Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Three-dimensional computed tomography-based differentiation of engaged versus displaced intertrochanteric fractures using the anterior fracture line: a cross-sectional study from Korea
- Jae-Suk Chang, Jin Yeob Park, Sang-Ok Chun, Chul-Ho Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2026;39(1):30-37. Published online January 25, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00318

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
With the advent of an aging society, osteoporotic fractures—particularly hip fractures—are increasing, with a 1-year mortality rate of 17%. Achieving stable fixation that enables early ambulation is essential but remains challenging because complex intertrochanteric (IT) fracture patterns are often underestimated on plain radiographs. Using three-dimensional computed tomography (3D-CT), this study analyzed whether the anterior fracture line lies medial or lateral to the IT line and examined its relationship with displacement or distal medullary canal engagement, highlighting the potential influence of the joint capsule and capsular ligaments on fracture morphology and fixation stability.
Methods
A retrospective review was conducted on 96 osteoporotic IT fractures in patients aged ≥60 years treated between April 2013 and December 2022 at National Police Hospital and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. Fractures were classified as engaged, completely displaced, and partially displaced based on 3D-CT findings. The anterior fracture-line position (medial or lateral to the IT line) and the status of the lesser trochanter (LT) were evaluated. The chi-square or Fisher exact test was used for statistical comparisons.
Results
In total, 96 patients were analyzed. Of these, 49 cases (51.0%) were classified as engaged type, 27 cases (28.1%) as completely displaced type, and 20 cases (20.8%) as partially displaced type. When comparing fracture pattern with anterior fracture-line position, the completely displaced type showed a significantly higher proportion of lateral anterior fracture lines than the other two types (P<0.001). However, no significant association was identified between fracture pattern and LT displacement. When the anterior fracture-line position and LT displacement were evaluated together, only the engaged type demonstrated a possible association between a lateral anterior fracture line and LT displacement, though the statistical significance was weak (P=0.047).
Conclusions
Fracture lines lateral to the IT line were strongly associated with displacement in IT fractures; however, their relationship with LT involvement, reflecting iliopsoas tendon traction, was not clearly demonstrated. Although the factors contributing to the engaged-type fracture remain uncertain, the statistical association between fracture pattern and anterior fracture-line position suggests that capsular structures may play a stabilizing role in select fracture configurations. Further studies are needed to clarify these anatomical interactions. Level of evidence:
- 151 View
- 5 Download

- Computed tomography plane reformatting to reduce projection error in measuring Pauwels angle of femoral neck fractures: a cross-sectional study
- Gyu Min Kong, Jae-Young Lim, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2026;39(1):38-47. Published online January 25, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00038

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objectives
This study aimed to assess fracture verticality in both coronal and axial planes after eliminating projection error in femoral neck fractures among non-older adults, and to demonstrate its clinical utility using computed tomography (CT)-based modeling at actual size.
Methods
This retrospective observational study enrolled 57 patients (30 males and 27 females), aged 20–65 years, with displaced femoral neck fractures. Based on CT images, an actual-size fracture model was constructed. The CT scanning plane was reformatted with the neck-shaft fragment realigned vertically to the ground and parallel to the femoral neck axis. Three consecutive images were used to generate coronal reformats at the centerline and posterior border to measure central and posterior coronal plane verticality as Pauwels’ angle (PA). The central image of the reformatted axial plane was used to assess axial plane verticality. Differences in verticality were analyzed using analysis of variance.
Results
Three coronal morphology types were identified: linear (n=30), concave (n=25), and convex (n=2). Two axial morphology types were observed: cephalad (n=35) and trochanteric (n=22). The mean central PA, posterior PA, and axial verticality were 55.43°±13.79°, 51.44°±11.13°, and 85.74°±18.41°, respectively. Only the central PA showed a significant difference (P<0.001). The PA was significantly higher in the linear coronal type between images (P<0.05) and in the trochanteric axial type (P<0.05).
Conclusions
After reformatting the scanning plane, the central PA showed significant variation between images. Femoral neck fractures of the linear type in the coronal plane and the trochanteric type in the axial plane demonstrated greater verticality than other morphological types. Level of evidence:
- 147 View
- 4 Download

- Relationship of lateral malleolar fracture patterns to posterior malleolar fracture morphology in supination-external rotation ankle fractures in Korea: a retrospective cohort stduy
- Jong-Eun Kim, Chan-Jin Park, Jun-Young Lee, Keun-Bae Lee, Gun-Woo Lee
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):212-220. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00234
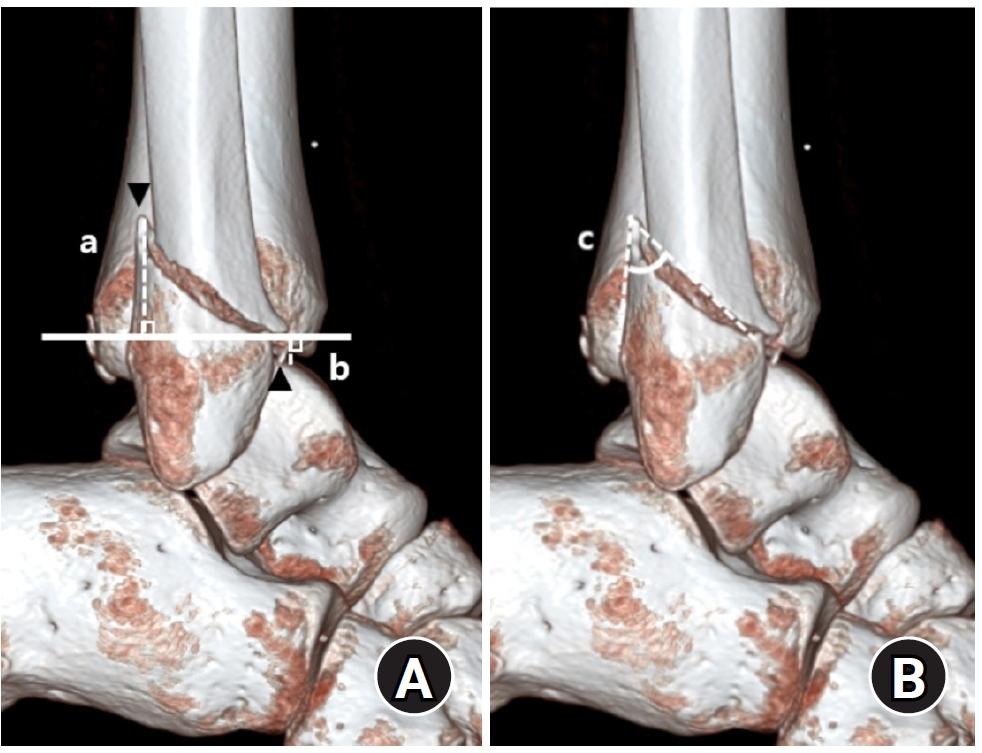
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Posterior malleolar fractures frequently accompany rotational ankle fractures. However, the morphological relationship between lateral and posterior malleolar fractures in supination-external rotation (SER) ankle fractures remains unclear. This study aimed to classify lateral malleolar fracture patterns in SER type 3 and 4 ankle fractures and investigated their associations with posterior malleolar fracture morphology.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 132 patients with SER type 3 or 4 ankle fractures and concurrent posterior malleolar fractures between January 2016 and December 2021. Lateral malleolar fractures were categorized as fibular fractures extending <4.5 cm proximal to the ankle joint (102 ankles) or fibular fractures extending ≥4.5 cm proximal to the ankle joint (30 ankles) based on posterior cortex height measured using three-dimensional computed tomography (3D-CT). Posterior malleolar fracture morphology was assessed using the Haraguchi and Bartonicek classifications. Quantitative parameters—including fracture height, angle, and articular involvement—were analyzed using 3D-CT imaging.
Results
Fibular fractures extending ≥4.5 cm proximal to the ankle joint were associated with a significantly higher frequency of Haraguchi type II and Bartonicek types 3 and 4 posterior malleolar fractures. This group also exhibited greater articular involvement (19.2% vs. 12.0%) and posterior cortical height (55.4 mm vs. 24.8 mm) compared to the <4.5 cm group (all P<0.001).
Conclusions
In SER type 3 and 4 ankle fractures, a fibular fracture extending ≥4.5 cm proximal to the ankle joint may be associated with posterior malleolar fractures exhibiting greater articular involvement and medial extension. Preoperative evaluation of the lateral malleolar fracture pattern may provide useful insights into posterior malleolar morphology and assist in surgical planning. However, these findings should be interpreted with caution due to inherent study limitations. Level of evidence: IV
- 982 View
- 20 Download

- Comparison of the Size of the Posterior Malleolar Fragment in Trimalleolar Ankle Fractures Measured Using Lateral Plain Radiography and Three-Dimensional Computed Tomography
- Gun-Woo Lee, Dong-Min Jung, Woo Kyoung Kwak, Keun-Bae Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(3):91-96. Published online July 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.3.91
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate and compare the accuracy of the size of the posterior malleolar fragment measured using lateral plain radiography and three-dimensional computed tomography (3DCT) in patients with ankle trimalleolar fractures.
Materials and Methods
This study enrolled 80 patients (80 ankles) with ankle trimalleolar fractures and analyzed the size of the posterior malleolar fragments using plain radiography and 3D-CT. The articular involvement of the posterior malleolar fragments was measured as a percentage of the articular surface in the sagittal length of the tibial plafond using lateral plain radiography, and the articular surface area was directly measured using 3D-CT. In addition, we classified the patients into three groups based on the morphology of the posterior malleolar fracture, according to the Haraguchi classification method, and evaluated and compared the accuracy of the size of the posterior malleolar fragments.
Results
The mean articular involvement of the posterior malleolar fragments on plain radiography was 27.6% (range, 6.0%-53.1%), which was significantly higher than the mean of 21.9% (range, 4.7%-47.1%) measured using 3D-CT (p=0.004). In the analysis, according to the fracture morphology, the mean difference between the two methods was the largest for type I fractures at 9.1% (range, 1.8%-19.5%) and the smallest for type II fractures at 1.1% (range, –7.7% to 8.8%).
Conclusion
The articular involvement of posterior malleolar fragments measured using plain radiography showed low accuracy and significantly higher values than the actual articular involvement. Therefore, careful evaluation using 3D-CT is crucial for accurate analysis and optimal treatment in patients with ankle trimalleolar fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship of lateral malleolar fracture patterns to posterior malleolar fracture morphology in supination-external rotation ankle fractures in Korea: a retrospective cohort stduy
Jong-Eun Kim, Chan-Jin Park, Jun-Young Lee, Keun-Bae Lee, Gun-Woo Lee
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(4): 212. CrossRef
- Relationship of lateral malleolar fracture patterns to posterior malleolar fracture morphology in supination-external rotation ankle fractures in Korea: a retrospective cohort stduy
- 505 View
- 10 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Comparison between X-ray and Three Dimensional Computed Tomography in Trimalleolar Ankle Fractures
- Sang Jun Song, Hyung Ku Yoon, Dong Eun Shin, Soo Hong Han, Jae Hwa Kim, Hyung Kun Park, Yong Sub Han
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(2):160-164. Published online April 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.2.160
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the accuracy of X-ray evaluation in classification, displacement and size of posterior malleolar fragment, comparing with three dimensional computed tomography (3D CT) in trimallelar ankle fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
20 cases of trimalleolar ankle fractures evaluated with preoperative 3D CT, and followed up periods were at least 2 years. All cases were classified according to the Danis-Weber and Lauge-Hansen classification. Displacement and size of posterior malleolar fragment were measured using PACS. The reliability between simple X-ray and 3D CT was evaluated in the Danis-Weber and Lauge-Hansen classification (kappa analysis). The correlation between simple X-ray and 3D CT was evaluated in displacement and size of posterior malleolar fragment (correlation analysis).
RESULTS
Degree of agreement of Danis-Weber classification in simple X-ray and 3D CT was 0.700 kappa value, and that of Lauge-Hansen was 0.605 kappa value. Measurement of simple X-ray and 3D CT about displaced status of posterior malleolar fragment showed statistically significant positive linear correlation (p= 0.000), but correlation of measurement of size in simple X-ray and CT was not statistically significant (p=0.102).
CONCLUSION
CT or operative field will be more accurate than simple X-ray to select the method of treatment and operation, especially when the displacement and size of posterior malleolar fragment are important to decide. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of the Size of the Posterior Malleolar Fragment in Trimalleolar Ankle Fractures Measured Using Lateral Plain Radiography and Three-Dimensional Computed Tomography
Gun-Woo Lee, Dong-Min Jung, Woo Kyoung Kwak, Keun-Bae Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2022; 35(3): 91. CrossRef
- Comparison of the Size of the Posterior Malleolar Fragment in Trimalleolar Ankle Fractures Measured Using Lateral Plain Radiography and Three-Dimensional Computed Tomography
- 647 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


