Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Articles
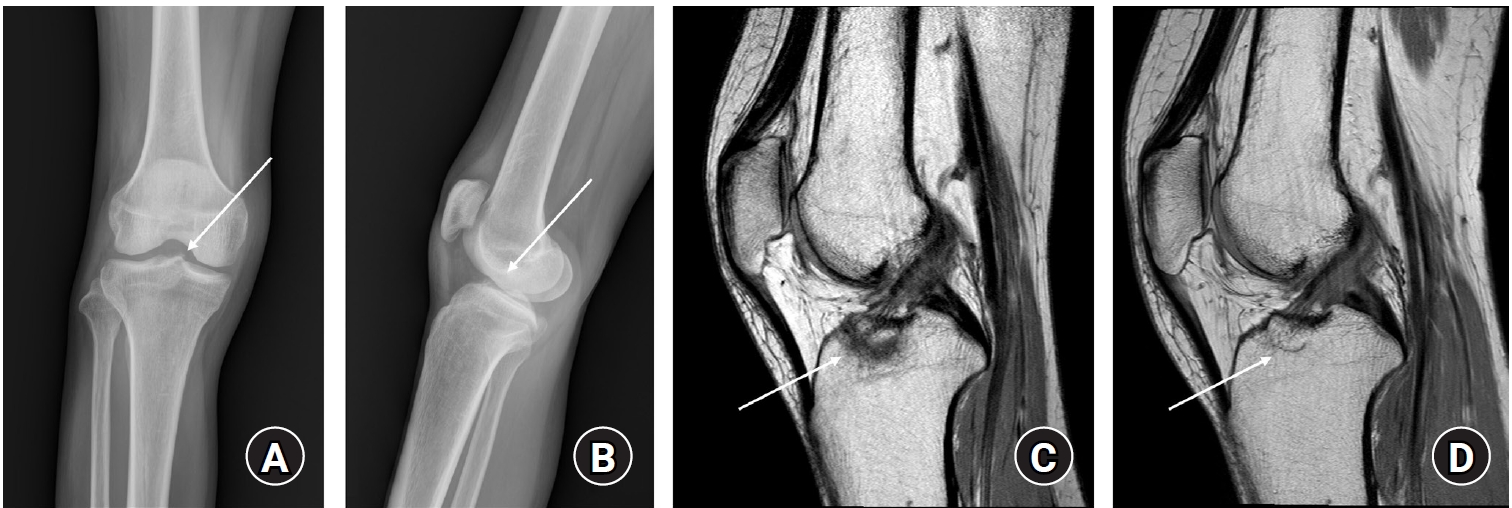
- Treatment of avulsion fractures around the knee
- Jeong-Hyun Koh, Hyung Keun Song, Won-Tae Cho, Seungyeob Sakong, Sumin Lim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):63-73. Published online March 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00073
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fractures of the knee occur when tensile forces cause a bone fragment to separate at the site of soft tissue attachment. These injuries, which frequently affect adolescent athletes, can involve the cruciate and collateral ligaments, arcuate complex, iliotibial band, and patellar and quadriceps tendons. Radiographs aid in the initial diagnosis, while computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging facilitate a comprehensive evaluation of injury severity and concomitant damage. Specific avulsion fracture types include: anterior cruciate ligament avulsions (tibial site, Meyers and McKeever classification), posterior cruciate ligament avulsions (tibial attachment, Griffith's classification), Segond fractures (anterolateral complex injury), iliotibial band avulsions, medial collateral ligament avulsions (reverse Segond, Stieda fractures), arcuate complex avulsions ("arcuate sign"), medial patellofemoral avulsions (patellar dislocations), and patellar/quadriceps tendon avulsions. The treatment depends on the fracture location, displacement, and associated injuries. Non-displaced fractures can be managed conservatively, while displaced fractures or those with instability require surgical reduction and fixation. Prompt recognition and appropriate intervention prevent complications such as deformity, nonunion, malunion, and residual instability. This review provides an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management of knee avulsion fractures to guide clinical decision-making.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
Jae-Ang Sim, Chul-Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(3): 152. CrossRef
- Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
- 9,017 View
- 110 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Avulsion Fractures of around the Hand
- Dong Whan Kim, Jung Il Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(3):158-168. Published online July 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.3.158
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An avulsion fracture occurs when soft tissues, including the tendons and ligaments, are forcibly detached from the main bone by an external force. The hand contains numerous anatomical structures, such as ligaments, tendons, and volar plates, which are essential for maintaining multidirectional motion and joint stability. Excessive force applied in a specific direction can damage these structures, leading to avulsion fractures around the joint. These fractures can result in severe complications if left untreated or improperly managed, including joint deformity, contracture, nonunion or malunion of the fracture, secondary osteoarthritis, and limited range of motion. Therefore, an accurate examination, diagnosis, and appropriate treatment are crucial for preventing these adverse outcomes. An avulsion fracture can be managed conservatively when the avulsed fragment does not compromise joint stability or motion. Nevertheless, surgical intervention is required to stabilize the fragment if it affects joint stability or motion. The use of internal fixation has become more prevalent because of recent advances in small implants for fixation.
- 677 View
- 12 Download

- Crush Syndrome: Traumatic Rhabdomyolysis, Reperfusion Injury
- Yong-Cheol Yoon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(2):62-68. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.2.62
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A crush injury causes damage to bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, and other tissues caused due to pressure. Crush syndrome is a reperfusion injury that occurs throughout the body after a crush injury and leads to traumatic rhabdomyolysis, in which muscle fibers are broken down. Owing to the decreased blood supply, inflammation, and changes in metabolic activity, fluids and electrolytes in the blood can move into tissues, causing hypovolemic shock. In addition, toxic substances resulting from cell destruction can circulate through the bloodstream, causing electrolyte imbalances, renal failure, arrhythmias, and cardiac arrest, with approximately 15% of patients with acute renal failure dying. The treatment for crush syndrome involves aggressive fluid therapy and correction of the electrolyte imbalances, while patients with acute renal failure may require dialysis. Surgical treatment may include debridement and irrigation of necrotic tissue, and fasciotomy is necessary to address compartment syndrome, a complication that may arise.
- 704 View
- 18 Download

Original Article
- Comparison of Surgical Outcomes for Lisfranc Joint Injuries: Dorsal Bridge Plating versus Transarticular Screw versus Combination
- Ba Rom Kim, Jun Young Lee, Sung Hun Yang, Seung Hyun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(1):17-24. Published online January 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.1.17
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
In Lisfranc joint injury, the traditional treatment has been open reduction and internal fixation with a transarticular screw. Despite this, additional complications, such as damage to the articular surface and breakage of the screw, have been reported. Therefore, this study compared the clinical and radiological outcomes of dorsal bridge plating with those of transarticular screws and combination treatment in Lisfranc joint injury.
Materials and Methods
Among the 43 patients who underwent surgical treatment due to Lisfranc joint injury from June 2015 to March 2021, 40 cases followed for more than six months after surgery were analyzed, excluding three patients: one lost to follow-up, one had to amputate, and one expired. The radiological parameters were measured using the Wilppula classification in the last follow-up. The clinical outcomes were evaluated using the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) midfoot score.
Results
The AOFAS midfoot score, according to the surgical method, was significantly higher in the dorsal bridge plating (p=0.003). The radiological outcomes showed significantly better anatomical reduction when dorsal bridge plating was used (p=0.040). According to the Wilppula classification, the AOFAS midfoot score improved as the quality of anatomical reduction improved (p=0.018). Finally, the AOFAS midfoot score decreased as the number of column fixations increased (p=0.002). There were two complications: screw breakage in dorsal bridge plating and superficial skin necrosis in the combination treatment. Skin defects caused by necrosis improved after negative pressure wound therapy and split-thickness skin graft.
Conclusion
In treating Lisfranc joint injuries, open reduction and internal fixation by dorsal bridge plating can be an appropriate treatment option. Nevertheless, studies, such as long-term follow-up research, on complications, such as osteoarthritis, will be needed.
- 468 View
- 5 Download

Review Article
- Lisfranc Joint Injury
- Bi O Jeong, Jungtae Ahn
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(2):83-89. Published online April 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.2.83
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The Lisfranc joint complex is composed of complex bony structures, ligaments, and soft tissues and has a systematic interrelationship. Sufficient radiologic modalities should be considered for an accurate initial diagnosis. Based on an accurate understanding of normal anatomy and restoration of anatomical relationships, the diagnosis should be obtained, and more discussion is needed on detailed treatment strategies.
- 649 View
- 12 Download

Case Report
- Injury of the Ascending Branch of the Lateral Femoral Circumflex Artery Caused by a Spike of the Displaced Lesser Trochanter in an Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture - A Case Report -
- Soon Ho Huh, Hong-Man Cho, Jiyeon Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(2):71-75. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.2.71
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Although vascular injuries associated with femoral intertrochanteric fractures have been reported infrequently, bleeding due to vascular injury can lead to severe complications that can be potentially life and limb-threatening. The authors report a case of an injury of the ascending branch of the lateral femoral convolutional artery in a patient who underwent surgical treatment for a femoral intertrochanteric fracture. Vascular injury occurred due to the sharp margin of displaced lesser trochanter five weeks after surgery. Percutaneous transcatheter embolization was done and improved without additional complications. Therefore, the surgeons need to be aware of possible associated vascular injuries caused by displaced lesser trochanter fragments in femoral intertrochanteric fractures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Delayed Deep Femoral Artery Injury Secondary to Migrated Lesser Trochanter Fragment After Intertrochanteric Fracture Fixation: A Case Report and Updated Literature Review
Slavko Čičak, Josip Kocur, Vedran Farkaš, Petra Čičak, Stjepan Ištvanić, Marko Lovrić, Marko Perić, Nenad Koruga, Tomislav Ištvanić
Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Vascular Complications Following Trans-Trochanteric Fracture: Case Report and Literature Review
Robert Bot, Adrian Tirla, Simona Daniela Cavalu
Reports.2025; 8(4): 191. CrossRef
- Delayed Deep Femoral Artery Injury Secondary to Migrated Lesser Trochanter Fragment After Intertrochanteric Fracture Fixation: A Case Report and Updated Literature Review
- 322 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Article
- Risk Factors for Subsequent Contralateral Hip Fracture following Osteoporotic Hip Fracture Surgery
- Kyung-Jae Lee, Jung-Hoon Choi, Hee-Uk Ye, Young-Hun Kim, Kyung-Hwan Lim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(2):51-56. Published online April 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.2.51
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the risk factors contributing to subsequent hip fractures in patients with osteoporotic hip fractures.
Materials and Methods
Between March 2008 and February 2016, 68 patients sustained a subsequent contralateral hip fracture after surgery for a primary osteoporotic hip fracture (Study group). The patients were compared with 475 patients who had been followed up for a minimum of one year with a unilateral osteoporotic hip fracture (Control group). The demographic data, bone mineral density (BMD), osteoporosis medication, osteoporotic fracture history, comorbid disease, type of surgery, preoperative, postoperative ambulatory capacity, and postoperative delirium in the two groups were compared.
Results
The demographic data, BMD, osteoporosis medication history, comorbid disease, type of surgery, and postoperative delirium were similar in the two groups. At three months after the primary surgery, the poor ambulatory capacity was significantly higher in the study group than the control group (p<0.001).
Conclusion
The ambulatory capacity after primary surgery is an important risk factor in the occurrence of subsequent hip fractures after osteoporotic hip fracture. Cause analysis regarding the poor ambulatory capacity after surgery will be necessary, and the development of a functional recovery program and careful management of the walking ability recovery will be needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Osteoporotic Hip Fracture: How We Make Better Results?
Byung-Chan Choi, Kyung-Jae Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2024; 37(1): 52. CrossRef
- Osteoporotic Hip Fracture: How We Make Better Results?
- 478 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Latent Superior Gluteal Artery Injury by Entrapment between the Fragments in Transverse Acetabular Fracture - A Case Report -
- Hyuk Jin Choi, Byung Chul Kim, Hoon Kwon, Jae Hoon Jang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(1):30-33. Published online January 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.1.30
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The superior gluteal artery is branched from the internal iliac artery and is located outside the pelvis through a greater sciatic notch. This anatomical characteristic makes the artery vulnerable to injury when pelvic fracture involves the sciatic notch. In the case of a superior gluteal artery injury, hemodynamic instability can occur, and appropriate evaluation and management are mandatory in the acute phase. On the other hand, if the initial detection of the injury is neglected due to a masked pattern, it can cause massive bleeding during surgery, resulting in difficult hemostasis. This paper reports an experience of a latent superior gluteal artery injury by entrapment between the fragments of a transverse acetabular fracture.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Superior gluteal artery injury in pelvic ring injury and acetabular fracture: Single center observational study
Hoon Kwon, Jae Hoon Jang, Nam Hoon Moon, Seung Joon Rhee, Dong Yeon Ryu, Tae Young Ahn
Journal of Orthopaedic Science.2024; 29(6): 1483. CrossRef
- Superior gluteal artery injury in pelvic ring injury and acetabular fracture: Single center observational study
- 418 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Articles
- Tendon Healing: A Review of Basic Science and Current Progress
- Young Woo Kwon, Pei Wei Wang, Jun-Ku Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(4):227-237. Published online October 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.4.227
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The tendon connects the muscles to the bones and transmits the loads generated by the muscles to the bones to move the joints, support the joints, and provide stability to the joints. Approximately 30% of patients complaining of musculoskeletal pain are associated with tendon disease, and approximately 50% of musculoskeletal injuries are caused by a tendon injury. Despite this frequent treatment of tendon damage, studies on the basic biology that provide scientific evidence for treatment, such as development, tendon injury, and healing, are still very limited. This review first summarizes the classification and composition of the tendon identified so far, the surrounding tissue, and the blood supply to the tendon. The limitations of the tendon recovery process after a tendon injury are also discussed. Finally, this review examines ways to improve tendon recovery and the biological approaches and tissue engineering that have been currently studied. In conclusion, innovative progress in promoting tendon healing has not been achieved despite the many advances in the basic structure of the tendon, and the cell and regulatory molecular factors involved in tendon recovery. Biological approaches and tissue engineering, which have become a recent issue, have shown many possibilities for the recovery of damaged cases, but further research will be needed until clinical application.
- 1,109 View
- 21 Download

- Fixation Options of Unstable Posterior Pelvic Ring Disruption: Ilio-Sacral Screw Fixation, S2AI Fixation, Posterior Tension Band Plate Fixation, and Spino-Pelvic Fixation
- Dong Hee Kim, Jae Hoon Jang, Myungji Shin, Gu Hee Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(4):240-247. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.4.240
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The fixation methods that can be used for unstable posterior pelvic ring injuries have undergone many innovative changes due to the recent development of surgical and imaging techniques. After understanding the appropriate indications of first and second sacroiliac screw fixation and spinopelvic fixation, innovative methods, including the trans-sacral screw fixation, posterior tension-band plate fixation, and the S2AI screw, would be chosen and applied. Considering the anatomical complexity and proximity to the surrounding vessels and nerves in the posterior fixation, the safe zone according to the fixation options should be well understood in preoperative planning. Moreover, the functional reduction of the posterior pelvic ring through the reduction and fixation of the anterior lesion should be achieved before placing the implant to reduce the number of malposition-related complications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Research through Computational Anatomy and Virtual Fixation
Ju Yeong Kim, Dong-Geun Kang, Gu-Hee Jung
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2023; 58(4): 299. CrossRef
- Clinical Research through Computational Anatomy and Virtual Fixation
- 558 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Reports
- Bilateral Gluteal Necrosis and Deep Infection after Transarterial Embolization for Pelvic Ring Injury in Patient with Hemodynamic Instability: A Case Report
- Sung Jin Park, Chang Ho Jeon, Nam Hoon Moon, Yong Geon Park, Jae Hoon Jang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(1):56-60. Published online January 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.56
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Transarterial embolization is accepted as effective and safe for the acute management in hemodynamically unstable patients with pelvic ring injury. However, transarterial embolization has potential complications, such as gluteal muscle/skin necrosis, deep infection, surgical wound breakdown, and internal organ infarction, which are caused by blocked blood flow to surrounding tissues and organs, and many studies on the complications have been reported. Here, we report an experience of the management of gluteal necrosis and infection that occurred after transarterial embolization, with a review of the relevant literature.
- 475 View
- 0 Download

- Capitellar Osteochondral Impacted Fracture of the Humerus in an Adult Female: A Case Report
- Jaekwang Yum, Minkyu Seong, Kyungil Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(4):154-158. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.4.154
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Capitellar osteochondral impaction fractures of the humerus are an uncommon injury and not encompassed by commonly used classification systems, such as that of Bryan and Morrey. Only a few cases of capitellar osteochondral impaction fractures have been reported. We report a case of a 53-year-old female with a capitellar osteochondral impaction fracture. The osteochondral fracture fragment of the capitellum was impacted and there was a step-off on the articular surface. Recovery of congruence in the capitellar articular surface was necessary. Satisfactory clinical and radiological results were obtained through the ‘lever arm’ reduction of the fracture fragment with a small osteotome and fixation with ‘raft’ K-wire.
- 241 View
- 0 Download

Original Article
- Surgical Outcome of Posterior Pelvic Fixation Using S1, S2 Screws in Vertically Unstable Pelvic Ring Injury
- Kwang Hee Yeo, Nam Hoon Moon, Jae Min Ahn, Jae Yoon Jeong, Jae Hoon Jang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(1):9-17. Published online January 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.1.9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Iliosacral screw fixation is an effective and less invasive method that is used widely for the definitive treatment of unstable pelvic ring injuries. On the other hand, fixation failures after iliosacral screw fixation have been reported in vertically unstable pelvic ring injuries. This study examined the surgical outcomes of posterior pelvic fixation using S1 and S2 screws in vertically unstable pelvic ring injuries.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between January 2011 and April 2016, 17 patients with vertically unstable pelvic ring injuries who met the minimum 1 year follow-up criteria were treated with internal fixation using posterior pelvic S1 and S2 screws. Their mean age was 43.9 years. According to the AO/OTA classification, 10 patients had C1, 6 had C2, and 1 had C3 injuries. Surgical treatments of single or multiple steps, where necessary, were performed by two surgeons. The clinical and radiologic outcomes were assessed retrospectively using radiographs and medical records.
RESULTS
Overall, 16 patients had bone healing without screw loosening; however, one patient could not maintain anterior pelvic fixation because of an open fracture and deep infection in the anterior pelvic ring. Of five patients who complained of neurological symptoms after injury, three had partially recovered from their neurological deficit. At the last follow-up, the clinical outcomes according to the Majeed score were excellent in 5, good in 6, fair in 4, and poor in 2 patients. The postoperative radiologic outcomes by Matta and Tornetta's method were excellent in 5, good in 8, and fair in 4 patients. Malposition of the S2 screw was identified in one case. The mean time to union was 14.6 weeks after surgery.
CONCLUSION
S1 and S2 screw fixation can be an effective treatment option for posterior pelvic stabilization in vertically unstable pelvic ring injuries when considering the surgical outcomes, such as screw loosening and loss of reduction. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fixation Options of Unstable Posterior Pelvic Ring Disruption: Ilio-Sacral Screw Fixation, S2AI Fixation, Posterior Tension Band Plate Fixation, and Spino-Pelvic Fixation
Dong-Hee Kim, Jae Hoon Jang, Myungji Shin, Gu-Hee Jung
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2019; 32(4): 240. CrossRef
- Fixation Options of Unstable Posterior Pelvic Ring Disruption: Ilio-Sacral Screw Fixation, S2AI Fixation, Posterior Tension Band Plate Fixation, and Spino-Pelvic Fixation
- 331 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Articles
- Lisfranc Joint Injuries: Diagnosis and Treatment
- Hyun Seok Yim, Sung Ha Hong, Ki Sun Sung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(4):283-293. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.4.283
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Injuries to the Lisfranc joint are relatively rare, but they are often misdiagnosed or inadequately treated, resulting in poor long-term outcomes. Understanding of anatomical structure and injury mechanism, careful clinical and radiographic evaluations are needed to recognize and treat Lisfranc joint injuries. In this article, we review the anatomy, biomechanics, injury mechanisms, injury classification, clinical presentation, radiographic evaluation, treatment, outcome, and complications of Lisfranc joint injuries.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lisfranc Sports Injuries: What Do We Know So Far?
Godsfavour C Maduka, Divinegrace C Maduka, Naeem Yusuf
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Acupuncture Treatment and Taping Therapy After Lisfranc Joint Injuries: A Case Report
Shin-Ae Kim, Su-Woo Kang, Eun-Ji Lee, Min-Kyung Kwak, Hui-Gyeong Jeong, Jae-Uk Sul
Journal of Acupuncture Research.2017; 34(4): 197. CrossRef
- Lisfranc Sports Injuries: What Do We Know So Far?
- 905 View
- 25 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Current Concepts of Fractures and Dislocation of the Hand
- Yong Cheol Yoon, Jong Ryoon Baek
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(2):143-159. Published online April 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.2.143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fractures and dislocation of the hand is a body injury involving complex structures and multiple functions, which frequently occur as they represent 10%-30% of all fractures. Such fractures and dislocation of the hand should be treated in the context of stability and flexibility; and tailored treatment is required in order to achieve the most optimal functional performance in each patient since deformation may occur if not treated, stiffness may occur with unnecessarily excessive treatment, and both deformation and stiffness may occur coincidently with inappropriate treatment. Stable injuries can be fixed with splintage whereas surgery is actively considered for unstable injuries. In addition, surgeons should keep in mind that as the surgical intervention is done aggressively, aggressive rehabilitation must be followed in correspondence with the surgical intervention. Successful outcome requires effort to prevent any potential complication including nerve hypersensitivity and infection. Finally, it is also important that the patient to know that swelling, stiffness, and pain may last for a long period of time until the recovery of fractures and dislocation of the hand.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current concepts in the management of phalangeal fractures in the hand
Hyun Tak Kang, Jun-Ku Lee
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(3): 109. CrossRef - Current Concepts in Management of Phalangeal Fractures
Yohan Lee, Sunghun Park, Jun-Ku Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2022; 35(4): 169. CrossRef
- Current concepts in the management of phalangeal fractures in the hand
- 542 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Articles
- Concomitant Carpal Injuries in Distal Radius Fractures: Retrospective Analysis by Plain Radiographs and Computed Tomography
- Chul Hyun Cho, Eun Seok Son
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(1):1-7. Published online January 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the incidence and characteristics of concomitant carpal bone fractures and ligament injuries and to analyze risk factors for carpal injuries in patients with distal radius fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 362 patients with 379 distal radius fractures were reviewed retrospectively. Associated carpal bone fractures and ligament injuries were evaluated by plain radiographs and computed tomography at the time of initial trauma. Correlation between associated carpal injuries and various parameters was also analyzed.
RESULTS
Of 379 distal radius fractures, 39 cases (10.3%) had one or more carpal bone fracture and 40 cases (10.6%) had carpal ligament injuries. Overall, carpal injuries occurred in 59 cases (15.6%) distal radius fractures. Associated carpal ligament injuries showed correlation with young age and associated carpal bone fractures showed correlation with AO type B distal radius fractures. Carpal injuries including fracture and ligament injury showed correlation with male, high energy trauma, or associated injuries beyond wrist.
CONCLUSION
The incidence of concomitant carpal injuries in patients with distal radius fractures is relatively high. Concomitant carpal injuries were more common in young age, male, high energy trauma, AO type B distal radius fractures, or associated injuries beyond wrist. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Korean Medicine Treatments for the Angular Deformity of Wrist Fracture with Disuse Osteopenia: A Case Report
Myung Jin Oh
Korean Journal of Acupuncture.2018; 35(4): 234. CrossRef - Comparison of Distal Radius Fractures with or without Scaphoid Fractures
Jin Rok Oh, Dong Woo Lee, Jun Pyo Lee
Journal of the Korean Society for Surgery of the Hand.2016; 21(1): 23. CrossRef
- Korean Medicine Treatments for the Angular Deformity of Wrist Fracture with Disuse Osteopenia: A Case Report
- 564 View
- 10 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Neurologic Injury within Pelvic Ring Injuries
- Ji Wan Kim, Dong Hoon Baek, Jae Hyun Kim, Young Chang Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(1):17-22. Published online January 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.1.17
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the incidence of neurologic injury in pelvic ring injuries and to assess the risk factors for neurologic injury related to pelvic fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixty-two patients with the pelvic ring injury were enrolled in the study from March 2010 to May 2013. When the neurologic injury was suspected clinically, the electro-diagnostic tests were performed. Combined injuries, fracture types, and longitudinal displacements were examined for correlations with the neurologic injury.
RESULTS
There were 7 cases of AO/OTA type A, 37 cases of type B, and 18 cases of type C. Among them, 25 patients (40%) had combined spine fractures, and the average of longitudinal displacement was 7 mm (1-50 mm). Of the 62 patients, 13 (21%) had neurologic injury related with pelvic fractures; 5 with lumbosacral plexus injury, 5 with L5 or S1 nerve injury, 2 with obturator nerve injury, and 1 case of lateral femoral cutaneous nerve injury. There were no relationships between the neurologic injuries and fracture types (p=0.192), but the longitudinal displacements of posterior ring and combined spine fractures were related to the neurologic injury within pelvic ring injury (p=0.006, p=0.048).
CONCLUSION
The incidence of neurologic injury in pelvis fracture was 21%. In this study, the longitudinal displacements of posterior ring and combined spine fractures were risk factors for neurological injury in pelvic ring injury. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surgical Outcome of Posterior Pelvic Fixation Using S1, S2 Screws in Vertically Unstable Pelvic Ring Injury
Kwang Hee Yeo, Nam Hoon Moon, Jae Min Ahn, Jae Yoon Jeong, Jae Hoon Jang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2018; 31(1): 9. CrossRef
- Surgical Outcome of Posterior Pelvic Fixation Using S1, S2 Screws in Vertically Unstable Pelvic Ring Injury
- 340 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Surgical Management of Comminuted Avulsion Fracture of the Proximal Fibula with Lateral Collateral Ligament Injury: Technical Note
- Jong Min Kim, Byeong Mun Park, Sang Hoo Lee, Seung Ju Jeon, Jun Beum Shin, Kyeong Seop Song
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(1):77-80. Published online January 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.1.77
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Anteromedial force to the knee in an extended position can cause an avulsion fracture of the proximal fibula with combined injuries to the posterolateral ligaments. Avulsion fractures of the proximal fibula are rare and current management of these fractures is based on few descriptions in literature. Various surgical methods of fixation for these fractures have been reported, but there is still no standard treatment modality. Anatomic reduction of these fractures is technically difficult, and failure of reduction may cause posterolateral instability, secondary arthritis and other complications. We present our experience with two such cases of comminuted avulsion fractures of the proximal fibular with posterolateral ligament ruptures surgically fixated with a locking compression hook plate and non absorbable sutures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fixation of fibular head avulsion fractures with the proximal tibiofibular screw: Technique guide and clinical experience
Ryan A. Paul, Shu Yang Hu, Ananya Pathak, Ryan Khan, Daniel B. Whelan
Trauma Case Reports.2025; 57: 101175. CrossRef - Treatment of avulsion fractures around the knee
Jeong-Hyun Koh, Hyung Keun Song, Won-Tae Cho, Seungyeob Sakong, Sumin Lim
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(2): 63. CrossRef - Treatment of Avulsion Fractures around the Knee
Sumin Lim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2024; 37(2): 117. CrossRef
- Fixation of fibular head avulsion fractures with the proximal tibiofibular screw: Technique guide and clinical experience
- 762 View
- 12 Download
- 3 Crossref

Original Articles
- Anatomical Study of Symphysis Pubis Using 3 Dimensional Computed Tomography in Koreans
- Ji Wan Kim, Jung Min Park, Jae Suk Chang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(1):32-36. Published online January 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.1.32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To acquire anatomical data for the normal pelvic bone structure using three-dimensional computed tomography (3D CT) and to propose the most appropriate angle and screw length for safe screw insertion during symphysis pubis plating.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We performed 3D CT analysis in 52 patients who required plating and selected a medial and lateral insertion point between the symphysis pubis and the pubic tubercle. Using a three-dimensional medical image analysis program, we evaluated the appropriate screw length, sagittal angle, and oblique angle at each point in this cohort.
RESULTS
At the medial point, the sagittal angle was determined to be 49.1degrees with an average screw length of 49.4 mm. At the lateral point, we calculated an average screw length of 49.1 mm, oblique angle of 23.2degrees, and sagittal angle of 45.7degrees. The screw length was longer in men than in women (4.6 mm and 7.3 mm, respectively) at the medial and lateral point.
CONCLUSION
At the symphysis pubis diastasis, we can insert the screw caudally at 49degrees with a minimal length of 37 mm at the medial point. We can insert the screw caudally at 46degrees, medially at 23degrees, with a minimal 34 mm length at the lateral point.
- 298 View
- 1 Download

- Operative Treatment of Unstable Pelvic Ring Injury
- Sang Hong Lee, Sang Ho Ha, Young Kwan Lee, Sung Won Cho, Sang Soo Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(4):243-249. Published online October 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.4.243
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyze the clinical and radiological results of the different fixation methods according to the type and displacement of unstable pelvic ring injuries.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty-three patients with unstable pelvic ring injuries from January 2005 to December 2009 were classified according to the AO/OTA classification system. When patients had been diagnosed with unstable pelvic ring injuries with partial instability, they were treated by anterior fixation with a plate and posterior percutaneous iliosacral screw fixation. When patients had been diagnosed with unstable pelvic ring injuries with complete instability, they were treated by open reduction and anterior to posterior fixation with a plate through the ilioinguinal approach. The radiological results were evaluated using Matta and Saucedo's method, and the clinical results were evaluated using Rommens and Hessmann's method.
RESULTS
The outcomes from the radiological evaluation were that the displacement of the posterior pelvic ring were improved by about 6.65 mm in unstable pelvic ring injuries with partial instability. The displacement of the posterior pelvic ring were improved by about 7.8 mm in unstable pelvic ring injuries with complete instability. The clinical results were excellent in 13 cases and good in 6 cases on latest follow-up.
CONCLUSION
Good results can be achieved by selecting the treatment method according to the type of unstable pelvic ring injurie and displacement. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Displacement of an anterior pelvic ring fracture after L5, S1, and iliac screw fixation: a case report
Euijin Cho, Joonghyuk Kim, Hyeongyu Lim, Kyeol Han, Yonghun Pee, Junhong Min, Il-Tae Jang, Jeesoo Jang
Journal of Korean Society of Geriatric Neurosurgery.2025; 21(1): 24. CrossRef - Functional outcomes in pelvic fractures and the factors affecting them– A short term, prospective observational study at a tertiary care hospital
Subhajit Ghosh, Sameer Aggarwal, Prasoon Kumar, Vishal Kumar
Journal of Clinical Orthopaedics and Trauma.2019; 10(5): 896. CrossRef - Outcome of Surgical Treatment of AO Type C Pelvic Ring Injury
Do Hyeon Moon, Nam Ki Kim, Jun Sung Won, Jang Seok Choi, Dong Hyun Kim
Hip & Pelvis.2014; 26(4): 269. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Humeral Proximal or Distal Shaft Fractures Using a 3.5/5.0 Metaphyseal Locking Plate
Hyoung Keun Oh, Suk Kyu Choo, Jung Il Lee, Dong Hyun Seo
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(4): 305. CrossRef
- Displacement of an anterior pelvic ring fracture after L5, S1, and iliac screw fixation: a case report
- 502 View
- 4 Download
- 4 Crossref

Case Report
- Missed Variation of the Essex-Lopresti Injury Associated with Type-I Monteggia Equivalent Lesion: A Case Report
- Young Sung Kim, Phil Hyun Chung, Suk Kang, Ho Min Lee, Jong Pil Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(3):219-222. Published online July 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.3.219
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The authors report the case of a patient with the combination of a Type I Monteggia equivalent lesion and Essex-Lopresti injury. This combination of injury is very rare, and an associated distal radioulnar injury is often missed. We hope our experience illustrates the need to examine the wrist joint carefully and to be aware of the potential for distal radioulnar joint instability in all patients with type I Monteggia equivalent lesions.
- 248 View
- 0 Download

Original Article
- Injury Severity and Patterns of Accompanying Injury in Spinal Fracture
- Hun Park, Kyung Jin Song, Kwang Bok Lee, Joo Hyun Sim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(3):203-207. Published online July 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.3.203
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To examine the relationship between injury severity and patterns of associated injury in spinal fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From March 2004 to March 2010, a retrospective study was conducted on 291 patients who had undergone surgeries due to spinal fractures. Spinal fractures were categorized as upper cervical, lower cervical, thoracic, thoracolumbar, and lumbar region, and the severity of fracture was measured using the Abbreviated Injury Scale and Injury Severity Score (ISS). We evaluated the correlation between the fracture site and the incidence and injury severity of the associated injury, and compared the neurologic damage according to the presence/absence of the associated injury.
RESULTS
Spinal fracture occurred in the thoracic (43.5%) and lower cervical (30.0%) levels, and associated injury developed in 134 patients (47%). The area of associated injury was in the extremity (41.2%), thorax (25.5%), head, neck, and face (21.9%). Lower cervical fracture (34.5%) had a lower prevalence than thoracic (81%) and lumbar fracture (61%). The average ISS of the associated injury was 17.14 for the thoracic fracture, 12.30 for the lower cervical fracture, 8.7 for the thoracolumbar fracture and 5.69 for the lumbar fracture. Neurologic damage was highly frequent in the lower cervical fracture and included 54 patients (62.1%) and was less frequent in the upper cervical fracture, which included 7 patients (17.9%) (p=0.032).
CONCLUSION
Although the associated injury was less frequent in the lower cervical spine among the spinal fractures that underwent surgical treatment, there was a high risk of neurologic damage in the case of associated injury; therefore, there is a need to pay special attention to patients that suffer damage in this area. In addition, since the degree of the associated injury in the thoracic and lower cervical fracture is significant, an appropriate management strategy for the associated injury must be considered. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Clinical Effects of Complex Korean Medicine Treatment in Patients with Cervical Spine Fracture Caused by Traffic Accident: A Report of 2 Cases
Si-Hoon Han, Gi-Eon Lee, Kyeong-Sang Jo, Da-Young Byun, Min-Seok Oh
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2018; 28(2): 113. CrossRef - Clinical results of early stabilization of spine fractures in polytrauma patients
Ki-Chul Park, Ye-Soo Park, Wan-Sik Seo, Jun-Ki Moon, Bo-Hyun Kim
Journal of Critical Care.2014; 29(4): 694.e7. CrossRef
- The Clinical Effects of Complex Korean Medicine Treatment in Patients with Cervical Spine Fracture Caused by Traffic Accident: A Report of 2 Cases
- 457 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

Case Report
- Treatment of a 3rd Lumbar Vertebra Translational Injury Combined with Incomplete Cauda Equina Syndrome in Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Case Report
- Jin Wan Kim, Young Chul Ko, Chul Young Jung, Il Soo Eun, Young June Kim, Chang Kyu Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(1):77-81. Published online January 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.1.77
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ankylosing spondylitis is a rheumatic disease in which mainly the spinal and sacroiliac joints are affected. Patients with ankylosing spondylitis are at significant risk for spinal fracture when exposed to even minor trauma. Most spinal fractures with ankylosing spondylitis occur in the cervical spine, whereas spinal fractures in thoracic or lumbar spine are rare, especially in the lower lumbar spine. Furthermore, neurologic symptoms in cases of lower lumbar spine fracture are rarer than in cases of cervical and thoracic spinal fracture. We have experienced a case of translation injury of the 3rd lumbar vertebra accompanied by incomplete cauda equine syndrome in ankylosing spondylitis and the authors gained good clinical results with surgical treatment. We have reported here on this case and have included a review of the relevant literature.
- 300 View
- 1 Download

Original Article
- Is CT Angiography a Reliable Tool for Diagnosis of Traumatic Vessel Injury in the Lower Extremities?
- Jong Hyuk Park, Kwang Bok Lee, Hyuk Park, Jun Mo Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(1):26-30. Published online January 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.1.26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Computed tomographic (CT) angiography is the first choice of diagnosis in traumatic vessel injury in the lower extremities, replacing angiography. The purpose of this study was to investigate the clinical reliability of CT angiography through a retrospective study.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Seventeen patients underwent CT angiography before surgery for traumatic vessel injury in the lower extremities from 2009 to 2010, and a comparative analysis of operative findings in all patients with a positive predictive value and sensitivity were measured.
RESULTS
In all patients, 16 artery ruptures and 1 compartment syndrome occurred. In 15 artery ruptures, preoperative findings of CT angiography and surgical findings were consistent, and the positive predictive value was 93.8%. One patient with posterior tibial artery rupture was revealed as normal in CT angiography; thus, sensitivity was 93.8% (15/16 patients), and the accuracy rate was 88.2% (15/17 patients).
CONCLUSION
Though CT angiography is a reliable tool for diagnosis in traumatic vessel injury in the lower extremities, a more invasive test will be needed, especially peripheral angiography or diagnostic exploration, in cases of relatively small vessel injuries around the ankle or compartment syndrome because of low accuracy.
- 291 View
- 0 Download

Case Report
- Multiple Non-contiguous Spine Fractures with Concomitant Injuries: A Case Report
- Soo Uk Chae, Yeung Jin Kim, Jung Hwan Yang, Ji Wan Lee, Jae In Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2011;24(3):267-270. Published online July 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.3.267
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Multiple non-contiguous spinal fracture is a special type of multi-level spinal injury, which is rare but most frequently occur in motor vehicle accident or a falling from a height. We report five patients of multiple non-contiguous spinal fractures. All patients underwent segmental pedicle screws fixation without fusion for preserving facet joints and minimizing blood loss and operation time. We performed necessary operation for any concomitant injuries at the same day.
- 364 View
- 6 Download

Original Articles
- TFCC Injury Associated with the Triquetral Dorsal Chip Fracture
- Seoung Joon Lee, Jin Ho Hwang, Min Seok Kang, Jong Woong Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(3):179-184. Published online July 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.3.179
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the usefulness of wrist arthroscopic examination in patient with persistent pain after the triquetral dorsal chip fracture and also to determine its relationship with TFCC injury in the triquetral dorsal chip fracture patient manifesting persistent pain.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study is based on six cases presenting persistent pain in the ulnar aspect after the triqeutral posterior cord fracture that were treated conservatively. Wrist arthroscopy was carried out for all six cases. All were preoperatively and postoperatively evaluated using VAS pain scale, grip power, ulnar grind test, Kleinman shearing test and lunotriquetral ballottment test.
RESULTS
Preoperatively, ulnar grind test yielded positive results in all six cases, Kleiman shearing test proved positive in three cases and lunotriquetral ballottment test yielded positive result in one case. In the arthroscopic findings, synovitis and TFCC injury were detected in all cases, and based on Palmer classification of TFCC injury, type IA was determined in five cases and type ID in one case. Arthroscopic TFCC partial resection and synovectomy were carried out. VAS pain scale improved from an average 8 points preoperatively to 3 points postoperatively. The difference of grip power between the normal and the other side improved from average of 15 lb preoperatively to 5 lb postoperatively. Based on postoperatively physical examination at 6 weeks, all cases yielded negative results in the ulnar grind test and Kleiman shearing test.
CONCLUSION
We think that TFCC injury is one of the causes of persistent pain after triquetral dorsal chip fracture. We recommend an arthroscopic TFCC partial resection as a valuable treatment option.
- 444 View
- 0 Download

- Staged Management of High Energy Proximal Tibia Fractures with Severe Soft Tissue Damage
- Seung Ryul Lee, Jae Hoon Yang, June Kyu Lee, Hyun Dae Shin, Kyung Cheon Kim, Kyu Woong Yeon, Young Mo Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(3):152-158. Published online July 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.3.152
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To find out the efficiency of two staged operation of patients with high energy proximal tibia fracture with severe soft tissue damage, the first step being external fixation, and the second, internal fixation with plates.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study group was the 42 patients who had followed for one year out of a group of 56, performed the first step external fixation and the second step internal fixation with plates retrospectively, from March 2003 to March 2007. The average age of the study group was 51.4, 26 men, and 16 women participating in this study. The average time of follow up was 32 months. In the final follow up, investigations of the radiological assessments and functional abilities of the bony fusion were carried out along with the complications of the soft tissue.
RESULTS
The duration after the first step external fixation until second step internal fixation to be performed was 14.9 (6~40) days in average. The final bone fusion took about 15 weeks, and according to the final follow up, the range of motion of the knee was around 110.8 degrees (6.2~117 degrees). In 31 cases, only the internal fixation was performed, while in 11 cases, soft tissue reconstruction was carried out with the internal fixations. As for the complications there were 2 cases of deep soft tissue infection, 2 cases of nonunion, 1 case of malunion and 1 case of knee joint stiffness.
CONCLUSION
In cases of proximal tibia fracture with severe soft tissue damage, external fixation was important to secure the safety of the fracture, carry forward the anatomical alignment, plan the soft tissue safety and manage the wound to decrease the number of microbial in the next operation, which is the internal fixation with plates.
- 357 View
- 2 Download

Case Reports
- Bipolar Clavicular Dislocation: A Case Report
- Han Jun Lee, Jae Sung Lee, Young Bong Ko
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(4):316-319. Published online October 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.4.316
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Bipolar clavicular dislocation is simultaneous dislocation of both poles of the clavicle (mainly an anterior dislocation of the sternoclavicular joint and a posterior dislocation of acromioclavicular joint) and rarely reported. We report a case of bipolar claviclular dislocation after a seat belt injury and describe its presumed mechanism and treatment with a review of literature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Case of the Month #177: Bipolar Clavicular Dislocation: Radiologic Evaluation of a Rare Traumatic Injury
Michael P. Loreto, Dawn Pearce
Canadian Association of Radiologists Journal.2012; 63(2): 156. CrossRef - Clavicle Midshaft Fracture with Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation: A Case Report
Chul-Hyun Cho, Chul-Hyung Kang, Soo-Won Jung, Hyuk-Jun Seo
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(4): 297. CrossRef
- Case of the Month #177: Bipolar Clavicular Dislocation: Radiologic Evaluation of a Rare Traumatic Injury
- 403 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Medial Transposition of Radial Nerve in Distal Humerus Shaft Fracture: A Report of Six Cases
- Sang Uk Lee, Weon Yoo Kim, Soo Hwan Kang, Yong Soo Park, Seung Koo Rhee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(3):240-243. Published online July 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.3.240
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Sometimes serious tension occurs in the radial nerve when doing internal fixation for distal humerus shaft fracture or neurorrhaphy for radial nerve injury. Medial transposition of radial nerve on fracture site can avoid direct radial nerve injury by fracture fragment, radial nerve tension by plating for distal humerus shaft fracture, and also safe from neural tension during neurorrhaphy of damaged radial nerve. We reported here total 6 cases of backward transposition of radial nerve including 2 cases of radial nerve injury associated with humerus fracture and 4 cases of comminuted fracture of humerus shaft.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Transhumeral Anterior Radial Nerve Transposition to Simplify Anticipated Future Humeral Reconstruction
David A. Muzykewicz, Reid A. Abrams
The Journal of Hand Surgery.2017; 42(7): 578.e1. CrossRef - Transfracture medial transposition of the radial nerve associated with plate fixation of the humerus
Ali Hassan Chamseddine, Amer Abdallah, Hadi Zein, Assad Taha
International Orthopaedics.2017; 41(7): 1463. CrossRef - Trans-fracture transposition of the radial nerve during the open approach of humeral shaft fractures
Ali H. Chamseddine, Hadi K. Zein, Abdullah A. Alasiry, Nader A. Mansour, Ali M. Bazzal
European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology.2013; 23(6): 725. CrossRef - Humerus Shaft Fractures in Leisure Sport 'Flyfish Riding' - 4 Cases Report -
Bong Gun Lee, Ki Chul Park, Youn Ho Choi, Woo Sung Jung, Kyu Tae Hwang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(4): 327. CrossRef
- Transhumeral Anterior Radial Nerve Transposition to Simplify Anticipated Future Humeral Reconstruction
- 457 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref

Original Article
- Alterations in Serum Levels of Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-kappa B Ligand and Osteoprotegerin in Patients with Head Injury and Fracture
- Shin Young Park, Kuen Tak Suh, Chang Hoon Ryu, Seung Hun Woo, Jung Sub Lee, Seong Gang Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2008;21(2):145-150. Published online April 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.2.145
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL), osteoprotegerin (OPG) have been shown to be important regulators of osteoclastogenesis during bone remodeling, and their expressions were examined during fracture healing in a mouse model of tibial fracture. However, studies linking RANKL and OPG in patients with head injury and fracture are lacking. We evaluated the changes in serum levels of RANKL and OPG in patients with head injury and fracture (head injury group) and in patients with fracture (fracture group) and compared these with levels found in healthy control subjects.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
18 male patients of head injury and fracture and 20 male patients of fracture alone were enrolled. 20 healthy men were recruited to serve as controls. Within the first few hours of admission to hospital, at 4, 8 and 12 weeks after injury 20 ml of blood were obtained from 18 patients with head injury and fracture and 20 patients with fracture only.
RESULTS
RANKL levels were significantly lower in the head injury group than in the fracture group at 8 and 12 weeks after injury. OPG levels were significantly higher in the head injury group than in the fracture group at 4, 8 and 12 weeks after injury. RANKL/OPG ratios were significantly lower in the head injury group than in the controls immediately after and 4, 8 and 12 weeks after injury, and were significantly lower in the head injury group than in the fracture group at 8 and 12 weeks after injury.
CONCLUSION
We have shown changes in the profiles of RANKL, OPG and RANKL to OPG ratio. The altered RANKL, OPG and RANKL/OPG ratio in the head injury group lasted longer than in those of the fracture group. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Affirmative Effect of Hwaweo-jeon (Huayu-jian) in Osteoblast Cells and Tibia Fracture-induced Mice
Soo-Hwan Lee, Kira Parichuk, Yun-yeop Cha
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2020; 30(1): 13. CrossRef
- Affirmative Effect of Hwaweo-jeon (Huayu-jian) in Osteoblast Cells and Tibia Fracture-induced Mice
- 393 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA

 First
First Prev
Prev


