Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 29(4); 2016 > Article
-
Review Article
- Lisfranc Joint Injuries: Diagnosis and Treatment
- Hyun Seok Yim, M.D., Sung Ha Hong, M.D., Ki Sun Sung, M.D., Ph.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2016;29(4):283-293.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.4.283
Published online: October 20, 2016
Department Orthopaedic Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Ki Sun Sung, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, 81 Irwon-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul 06351, Korea. Tel: 82-2-3410-1531·Fax: 82-2-3410-0061, kissung@gmail.com
Copyright © 2016 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 1,744 Views
- 40 Download
- 2 Crossref
Abstract
- Injuries to the Lisfranc joint are relatively rare, but they are often misdiagnosed or inadequately treated, resulting in poor long-term outcomes. Understanding of anatomical structure and injury mechanism, careful clinical and radiographic evaluations are needed to recognize and treat Lisfranc joint injuries. In this article, we review the anatomy, biomechanics, injury mechanisms, injury classification, clinical presentation, radiographic evaluation, treatment, outcome, and complications of Lisfranc joint injuries.
- 1. Collett HS, Hood TK, Andrews RE. Tarsometatarsal fracture dislocations. Surg Gynecol Obstet, 1958;106:623-626.
- 2. Myerson M. The diagnosis and treatment of injuries to the Lisfranc joint complex. Orthop Clin North Am, 1989;20:655-664.
- 3. Benirschke SK, Meinberg E, Anderson SA, Jones CB, Cole PA. Fractures and dislocations of the midfoot: Lisfranc and chopart injuries. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2012;94:1325-1337.Article
- 4. Hardcastle PH, Reschauer R, Kutscha-Lissberg E, Schoffmann W. Injuries to the tarsometatarsal joint. Incidence, classification and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1982;64:349-356.ArticlePDF
- 5. Goossens M, De Stoop N. Lisfranc's fracture-dislocations: etiology, radiology, and results of treatment. A review of 20 cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1983;(176):154-162.
- 6. Peicha G, Labovitz J, Seibert FJ, et al. The anatomy of the joint as a risk factor for Lisfranc dislocation and fracture-dislocation. An anatomical and radiological case control study. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2002;84:981-985.
- 7. Panchbhavi VK, Andersen CR, Vallurupalli S, Yang J. A minimally disruptive model and three-dimensional evaluation of Lisfranc joint diastasis. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2008;90:2707-2713.Article
- 8. Ouzounian TJ, Shereff MJ. In vitro determination of midfoot motion. Foot Ankle, 1989;10:140-146.ArticlePDF
- 9. Wiley JJ. The mechanism of tarso-metatarsal joint injuries. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1971;53:474-482.ArticlePDF
- 10. Quenu E, Kuss G. Etude sur les luxations du metatarse. Rev Chir Paris, 1909;39:281.
- 11. Myerson MS, Fisher RT, Burgess AR, Kenzora JE. Fracture dislocations of the tarsometatarsal joints: end results correlated with pathology and treatment. Foot Ankle, 1986;6:225-242.ArticlePDF
- 12. Nunley JA, Vertullo CJ. Classification, investigation, and management of midfoot sprains: Lisfranc injuries in the athlete. Am J Sports Med, 2002;30:871-878.ArticlePDF
- 13. Ross G, Cronin R, Hauzenblas J, Juliano P. Plantar ecchymosis sign: a clinical aid to diagnosis of occult Lisfranc tarsometatarsal injuries. J Orthop Trauma, 1996;10:119-122.Article
- 14. Foster SC, Foster RR. Lisfranc's tarsometatarsal fracture-dislocation. Radiology, 1976;120:79-83.Article
- 15. Coss HS, Manos RE, Buoncristiani A, Mills WJ. Abduction stress and AP weightbearing radiography of purely ligamentous injury in the tarsometatarsal joint. Foot Ankle Int, 1998;19:537-541.ArticlePDF
- 16. Stein RE. Radiological aspects of the tarsometatarsal joints. Foot Ankle, 1983;3:286-289.ArticlePDF
- 17. Faciszewski T, Burks RT, Manaster BJ. Subtle injuries of the Lisfranc joint. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1990;72:1519-1522.Article
- 18. Goiney RC, Connell DG, Nichols DM. CT evaluation of tarsometatarsal fracture-dislocation injuries. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1985;144:985-990.Article
- 19. Preidler KW, Wang YC, Brossmann J, Trudell D, Daenen B, Resnick D. Tarsometatarsal joint: anatomic details on MR images. Radiology, 1996;199:733-736.Article
- 20. Preidler KW, Peicha G, Lajtai G, et al. Conventional radiography, CT, and MR imaging in patients with hyperflexion injuries of the foot: diagnostic accuracy in the detection of bony and ligamentous changes. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1999;173:1673-1677.Article
- 21. Raikin SM, Elias I, Dheer S, Besser MP, Morrison WB, Zoga AC. Prediction of midfoot instability in the subtle Lisfranc injury. Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging with intraoperative findings. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2009;91:892-899.
- 22. Claassen L, Uden T, Ettinger M, Daniilidis K, Stukenborg-Colsman C, Plaass C. Influence on therapeutic decision making of SPECT-CT for different regions of the foot and ankle. Biomed Res Int, 2014;2014:927576. ArticlePDF
- 23. Myerson MS, Cerrato RA. Current management of tarsometatarsal injuries in the athlete. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2008;90:2522-2533.
- 24. Brunet JA, Wiley JJ. The late results of tarsometatarsal joint injuries. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1987;69:437-440.ArticlePDF
- 25. Kuo RS, Tejwani NC, Digiovanni CW, et al. Outcome after open reduction and internal fixation of Lisfranc joint injuries. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2000;82:1609-1618.Article
- 26. Alberta FG, Aronow MS, Barrero M, Diaz-Doran V, Sullivan RJ, Adams DJ. Ligamentous Lisfranc joint injuries: a biomechanical comparison of dorsal plate and transarticular screw fixation. Foot Ankle Int, 2005;26:462-473.ArticlePDF
- 27. Pelt CE, Bachus KN, Vance RE, Beals TC. A biomechanical analysis of a tensioned suture device in the fixation of the ligamentous Lisfranc injury. Foot Ankle Int, 2011;32:422-431.ArticlePDF
- 28. Marsland D, Belkoff SM, Solan MC. Biomechanical analysis of endobutton versus screw fixation after Lisfranc ligament complex sectioning. Foot Ankle Surg, 2013;19:267-272.Article
- 29. Lau S, Howells N, Millar M, De Villiers D, Joseph S, Oppy A. Plates, screws, or combination? Radiologic outcomes after Lisfranc fracture dislocation. J Foot Ankle Surg, 2016;55:799-802.Article
- 30. Dubois-Ferrière V, Lübbeke A, Chowdhary A, Stern R, Dominguez D, Assal M. Clinical outcomes and development of symptomatic osteoarthritis 2 to 24 years after surgical treatment of Tarsometatarsal joint complex injuries. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2016;98:713-720.Article
- 31. Sheibani-Rad S, Coetzee JC, Giveans MR, DiGiovanni C. Arthrodesis versus ORIF for Lisfranc fractures. Orthopedics, 2012;35:e868-e873.Article
- 32. Smith N, Stone C, Furey A. Does open reduction and internal fixation versus primary arthrodesis improve patient outcomes for Lisfranc trauma? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2016;474:1445-1452.ArticlePDF
- 33. Myerson MS. Management of compartment syndromes of the foot. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1991;(271):239-248.Article
- 34. Sangeorzan BJ, Veith RG, Hansen ST Jr. Salvage of Lisfranc's tarsometatarsal joint by arthrodesis. Foot Ankle, 1990;10:193-200.ArticlePDF
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
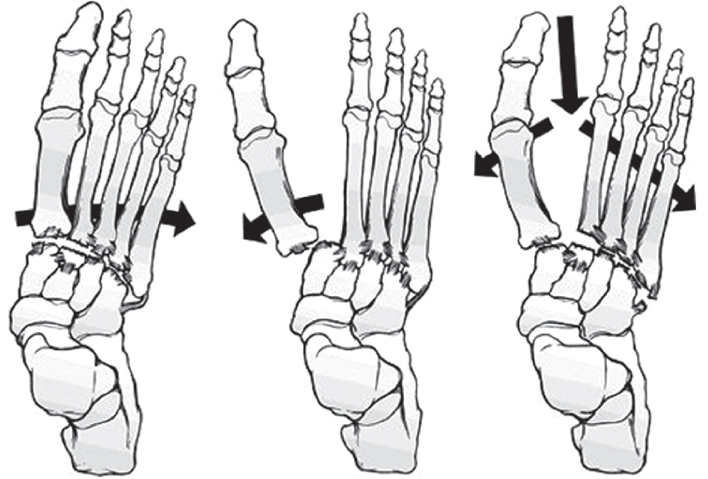
Quenu and Kuss classification of Lisfranc joint injuries. Data from the article of Quenu and Kuss (Rev Chir Paris 1909;39:281).10)

Fig. 2

Hardcastle & Myerson classification of Lisfranc joint injuries. Data from the article of Myerson (Orthop Clin North Am 1989;20:655-664).2)

Fig. 3

Nunley classification of Lisfranc joint injuries. Data from the article of Nunley and Vertullo (Am J Sports Med 2002;30:871-878).12)

Fig. 5

Normal radiographic parameters of the Lisfranc joint on anteroposterior view, 30° oblique view, and lateral view.

Fig. 7

(A) Normal radiographs on anteroposterior and oblique view in patient with persisting pain and discomfort. (B) Osteoarthritic changes at 1st, 2nd, and 3rd tarsometatarsal joint in single-photon emission computed tomographycomputed tomography. (C) Open reduction with internal fixation of Lisfranc joint injuries using mini plate & screw.

Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Lisfranc Sports Injuries: What Do We Know So Far?
Godsfavour C Maduka, Divinegrace C Maduka, Naeem Yusuf
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Acupuncture Treatment and Taping Therapy After Lisfranc Joint Injuries: A Case Report
Shin-Ae Kim, Su-Woo Kang, Eun-Ji Lee, Min-Kyung Kwak, Hui-Gyeong Jeong, Jae-Uk Sul
Journal of Acupuncture Research.2017; 34(4): 197. CrossRef
Lisfranc Joint Injuries: Diagnosis and Treatment
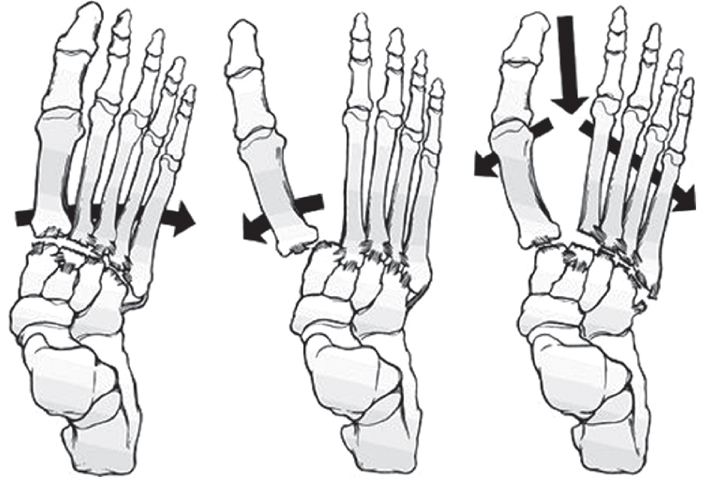
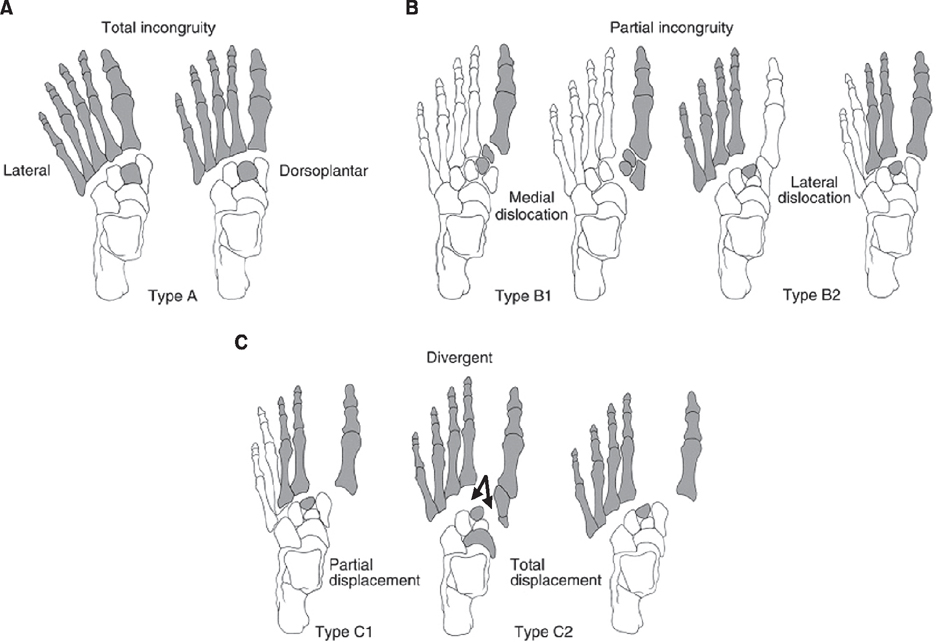


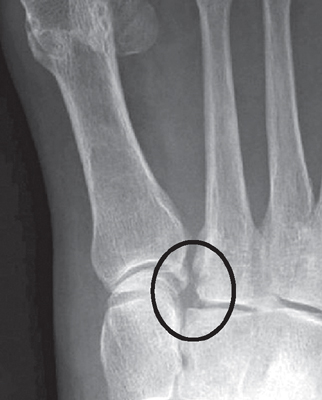

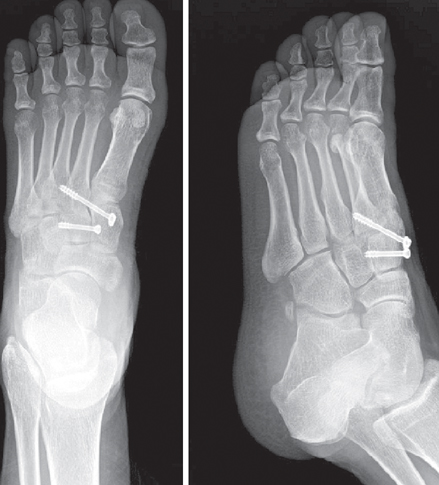

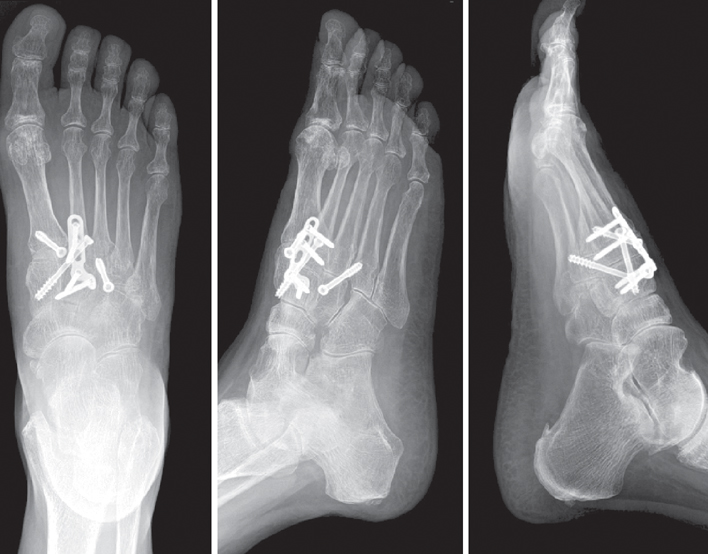
Fig. 1
Quenu and Kuss classification of Lisfranc joint injuries. Data from the article of Quenu and Kuss (Rev Chir Paris 1909;39:281).10)
Fig. 2
Hardcastle & Myerson classification of Lisfranc joint injuries. Data from the article of Myerson (Orthop Clin North Am 1989;20:655-664).2)
Fig. 3
Nunley classification of Lisfranc joint injuries. Data from the article of Nunley and Vertullo (Am J Sports Med 2002;30:871-878).12)
Fig. 4
Plantar ecchymosis sign.
Fig. 5
Normal radiographic parameters of the Lisfranc joint on anteroposterior view, 30° oblique view, and lateral view.
Fig. 6
Fleck sign indicating avulsion of the Lisfranc ligament.
Fig. 7
(A) Normal radiographs on anteroposterior and oblique view in patient with persisting pain and discomfort. (B) Osteoarthritic changes at 1st, 2nd, and 3rd tarsometatarsal joint in single-photon emission computed tomographycomputed tomography. (C) Open reduction with internal fixation of Lisfranc joint injuries using mini plate & screw.
Fig. 8
Closed reduction with internal fixation for a subtle Lisfranc joint injury.
Fig. 9
Open reduction with internal fixation for Lisfranc joint injury using K-wire and cannulated screw.
Fig. 10
Open reduction with internal fixation for Lisfranc joint injury using mini plate & screw.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
Fig. 8
Fig. 9
Fig. 10
Lisfranc Joint Injuries: Diagnosis and Treatment

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS





 Cite
Cite

