, 33 patients were treated with miniplate in displaced neck fracture (IIa), with compression screw in displaced head fracture (IIb), with miniplate and/or compression screw in displaced head and neck fracture (IIc), with compression screw and miniplate in comminution fracture (III) or excision of head in irreducible state. The clinical results were evaluated by An and Morrey's functional rating index.
RESULTS
Functional rate score averaged 92.7 in type IIa, 88.4 in IIb, 86.4 in IIc, 83.5 in type III with reduced fracture, 75.0 in type III with excised head, and 75.5 in type IV. Complications included heterotopic ossification (2 cases), metal loosening (1 case), malunion (1 case), partial ankylosis of elbow (3 cases), posttraumatic arthritis (1 case).
CONCLUSION
These results supported the recommendation for internal fixation with compression screw in isolated radial head fracture (IIb) and with miniplate in fracuture combined with displaced neck (IIa, IIc, indicated some III). We concluded that sub-classification is useful for dicision making in radial head or neck fracture's treatment.
- 388 View
- 0 Download

- Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Comminuted Subtrochanteric Fracture of the Femur
- Chang Wug Oh, Jong Keon Oh, Sung Jung Kim, Shin Yoon Kim, Seung Hoon Baek, In Ho Jeon, Poong Taek Kim, Sang Won Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(4):407-411. Published online October 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.4.407
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the outcomes of patients with comminuted subtrochanteric femoral fractures using minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) technique.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twelve patients with a mean age of 38.2 years, who sustained comminuted subtrochanteric femoral fractures, were treated using MIPO technique. All patients suffered these fractures either from traffic accidents (6) or falls from height (6). Average follow-up was 4.3 years (range, 29~78 months). Patients were assessed radiographically and clinically with regards to time to union, malunion, and complications. According to the Seinsheimer's classification, there were 1 type III, 7 type IV, and 4 type V. Type C fractures were ten according to AO-OTA classification.
RESULTS
Union was achieved in 7 of 12 cases, in an average of 23.4 weeks (range, 12~42 weeks). Three definite non-unions with implant failures, needed the procedure of implant change and bone graft. In other two patients, early bone graft was performed for anticipated nonunion of comminuted area. The most common complication was metal failures (2 plate failures and 3 screw breakages). Limb length shortening of 1.5 cm occurred in one patient, and external rotation malunion of 15 degrees was noted in one patient. No patients developed infection.
CONCLUSION
Preserving biology of the fracture fragments, the use of MIPO technique using DCS has proven to be less successful in comminuted subtrochanteric fractures, comparing to fractures in other areas. To avoid mechanical failure, the careful and protective weight bearing is needed until the callus-bridging is seen in the commniuted area. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Femoral Mid-Diaphyseal Fractures
Hyoung-Keun Oh, Suk-Kyoo Choo, Jong-In Kim, Sung-Jong Woo
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2013; 26(2): 140. CrossRef - Fixation of the Femoral Subtrochanteric Fracture with Minimally Invasive Reduction Techniques
Chul-Hyun Park, Chul-Wung Ha, Sang-Jin Park, Min-Su Ko, Oog-Jin Shon
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2013; 26(2): 112. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis of Subtrochanteric Femoral Fractures
Chang-Wug Oh
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(2): 123. CrossRef - What is an Ideal Treatment?
Chang-Wug Oh
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2008; 21(4): 347. CrossRef
- Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Femoral Mid-Diaphyseal Fractures
- 642 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


