Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 25(1); 2012 > Article
-
Original Article
- Is CT Angiography a Reliable Tool for Diagnosis of Traumatic Vessel Injury in the Lower Extremities?
- Jong-Hyuk Park, M.D., Kwang-Bok Lee, M.D., Ph.D., Hyuk Park, M.D., Jun-Mo Lee, M.D., Ph.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2012;25(1):26-30.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.1.26
Published online: January 31, 2012
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chonbuk National Univeristy Hospital, Research Institute of Clinical Medicine, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Kwang-Bok Lee, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chonbuk National University Hospital, 634-18, Geumam-dong, Deokjin-gu, Jeonju 561-712, Korea. Tel: 82-63-250-2586, Fax: 82-63-271-6538, osdr2815@naver.com
• Received: July 4, 2011 • Revised: July 28, 2011 • Accepted: August 20, 2011
Copyright © 2012 The Korean Fracture Society
- 483 Views
- 0 Download
Abstract
-
Purpose
- Computed tomographic (CT) angiography is the first choice of diagnosis in traumatic vessel injury in the lower extremities, replacing angiography. The purpose of this study was to investigate the clinical reliability of CT angiography through a retrospective study.
-
Materials and Methods
- Seventeen patients underwent CT angiography before surgery for traumatic vessel injury in the lower extremities from 2009 to 2010, and a comparative analysis of operative findings in all patients with a positive predictive value and sensitivity were measured.
-
Results
- In all patients, 16 artery ruptures and 1 compartment syndrome occurred. In 15 artery ruptures, preoperative findings of CT angiography and surgical findings were consistent, and the positive predictive value was 93.8%. One patient with posterior tibial artery rupture was revealed as normal in CT angiography; thus, sensitivity was 93.8% (15/16 patients), and the accuracy rate was 88.2% (15/17 patients).
-
Conclusion
- Though CT angiography is a reliable tool for diagnosis in traumatic vessel injury in the lower extremities, a more invasive test will be needed, especially peripheral angiography or diagnostic exploration, in cases of relatively small vessel injuries around the ankle or compartment syndrome because of low accuracy.
- 1. Anderson RJ, Hobson RW 2nd, Lee BC, et al. Reduced dependency on arteriography for penetrating extremity trauma: influence of wound location and noninvasive vascular studies. J Trauma, 1990;30:1059-1063.
- 2. Bergstein JM, Blair JF, Edwards J, et al. Pitfalls in the use of color-flow duplex ultrasound for screening of suspected arterial injuries in penetrated extremities. J Trauma, 1992;33:395-402.Article
- 3. Busquéts AR, Acosta JA, Colón E, Alejandro KV, Rodríguez P. Helical computed tomographic angiography for the diagnosis of traumatic arterial injuries of the extremities. J Trauma, 2004;56:625-628.Article
- 4. Lee SJ. Posterior thigh compartment syndrome as a result of pseudoaneurysm of the popliteal artery in the distal femoral fracture: a case report. J Korean Fract Soc, 2007;20:277-281.
- 5. Miller-Thomas MM, West OC, Cohen AM. Diagnosing traumatic arterial injury in the extremities with CT angiography: pearls and pitfalls. Radiographics, 2005;25:Suppl 1. S133-S142.Article
- 6. Pieroni S, Foster BR, Anderson SW, Kertesz JL, Rhea JT, Soto JA. Use of 64-row multidetector CT angiography in blunt and penetrating trauma of the upper and lower extremities. Radiographics, 2009;29:863-876.
- 7. Pyo YB, Shin DM, Kim PO. Treatment of acute compartment syndrome with tibial fracture. J Korean Soc Fract, 1996;9:614-621.
- 8. Reuss PM, Rosen RJ, Adelman M. Compartment syndrome complicating lower extremity thrombolysis. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 1999;10:1075-1082.
- 9. Rieger M, Mallouhi A, Tauscher T, Lutz M, Jaschke WR. Traumatic arterial injuries of the extremities: initial evaluation with MDCT angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2006;186:656-664.
- 10. Shah N, Anderson SW, Vu M, Pieroni S, Rhea JT, Soto JA. Extremity CT angiography: application to trauma using 64-MDCT. Emerg Radiol, 2009;16:425-432.
- 11. Soto JA, Múnera F, Cardoso N, Guarín O, Medina S. Diagnostic performance of helical CT angiography in trauma to large arteries of the extremities. J Comput Assist Tomogr, 1999;23:188-196.
- 12. Soto JA, Múnera F, Morales C, et al. Focal arterial injuries of the proximal extremities: helical CT arteriography as the initial method of diagnosis. Radiology, 2001;218:188-194.
- 13. Uyeda JW, Anderson SW, Sakai O, Soto JA. CT angiography in trauma. Radiol Clin North Am, 2010;48:423-438.
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
Case 17.
(A) Plain radiogram shows the comminuted fracture on both femur and tibia shaft.
(B) CT angiography shows soft tissue and muscle swelling on femoral supracondylar area.
(C) CT angiography reveals the abrupt disruption of popliteal artery in the knee area, however, there is no vessel injury in intraoperative finding.


Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

Is CT Angiography a Reliable Tool for Diagnosis of Traumatic Vessel Injury in the Lower Extremities?
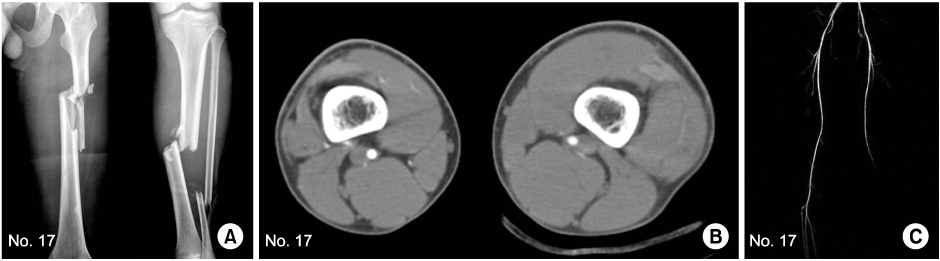

Fig. 1
Case 17.
(A) Plain radiogram shows the comminuted fracture on both femur and tibia shaft.
(B) CT angiography shows soft tissue and muscle swelling on femoral supracondylar area.
(C) CT angiography reveals the abrupt disruption of popliteal artery in the knee area, however, there is no vessel injury in intraoperative finding.
Fig. 2
Case 12.
(A) Plain radiogram shows comminuted ankle fracture.
(B) CT angiography shows that there is no definite vessel injury except the weak patency of dye in the posterior tibial artery.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Is CT Angiography a Reliable Tool for Diagnosis of Traumatic Vessel Injury in the Lower Extremities?
Summary of cases
*MVA: motor vehicle accident.
Positive predictive value and sensitivity of CT angiography
Table 1
Summary of cases
*MVA: motor vehicle accident.
Table 2
Positive predictive value and sensitivity of CT angiography

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS



 Cite
Cite

