Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Comparative results of the femoral neck system versus the dynamic hip screw for stable femoral neck fractures in older adults in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
- Byung-Chan Choi, Byung-Woo Min, Kyung-Jae Lee, Jun-Sik Hong
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):203-211. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00276
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study aimed to compare the clinical and radiological outcomes of the femoral neck system (FNS) and the dynamic hip screw (DHS) for the internal fixation of stable femoral neck fractures in older adults.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study included 48 matched older adult patients based on sex, age, BMI, and osteoporosis status, who had undergone internal fixation with either FNS or DHS for stable femoral neck fractures between January 2010 and December 2022. To minimize selection bias, a 1:1 case-control matching was performed based on sex, age, body mass index (BMI), and the presence of osteoporosis. A total of 48 patients (24 in each group) were included. We compared perioperative data (operation time, hemoglobin change, transfusion rate), functional outcomes using the Koval score, and radiological outcomes, including union rate, femoral neck shortening, and complication rates.
Results
The mean operation time was significantly shorter in the FNS group than in the DHS group (60.9 minutes vs. 70.8 minutes; P=0.007). There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in the union rate (87.5% in FNS vs. 95.8% in DHS), femoral neck shortening, final Koval score distribution, or overall complication rates (12.5% in both groups).
Conclusions
For treating stable femoral neck fractures in older adults, the FNS demonstrated comparable clinical and radiological outcomes to the DHS, with the distinct advantage of a shorter operation time. While these findings suggest that the FNS is a promising and safe alternative that may reduce the surgical burden, definitive conclusions are precluded by the small sample size, warranting further research to corroborate these results. Level of evidence: IV.
- 133 View
- 4 Download

- Risk factors of surgical complications after use of the femoral neck system: a random forest analysis
- Chul-Ho Kim, Hyun-Chul Shon, Han Soul Kim, Ji Wan Kim, Eic Ju Lim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):160-167. Published online July 23, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00157
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The femoral neck system (FNS), a novel fixation device for managing femoral neck fractures (FNFs), has gained popularity in recent years. However, analyses of the surgical complications and reoperation risks associated with the use of FNS remain limited.
Methods
This retrospective observational study analyzed 57 patients who had undergone FNS fixation for FNF at two university hospitals between July 2019 and February 2024. Demographic, perioperative, and outcome variables, including age, sex, fracture classification (Garden, Pauwels, and AO), implant characteristics, tip-apex distance (TAD), neck shortening, and neck-shaft alignment, were analyzed. In addition to univariate analysis, a machine learning analysis was conducted using a random forest classifier with stratified sampling (80% training, 20% testing). The accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and area under the receiver’s operating curve were calculated to assess model performance.
Results
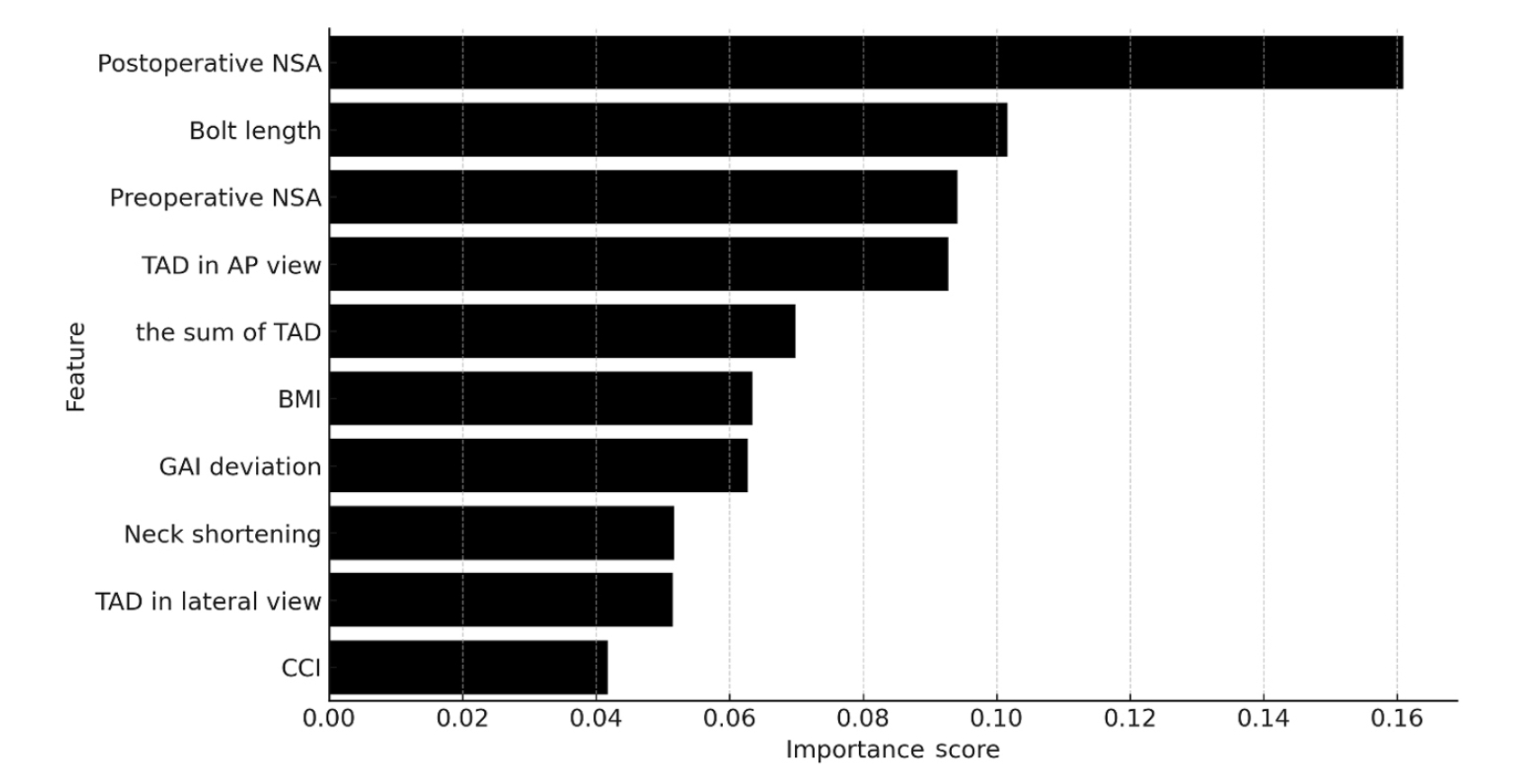
Ten patients experienced osteonecrosis of the femoral head (n=6), implant cut-out or penetration (n=3), and peri-implant fracture (n=1). Univariate analysis revealed that the TAD in the complication group was significantly shorter than that in the control group (12.1 vs. 16.7 mm; P=0.012). Additionally, neck shortening in the complication group was greater than that in the control group (4.9 vs. 2.3 mm; P=0.011). The random forest model achieved an accuracy of 83.3% and identified postoperative neck-shaft angle (NSA) as the most important predictor of complications (feature importance, 0.161), followed by bolt length (0.102) and preoperative NSA (0.094).
Conclusions
Risk factor analysis conducted using a random forest model identified postoperative NSA as the most important feature associated with postoperative complications following FNS. Therefore, care should be taken to normalize the postoperative NSA during FNF surgery. Level of Evidence: III.
- 520 View
- 24 Download

- Comparison of Clinical Outcomes for Femoral Neck System and Cannulated Compression Screws in the Treatment of Femoral Neck Fracture
- Jae Kwang Hwang, KiWon Lee, Dong-Kyo Seo, Joo-Yul Bae, Myeong-Geun Song, Hansuk Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(3):77-84. Published online July 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.3.77
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study compared the clinical and radiological results of the femoral neck system (FNS) and cannulated compression screws (CCS) for the fixation of femoral neck fractures.
Materials and Methods
Patients who underwent FNS or CCS internal fixation for femoral neck fractures between January 2016 and January 2022 were analyzed retrospectively. The hip joint function using the Harris hip score (HHS) was evaluated three months and one year after surgery. The operation time, fracture healing time, and associated surgical complications in the two groups were compared and analyzed statistically.
Results
Seventy-nine patients were categorized into 38 FNS and 41 CCS groups. The FNS group had a longer operation time and higher postoperative HHS at three months (p<0.01). Femoral neck shortening was lower in the FNS group (p=0.022). There were no significant differences in the fracture healing time and other complications.
Conclusion
There were no differences in most clinical outcomes and complications between the two groups except for the three-month HHS and femoral neck shortening. This study suggests that FNS could be an alternative to CCS for treating femoral neck fractures.
- 486 View
- 14 Download

- Computational Simulation of Femoral Neck System and Additional Cannulated Screws Fixation for Unstable Femoral Neck Fractures and the Biomechanical Features for Clinical Applications
- Ju-Yeong Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(1):1-9. Published online January 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
To identify the biomechanical features for clinical applications through a computational simulation of the fixation of the Femoral Neck System (FNS) with additional cannulated screws for a Pauwels type III femoral neck fractures.
Materials and Methods
Thirty cadaveric femurs underwent computed tomography, and the images were transferred to the Mimics ® program, resulting in three-dimensional proximal femur models. A three-dimensional scan of the FNS and 6.5 mm and 7.0 mm cannulated screws was performed to enable computerized virtual fixation of FNS with additional cannulated screws for unstable femoral neck fractures. Furthermore, the cannulated screw used for additional fixation was modeled and used as a cylinder within the Ansys program. The biomechanical characteristics of these models were investigated by applying a physiological load virtually.
Results
The maximum von Mises stress value at bone was 380.14 MPa in FNS and 297.87 MPa in FNS+7.0 mm full-thread cannulated screw. The maximum von Mises stress value at FNS was 786.83 MPa in FNS and 435.62 MPa in FNS+7.0 mm full-thread cannulated screw. The FNS group showed the highest maximum von Mises stress values at bone and FNS. For total deformation, the maximum deformation value was 10.0420 mm in FNS and 9.2769 mm in FNS+7.0 mm full-thread cannulated screws. The FNS group represented the highest maximum deformation compared to the other groups.
Conclusion
Considering the anatomical spatiality and biomechanical characteristics of the FNS in unstable femoral neck fractures, when one 7.0 mm full thread cannulated screw was also fixed to the anterosuperior portion of the FNS, significant biomechanical stability was demonstrated.
- 492 View
- 6 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA
 First
First Prev
Prev


