Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
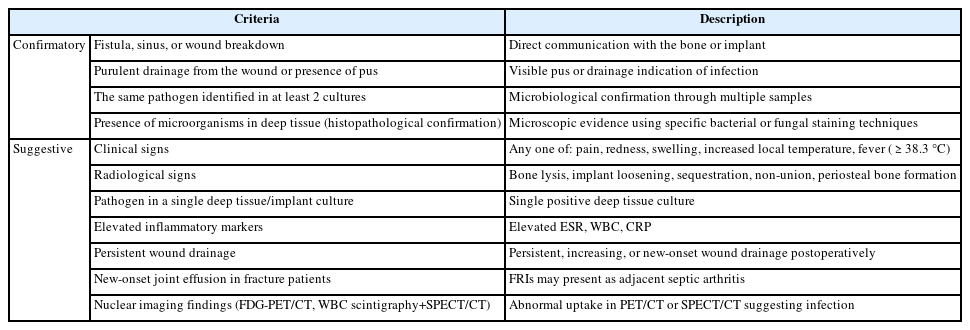
- Fracture-related infections: a comprehensive review of diagnosis and prevention
- HoeJeong Chung, Hoon-Sang Sohn
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):86-95. Published online April 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00164
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fracture-related infections are challenging complications in orthopedic trauma that often require prolonged treatment and impose a significant healthcare burden. Accurate diagnosis and effective prevention strategies are essential for minimizing their occurrence. A recent international consensus has established standardized diagnostic criteria based on clinical, microbiological, radiological, and histopathological findings. Prevention is the top priority and involves a thorough preoperative risk assessment, along with glycemic control, nutritional optimization, and management of comorbidities, as well as intraoperative and postoperative measures such as appropriate antibiotic prophylaxis, surgical site antisepsis, and meticulous wound care. A multidisciplinary approach involving orthopedic surgeons, infectious disease specialists, and microbiologists is crucial for successfully reducing the burden of fracture-related infections.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Personalized Approaches to Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies in Periprosthetic Fracture-Related Infections (PFRIs): Case Series and Literature Review
Marianna Faggiani, Marco Zugnoni, Matteo Olivero, Salvatore Risitano, Giuseppe Malizia, Silvia Scabini, Marcello Capella, Stefano Artiaco, Simone Sanfilippo, Alessandro Massè
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2025; 15(12): 576. CrossRef - Pathogen-Specific Risk for Iterative Surgical Debridement in Orthopedic Infections: A Prospective Multicohort Analysis
Flamur Zendeli, Anna Jędrusik, Raymond O. Schaefer, David Albrecht, Michael Betz, Felix W. A. Waibel, Tanja Gröber, Nathalie Kühne, Sören Könneker, İlker Uçkay
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(24): 8750. CrossRef
- Personalized Approaches to Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies in Periprosthetic Fracture-Related Infections (PFRIs): Case Series and Literature Review
- 6,756 View
- 274 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Article
- Comparison of Results between Minimally Invasive Plate Fixation and Antegrade Intramedullary Nailing of Recon-Type in Low-Energy Injury Distal Femoral Shaft Fractures
- Hong Moon Sohn, Gwangchul Lee, Ba Rom Kim, Jung Soo Oh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(2):87-94. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.2.87
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study compared the outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis and antegrade intramedullary nailing for low-energy fracture of the distal femoral shaft.
Materials and Methods
A study was conducted on 30 patients who underwent surgery for low-energy fractures of the distal femoral shaft between January 2016 and April 2022. The study compared 15patients who underwent minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (Group P) with 15 patients who underwent recon-type antegrade intramedullary nailing (Group N). We evaluated intraoperative blood loss, operative time, C-arm exposure time, bone density, final union status, anatomical reduction, and clinical evaluation. The complications were also examined, and statistical analysis was conducted to compare the two groups.
Results
The blood loss, surgery time, and C-arm time were similar in the two groups. The radiographic assessments and clinical evaluations were also similar in the two groups. The clinical results showed no difference between the groups. Group N had one case of nonunion and one case of delayed union, while Group P had one case of nonunion and one case of peri-prosthetic fracture.
Conclusion
Antegrade intramedullary nailing of the recon-type demonstrated comparable results to minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Hence, antegrade intramedullary nailing of the recon-type, which enhances stability by fixing the entire femur and providing additional fixation in the distal portion, is deemed appropriate for treating distal femoral shaft fractures.
- 788 View
- 17 Download

Review Articles
- Fluid Management of Trauma Patients
- Yo Huh, Jaeri Yoo
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(2):69-76. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.2.69
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fluid therapy is one of the fundamental treatments for the management of trauma patients. Apart from supplementary hydration, fluid therapy is also applied for resuscitation. Especially in cases of hypovolemic shock due to bleeding, fluid therapy needs to be carefully adjusted to correct the shock. The importance of fluid therapy is increasing not only in resuscitation and treatment after hospitalization but also in pre-hospital care. Fluid therapy needs to be adjusted based depending each patient’s volume status. The various classifications of fluids include crystalloid solutions, glucose solutions, and colloid solutions. Although not included as a fluid therapy, blood transfusion is increasingly gaining more importance than fluid therapy in unstable trauma patients. Early appropriate fluid therapy is crucial in the treatment of hemodynamically unstable patients such as multiple trauma and massive bleeding, whereas comprehensive fluid therapy should be applied by considering the characteristics of specific injuries such as fractures, vascular damage, and cerebral hemorrhage, as well as the age groups (children, the elderly, and pregnant women).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of the Eye Care Protocol in the Intensive Care Unit Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Kyu Won Lim, Shin Young Ha, In Soon Kang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2024; 54(3): 432. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of the Eye Care Protocol in the Intensive Care Unit Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- 2,044 View
- 83 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Crush Syndrome: Traumatic Rhabdomyolysis, Reperfusion Injury
- Yong-Cheol Yoon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(2):62-68. Published online April 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.2.62
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A crush injury causes damage to bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, and other tissues caused due to pressure. Crush syndrome is a reperfusion injury that occurs throughout the body after a crush injury and leads to traumatic rhabdomyolysis, in which muscle fibers are broken down. Owing to the decreased blood supply, inflammation, and changes in metabolic activity, fluids and electrolytes in the blood can move into tissues, causing hypovolemic shock. In addition, toxic substances resulting from cell destruction can circulate through the bloodstream, causing electrolyte imbalances, renal failure, arrhythmias, and cardiac arrest, with approximately 15% of patients with acute renal failure dying. The treatment for crush syndrome involves aggressive fluid therapy and correction of the electrolyte imbalances, while patients with acute renal failure may require dialysis. Surgical treatment may include debridement and irrigation of necrotic tissue, and fasciotomy is necessary to address compartment syndrome, a complication that may arise.
- 1,289 View
- 29 Download

Case Reports
- Extensive Multiple Morel-Lavallée Lesions: A Case Report
- Kyu Dong Shim, Won Rak Choi, Ye Soo Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(3):142-145. Published online July 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.3.142
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Morel-Lavallée is a rare lesion caused by post-traumatic soft tissue injury. It usually occurs around the greater trochanter, and it occurs very rarely in the lumbar region. It is often difficult to be diagnosed in the emergency room. Delayed diagnosis may result in the need for open surgery. The authors report a patient with extensive multiple Morel-Lavallée lesions in the thoracolumbar, buttock, and thigh after trauma and provide a literature review.
- 433 View
- 1 Download

- Acute Patellar Osteomyelitis in a Child after a Blunt Trauma: Case Report
- Hoe Jeong Chung, Doo Sup Kim, Jun Seop Yeom, Young Hwan Jang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(4):270-275. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.4.270
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Osteomyelitis of the patella is a very uncommon condition that occurs mostly in the pediatric population. In addition to its rarity, nonspecific and variable clinical presentations usually lead to postponement in making the correct diagnosis. Moreover, it is often missed as prepatellar bursitis or septic arthritis of the knee. Nonetheless making early diagnosis and initiating prompt treatment is most important to preventing this condition from becoming chronic. In this case report, the authors encountered this rare condition of the patella in a child that was first misdiagnosed with pyogenic arthritis or prepatellar bursitis of the knee. The delay in making the diagnosis led to intractable progression of the disease, and sequestrectomy was required to stabilize the condition.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Osteomyelitis of the Patella With Extension Into Parapatellar Soft Tissues in a Six-Year-Old Boy: A Case Report
Abdulla Abdelwahab, Faatimah Irfaanah Muzammil, Abdulla Nidal, Mason Alnouri, Sattar Alshryda
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Osteomyelitis of the Patella With Extension Into Parapatellar Soft Tissues in a Six-Year-Old Boy: A Case Report
- 800 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Article
- The Mid-Term Result after Osteosynthesis of Intra-Articular Fractures of Distal Femur
- Sam Guk Park, Jeong Jae Moon, Oog Jin Shon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(4):242-249. Published online October 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.4.242
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study was to evaluate the radiological and clinical mid-term results and the presence of post-traumatic osteoarthritis after osteosynthesis in patients under the age of 50 years undergoing osteosynthesis for distal femur intra-articular fractures (AO/OTA 33-B & C) from high-energy trauma.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between January 2008 and January 2013, a total of twenty-one patients with more than three years of follow-up were enrolled. Recovery of the alignment of the lower extremity, union period, and the presence of post-traumatic osteoarthritis were confirmed by follow-up radiographs. Clinically, the range of motion, pain on fracture lesion, and Knee Society score (KSS) were evaluated.
RESULTS
The average duration of union was 18.2 weeks (10-28 weeks), and the alignment of the lower extremity was within normal range in all patients. Seven patients showed post-traumatic osteoarthritis at the final follow-up after more than three years. The presence of post-traumatic osteoarthritis was associated with the classification of fractures, coronal plane fracture, and age. The average range of motion, knee score among KSS, and function score at the last follow-up were 128.7°, 86.1, and 85.1, all showing a greater improvement when compared with the one-year follow-up scores.
CONCLUSION
The mid-term result was radiologically and clinically satisfactory. Furthermore, only 33.3% of patients showed a slight progress of post-traumatic osteoarthritis, which critically effects the prognosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Incidence of nonunion after surgery of distal femoral fractures using contemporary fixation device: a meta‐analysis
Byung-Ho Yoon, In Keun Park, Youngwoo Kim, Hyoung-Keun Oh, Suk Kyu Choo, Yerl-Bo Sung
Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery.2021; 141(2): 225. CrossRef
- Incidence of nonunion after surgery of distal femoral fractures using contemporary fixation device: a meta‐analysis
- 681 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Article
- Reconstruction of a Traumatic Soft Tissue Defect
- Jong Woong Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(4):256-265. Published online October 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.4.256
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Soft tissue defect combined with an open fracture is a very challenging problem to the orthopaedic surgeon. Many complicated open fractures remain with soft tissue defect, chronic osteomyelitis, and sometimes terminate with major limb amputation. Soft tissue defect should be reconstructed as soon as possible, particularly when the bone, tendon, or neurovascular structures are exposed. Exposure for longer than a week significantly increases the risk of secondary infection and tissue necrosis. For the simple soft tissue defect, negative pressure wound closure technology has been introduced and many superficial wounds have been treated successfully using this method. For the more complicated wounds, many kinds of local flaps, pedicled flaps, muscle and fascisocutaneous flaps can be indicated according to the characteristics of the wounds. The free flaps including free vascularized bone graft can be considered as a final choice for the most difficult wound problems. In this article, various reconstruction strategies for soft tissue defect after traumatic open fracture are reviewed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by
- 834 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Articles
- Analysis of Missed Fractures in Polytrauma Patients
- Ki Chul Park, Hyun Uk Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(4):281-286. Published online October 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.4.281
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to determine the frequency of missed fractures in severe multiple trauma patients and to analyze any differences in treatment plan, after whole body bone scan.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From September 2012 to December 2013, 49 patients were confirmed to have multiple trauma with an injury severity score (ISS) of 16 or higher. Whole body bone scan was performed at an average of 15.7 days (7-25) after injury. Missed fractures were diagnosed according to physical examination and additional radiologic reports. Locations and patterns of missed fractures were analyzed. We evaluated any differences in treatment plan after the diagnosis of missed fractures.
RESULTS
Missed fractures were diagnosed in 14 patients (16 cases) on the whole body bone scan. The most frequent location was the knee (three cases), followed by rib, clavicle, carpal bone, and foot. Seven cases were occult fractures, five cases were undisplaced fractures and four cases were displaced fractures. Conservative treatment was administered in 15 patients and surgery was necessary in one patient.
CONCLUSION
Delayed or missed diagnosis of fractures occurred frequently in patients of multiple trauma with a high ISS. Whole body bone scan appears to be effective in finding missed fractures in the whole body. Definitive assessment should be supplemented after initial trauma care in order to reduce the rate of missed fractures.
- 657 View
- 4 Download

- Injury Severity and Patterns of Accompanying Injury in Spinal Fracture
- Hun Park, Kyung Jin Song, Kwang Bok Lee, Joo Hyun Sim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(3):203-207. Published online July 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.3.203
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To examine the relationship between injury severity and patterns of associated injury in spinal fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From March 2004 to March 2010, a retrospective study was conducted on 291 patients who had undergone surgeries due to spinal fractures. Spinal fractures were categorized as upper cervical, lower cervical, thoracic, thoracolumbar, and lumbar region, and the severity of fracture was measured using the Abbreviated Injury Scale and Injury Severity Score (ISS). We evaluated the correlation between the fracture site and the incidence and injury severity of the associated injury, and compared the neurologic damage according to the presence/absence of the associated injury.
RESULTS
Spinal fracture occurred in the thoracic (43.5%) and lower cervical (30.0%) levels, and associated injury developed in 134 patients (47%). The area of associated injury was in the extremity (41.2%), thorax (25.5%), head, neck, and face (21.9%). Lower cervical fracture (34.5%) had a lower prevalence than thoracic (81%) and lumbar fracture (61%). The average ISS of the associated injury was 17.14 for the thoracic fracture, 12.30 for the lower cervical fracture, 8.7 for the thoracolumbar fracture and 5.69 for the lumbar fracture. Neurologic damage was highly frequent in the lower cervical fracture and included 54 patients (62.1%) and was less frequent in the upper cervical fracture, which included 7 patients (17.9%) (p=0.032).
CONCLUSION
Although the associated injury was less frequent in the lower cervical spine among the spinal fractures that underwent surgical treatment, there was a high risk of neurologic damage in the case of associated injury; therefore, there is a need to pay special attention to patients that suffer damage in this area. In addition, since the degree of the associated injury in the thoracic and lower cervical fracture is significant, an appropriate management strategy for the associated injury must be considered. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Clinical Effects of Complex Korean Medicine Treatment in Patients with Cervical Spine Fracture Caused by Traffic Accident: A Report of 2 Cases
Si-Hoon Han, Gi-Eon Lee, Kyeong-Sang Jo, Da-Young Byun, Min-Seok Oh
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2018; 28(2): 113. CrossRef - Clinical results of early stabilization of spine fractures in polytrauma patients
Ki-Chul Park, Ye-Soo Park, Wan-Sik Seo, Jun-Ki Moon, Bo-Hyun Kim
Journal of Critical Care.2014; 29(4): 694.e7. CrossRef
- The Clinical Effects of Complex Korean Medicine Treatment in Patients with Cervical Spine Fracture Caused by Traffic Accident: A Report of 2 Cases
- 706 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Is CT Angiography a Reliable Tool for Diagnosis of Traumatic Vessel Injury in the Lower Extremities?
- Jong Hyuk Park, Kwang Bok Lee, Hyuk Park, Jun Mo Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(1):26-30. Published online January 31, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.1.26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Computed tomographic (CT) angiography is the first choice of diagnosis in traumatic vessel injury in the lower extremities, replacing angiography. The purpose of this study was to investigate the clinical reliability of CT angiography through a retrospective study.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Seventeen patients underwent CT angiography before surgery for traumatic vessel injury in the lower extremities from 2009 to 2010, and a comparative analysis of operative findings in all patients with a positive predictive value and sensitivity were measured.
RESULTS
In all patients, 16 artery ruptures and 1 compartment syndrome occurred. In 15 artery ruptures, preoperative findings of CT angiography and surgical findings were consistent, and the positive predictive value was 93.8%. One patient with posterior tibial artery rupture was revealed as normal in CT angiography; thus, sensitivity was 93.8% (15/16 patients), and the accuracy rate was 88.2% (15/17 patients).
CONCLUSION
Though CT angiography is a reliable tool for diagnosis in traumatic vessel injury in the lower extremities, a more invasive test will be needed, especially peripheral angiography or diagnostic exploration, in cases of relatively small vessel injuries around the ankle or compartment syndrome because of low accuracy.
- 484 View
- 0 Download

Case Report
- Traumatic Simultaneous Bilateral Hip Dislocation in the Elderly Patient: A Case Report
- Koing Woo Keon, Sang Bong Ko
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(4):335-338. Published online October 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.4.335
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Traumatic simultaneous bilateral hip dislocation is reported rarely, but the most of them are limited in young patients. The authors managed the elderly patients whose both hip was dislocated traumatically, simultaneously and who didn't have any other underlying disease and other associated fracture - femur, hip joint and pelvis, with a review of the relevant literature.
- 413 View
- 1 Download

Original Articles
- Arthroscopic Repair for Traumatic Peripheral Tear of Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex
- Seung Ju Jeon, Chan Sam Moon, Ho Seung Jeon, Haeng Kee Noh, Sung Hwan Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(4):330-334. Published online October 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.4.330
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To assess the results of an arthroscopic repair for traumatic peripheral tears of triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC, Palmer type Ib).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
10 patients with traumatic peripheral TFCC tear were treated with outside-in technique with arthroscope and evaluated with an average follow-up of 19 months (range, 15 to 28 months). The clinical outcomes were assessed with investigation of pain, range of motion, grip strength, return to job and patient's satisfaction.
RESULTS
The arthroscopic repair of traumatic peripheral TFCC tear resulted in significant pain relief and increase in functional ability of wrist, that is, 8 excellent, 1 good and 1 fair results. At last follow-up, the average of flexion was 79° (range 76~86°), average of extension was 78° (range 70~84°), average pronation was 85° (range 75~91°) and average supination was 87° (range 79~92°). Nine patients except one were back to their original job.
CONCLUSION
Arthroscopic repair of traumatic peripheral TFCC tear could be used for pain relief and increase in functional ability of wrist.
- 460 View
- 1 Download

- Result of Early Active Range of Motion Exercise after Bankart Repair of Traumatic Anterior Instability
- Haeng Kee Noh, Jong Woong Park, Jung Il Lee, Jung Ho Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(1):53-57. Published online January 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.1.53
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate prospectively the results of early active exercise after open Bankart repair of traumatic anterior shoulder instability.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January, 2001 to June, 2003, 26 patients who were followed up at least 1 year after open Bankart repair for traumatic anterior shoulder instability were evaluated. Average age was 23.9 years old (range, 19~43) with 24 males and 2 females. We evaluated them using the functional shoulder scores (modified Rowe score, ASES score), range of motion, VAS pain scale, patient's subjective satisfaction and return to unlimited daily living activity.
RESULTS
The shoulder functional scores increased significantly. At last follow up, the final range of motion were flexion in average 5° deficit in comparison to normal side, external rotation in average 10o deficit, and internal rotation in T9. The patient's subjective satisfaction was good in 2l patients (81%). Return to unlimited daily activity was possible in 23 patients (88.5%), and 19 patients (73%) rejoined to sports activity before injury. There were complications including anterior recurrent subluxation in 1 case, weakness of subscapularis muscle in 1 case.
CONCLUSION
In traumatic anterior shoulder instability, early active range of motion exercise after open Bankart repair does not decrease shoulder stability. Early exercise can be useful for returning to previous level of sports activity in young active patients.
- 565 View
- 3 Download

Case Reports
- Nontraumatic Myositis Ossificans with an Unusual Location: Case Report
- Kwang Suk Lee, Sang Bum Kim, Dae Hee Lee, Hyung Joon Cho
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(4):481-484. Published online October 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.4.481
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Myositis Ossificans is known to be a benign heterotopic pseudomalignant bone formation in muscle and other soft tissue. When it is revealed as a localized form, 75% of the cases are associated with significant blunt trauma. We report a rare case of a nontraumatic ossificans in the lower leg of a 59-year-old woman, which has been spontaneously developed for 15 years.
- 345 View
- 0 Download

- Neglected Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation in a Crutch-walking Patient: A Case Report
- Yong Min Kim, Hyun Chul Shon, Dong Soo Kim, Eui Sung Choi, Kyung Jin Park, Se Hyuk Im
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(4):474-477. Published online October 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.4.474
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Traumatic posterior hip dislocation should be reduced emergently, but diagnosis could be delayed in a patient with head trauma or in developing countries. We have experienced neglected posterior hip dislocation for three months in a crutch-walking patient who had ipsilateral tibia fracture and alert mentality. Open reduction followed by six-weeks skeletal traction was performed. At one year follow-up, the reduced hip showed good range of motion with no evidence of avascular necrosis.
- 470 View
- 1 Download

Original Articles
- Clavicle Fracture in Newborn
- Kyeong Seop Song, Byeong Mun Park, Young Hun Kang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(1):55-58. Published online January 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.1.55
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to identify the incidence of clavicle fracture in birth trauma associated with delivery, fetal presentation, birth weight and to identify the difference of the prognosis of clavicle fracture when immobilization was performed or not.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Among the 12,738 live births from March 1996 to December 2000, we reveiwed retrospectively the medical records and radiographs of 39 cases of clavicle fracture which were followed for more than 6 months. Statistical analysis was measured P-value. Except 11 cases that diagnosis was delayed, 27 cases were treated with figure of 8-bandage, and 1 case, which was combined with humerus fracture, was treated with long arm cast.
RESULTS
Among 39 cases infants of clavicle fracture, 36 cases (0.57%) were delivered through vaginal delivery, 3 cases (0.04%) through ceasarean section. Fetal presentations were cephalic presentation in 29 cases, shoulder dystocia in 8 cases, breech presentation in 2 cases. The mean birth weight was 3.8 kg, the high prevalence (8.5%) was identified on large birth weight infants more than 4 kg (p<0.05). The fracture site was proximal portion in 12 cases, middle portion in 27 cases and right clavicle in 24 cases, left clavicle in 13 cases and both clavicle in 1 case. The combined injuries were the brachial plexus palsy (2 cases), skull fracture (1 case) and cephalhematoma (1 case). Finally all cases of clavicle fracture were shown radiographically bony union within 3 weeks.
CONCLUSION
The newborn clavicle fractures were remarkably low incidence in cesarean section delivery and were easily neglected, and were detected accidentally on simple chest X-ray that was performed for upper respiratory infection. As a conclusion, it is necessary of screening test through careful physical examination and X-ray interpretation.
- 566 View
- 12 Download

- Modified Phemister Operation for Acromioclavicular Dislocation
- Jin Yung Park, Gun Nam Kim, Byung Sam Min, Moon Jib Yoo
- J Korean Soc Fract 2001;14(3):456-462. Published online July 31, 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2001.14.3.456
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical results after modified Phemister operation for complete dislocation of acromioclavicular joint.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty-seven cases of Fifty-three cases complete dislocation of acromioclavicular joint which were treated modified Phemister operation, follow up for at least one year, were evaluated. After operation, applied Kenny-Howard brace for six weeks and removed the inserted pins at ten to twelve weeks postoperatively. The ROM exercise was started at postoperative six weeks and meticulous ROM exercise was begun at pin removal. The clinical results were evaluated with range of movement, comparision of the coracoclavicular distance after surgery with that of follow up, and complications.
RESULTS
The range of motion were forward elevation 150 degree, external rotation 71 degree, external rotation at 90 degree abduction 77 degree, and internal rotation T8. The comparision of coracoclavicular distance after surgery(0,6mm) with that of follow up(1.0mm) showed no significant ligament laxity. The complication were subluxation in 2 cases, heterotrophic calcification in 3cases, broken K-wire in 2cases, pin site infection in 7cases and distal clavicle osteolysis in 3cases, which were healed at follow up radiographically.
CONCLUSION
To prevent of redislocation of acromioclavicular joint, we tried to insert the pin during relatively long period for sufficient healing of ruptured coracoclavicular ligament. Although immobilization period was relatively long period, clinical results were good.
- 454 View
- 1 Download

Case Report
- Atraumatic Avulsion Fracture of Calcaneal Tuberosity in a Patient with Peripheral Neuropathy: A Case Report
- Woo Chun Lee, Ki Heon Nam
- J Korean Soc Fract 2001;14(1):85-90. Published online January 31, 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2001.14.1.85
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Atraumatic calcaneal fractures associated with neurological abnormalities have been reported by several authors, and most of them are associated with diabetes. Chronic alcoholism is also a cause of neurological abnormality and neuropathic arthropathies associated with chronic alcoholism were reported. However we could not find any report of atraumatic calcaneal avulsion fracture associated with chronic alcoholism. We have treated a calcaneal avulsion fracture in a chronic alcoholic patient with open reduction and internal fixation, and the result was not satisfactory. We suggest that conservative treatment is better for the atraumatic calcaneal avulsion fracture in a chronic alcoholic patient with severe osteoporosis and neurological abnormalities.
- 2,428 View
- 0 Download

Original Articles
- Musculo-skeletal trauma of the children
- Ha Yong Kim, Kun Young Park, Kwang Won Lee, Jae Hoon Ahn, Jin Sup Yeom, Won Sik Choy
- J Korean Soc Fract 2001;14(1):128-134. Published online January 31, 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2001.14.1.128
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The aim of study was to analyze the patterns of musculo-skeletal trauma of the children.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From 1997 to 1999, the included for the study were 108 children, who had been admitted for the orthopedic treatment and followed-up. The analysis were done as for 1) children s biological characteristics, 2) the situations of trauma, 3) causes of trauma, 4) types of trauma and 5) locations of fractures.
RESULTS
The average age was 8.5 years at the time of trauma. Sixty cases (56%) were between 5 and 9 years old. Boys were 3 times more common than girls. Second children (61cases, 57%) were more prone to trauma. Half of trauma took place between July and October, and one third of trauma (36 cases, 33%) happened on the street. Ninety eight children (91%) were admitted due to fracture, and supracondyle fracture of humerus was the most common cause(48 cases).
CONCLUSION
Many of accidents could be attributed to children's mischievous play resulted from curiosity and freedom of thought. For the prevention of these accidents, therefore, environment should be restructured from the point of child's view, and not only the design of facility itself but also proper management and education on the facilities should be taken. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Pattern of Occurrence of Fractures in Children and Adolescents and Its Managements Based on the Database of the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service
Yong-Wook Kwon, Soon-Hyuck Lee, Hyun-Woo Kim, Jin-Ho Hwang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2014; 27(4): 308. CrossRef
- The Pattern of Occurrence of Fractures in Children and Adolescents and Its Managements Based on the Database of the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service
- 530 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Result Of Surgical Treatment Of The Femur Unstable Intertrochanteric Fracture Using Compression Hip Screw: Analysis Of Effect Of Degree Of Force On Trauma And Degree Of Osteoporosis
- Ki Do Hong, Sung Sik Ha, Sang Weon Park
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(4):795-803. Published online October 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.4.795
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyise the effect of degree of force on trauma and degree of osteoporosis in femoral unstable intertrochanteric fracture's result of treatment using compression hip screw.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January 1993 to December 1997, 55 patients who were operated with compression hip screw and followed up for more than 1 year were devided into high and low energy injured group by the mechanism of the trauma and also devided low(gradeIV,V,VI) and high grade osteoporosis group(gradeI,II,III) by Singh's index. We analize and compare the result of treatment in each groups.
RESULTS
The averrage rate of mechanincal complication was 24%. The mechanical complication rate of the high grade osteoporosis group(34%) was higher than low grade osteoporosis group(9%)(p<0.05). The average subsidence of compression screw was 9.9mm and it shows significant difference between low(7.8mm ) and high grade osteoporosis group(11.5mm )(p<0.05). The average increased varus deformity of neckshaft angel during follow up was 3.8degrees and it shows singnificant defference between high energy injuried group(4.6degrees ) and low energy injuried group(2.7degrees)(p<0.05). No difference was seen in each groups for time of bone union(p>0.05). In view of functional recovery by Clawson's method, no difference between pre-injury and postoperative state was seen in 7 cases(22%) in high grade osteoporosis group and 13 cases(57%) in low grade osteoporosis group, thus worse functional recovery was seen in high grade osteoporosis group.
CONCLUSIONS
We observed higher mechanical complication rate, more compression screw subsidence and worse functional recovery in high grade osteoporosis group and more varus deformity in high energy injured group. Thus we need more attension to treatment and follow up in high energy injured, severe osteoporotic unstable intertrochanteric fracture.
- 414 View
- 1 Download

- Reconstruction of Neglected Traumatic Radial Head Dislocation in Children
- Dong Yeon Lee, Tae Joon Cho, In Ho Choi, Chin Youb Chung, Young Jin Sohn
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(4):1024-1032. Published online October 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.4.1024
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the clinical result of surgical reconstruction of the old traumatic radial head dislocation in children, and to delineate the optimal surgical procedure for it.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fifteen cases of the old traumatic radial head dislocation were included in this study, which had surgical reconstruction at the age of 15 years or less. Preoperative and postoperative clinical symptom, range of joint motion, and radiologic findings were reviewed. Reconstructions were performed by combination of various procedures, and the advantages and disadvanges of each procedures were analyzed.
RESULTS
All the preoperative complaints were relieved by the operation. In twelve cases out of 15, the radial head reduction was well maintained. The reasons for the loss of reduction were non-union of ulnar osteotomy site, and the neglected angular deformity at the proximal radius. Although forearm pronation was decreased in most cases, they did not affect most of the daily activities except in cases where the radioulnar osseocartilaginous bridge were complicated.
CONCLUSION
Our results justify the surgical reconstruction of neglected traumatic radial head dislocations in children. Complete clearing of radiocapitellar joint, accurate bony realignment and rigid fixation, appropriate annular ligament reconstruction, and temporary fixation with transcapitellar pin may ensure satisfactory result.
- 475 View
- 9 Download

Case Reports
- Neglected Unilateral Subluxation of Facet Joint in Lumbar Spine of Multiple Trauma Patient: A Case Report
- Ye Soo Park, Min Kun Kim, Jae Lim Cho
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(1):52-55. Published online January 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.1.52
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Unilateral dislocation or subluxation of a facet in lumbar spine is extremely rare, so it has been often neglected. The mechanism of injury is hyperflexion and distraction forces. As for the treatment of lumbar facet dislocation and subluxation, open reduction and internal fixation by the posterior approach has been recommended because the injuries are resistant to closed reduction and they may cause chronic instability. We report a case of neglected unilateral subluxation of facet joint in lumbar spine of multiple trauma patient, which was treated by open reduction and internal fixation with posterolateral fusion. In the multiple trauma patients, it is mandatory to the meticulous diagnosis and treatment.
- 487 View
- 4 Download

- Traumatic dislocation of hip in children: A Case Report of 30 Months Followup
- Soo Jae Yim, Yeon Cheol Jeong, Seung Ryool Yoon, Joong Geun Choi, You Sung Suh, Yon Il Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1999;12(2):361-364. Published online April 30, 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1999.12.2.361
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Traumatic hip dislocation in childhood is rare. Factors predisposing to abnormal results are delayed reduction and severe trauma. We experienced 8 year-old girl with traumatic posterior hip dislocation and treated with immediate closed reduction. At 30 months follow-up, our patient had good functional and good roentgenographic result with no posttraumatic arthritis or posttraumatic avascular necrosis. So we report this case with review of literature.
- 315 View
- 0 Download

- Traumatic Refracture : Report of 3 cases
- Byung Ill Lee, Young Hoon Cho, Jae Eung Yoo, Soo Kyun Rah
- J Korean Soc Fract 1997;10(4):940-944. Published online October 31, 1997
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1997.10.4.940
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Traumatic refracture refers to a recurrence of a fracture by a major trauma, after it had gained complete union from an earlier rracture through internal fixation. We report 3 cases of our experience in this relatively rare injury of long bone.
- 332 View
- 0 Download

- Traumatic Bilateral Anterior and Posterior Dislocations of the Hips with a Unilateral Acetabular Posterior Column Fracture (Thompson and Epstein type IV): A Case Report
- Young Sik Lee, Jung Dae Oh, Jin Tae Choi, Gyeong Rin Lim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1997;10(4):766-771. Published online October 31, 1997
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1997.10.4.766
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A rare case of traumatic bilateral anterior and posterior dislocations of the hips occurred by passenger traffic accident . The right hip was dislocated posterosuperior to the right acetabulum with a linear acetabular posterior column tracture(Thompson and Epstein type IV) and left hip was dislocated anteroinferior to the left acetabulum(modified classification of Epstein type II A). The dislocations were successfully reduced by the Bigelows method for the right hip and the reverse Bigelows method for the left hip, and 4 weeks of Bucks traction was applied. He was able to return to full activity after 4 months. There was no sign of avascular necrosis at 3 years and 11 months follow-up.
- 392 View
- 1 Download

- Simultaneous Asymmetric Bilateral Traumatic Hip Dislocation: A Cases Report
- Byung Ill Lee, Bo Weon Jeong, Jae Eung Yoo, You Sung Suh, Soo Kyun Rah, Chang Uk Choi
- J Korean Soc Fract 1996;9(1):225-228. Published online January 31, 1996
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1996.9.1.225
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hip dislocation represents 2 to 5% of all joint dislocations. Bilaterat dislocation of the hip joints is reported about 1.25% of all cases fo hip dislocations and therefore 0.025 to 0.050% of all joint dislocations. Dislocations in which one hip dislocates anteriorly and the other posteriorly are even rarer. Of all traumatic bilateral hip dislocations, bilateral simultaneous anterior and posterior dislocations in 40% of cases. This paper is a case report of a traumatic bilateral anterior and posterior dislocation of hips in a 24 year-old man injured by motor vehicle accident as a passenger. The patient was treated by means of closed reduction, traction and physical therapy. We report such a case.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Traumatic Bilateral Anterior Hip Dislocation: A Case Report
Sung-Taek Jung, Hyun-Jong Kim, Myung-Sun Kim, Young-Jin Kim, Sang-Kwan Cho
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2008; 21(1): 62. CrossRef
- Traumatic Bilateral Anterior Hip Dislocation: A Case Report
- 545 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- Medical Certiflcate in Orthopedic Trauma Patient: reasonable duration of expected treatment
- Bu Hwan Kim, Yong Kyun In
- J Korean Soc Fract 1995;8(3):675-677. Published online July 31, 1995
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1995.8.3.675
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Medical certificates in orthopedic trauma patients should be issued cautiously because of the important roles of the documents to the offenders and victims of accidents. But in real practice, we can find only a few references which can help doctors to decide the "duration of expected treatment" in trauma patients. A pamphlet issued by Korean Orthopedic Association "Guide to the medical certification in trauma patient" helped us a lot but it was published too long ago and had a few problems, so we suggests some ideas for revising the pamphlet.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- PARK Formula Can Replace "Guide to Medical Certificate" Published by Korean Medical Association in Deciding the Treatment Duration
Chan Yong Park, Kwang Hee Yeo, Sora Ahn
Journal of Trauma and Injury.2018; 31(2): 58. CrossRef
- PARK Formula Can Replace "Guide to Medical Certificate" Published by Korean Medical Association in Deciding the Treatment Duration
- 561 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- A Clinical Study of Traumatic Posterior Fracture-Dislocation of the Hip: 13 cases with operative treatment
- Won Yoo Kim, Jin Young Kim, Kun Young Park, Chang Boon Jeong
- J Korean Soc Fract 1994;7(2):457-464. Published online November 30, 1994
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1994.7.2.457
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Traumatic Posterior hip fracture-dislocation is uncommon injury, which induces the traumatic arthritis, joint contracture and avascular necrosis of the femoral head as a late complication. Among 23 patients with traumatic fracture-dislocation of the hips, 13 patients who underwent operative intervention were reviewed retrospectively: all patients were men ranging from 24 to 59 years old. A dash-board injury of car accident was leading cause of the traumatic dislocation in this series(9 cases, 64%). Associated injuries were found in 11 cases(84%). In follow-up ranging from 12 months to 36 months(averge, 18 months). Ten were treated by closed reduction; 6, by closed reduction followed by subsequent open reduction and internal fixation for unstable fracture of the acetabulum; 3, by primary open reduction; and 4, delayed open reduction. The results according to the Epstein and Thompson clinical criteria for evaluating results were good at 5 of 6 patients treated by closed reduction followed by open reduction for acetabular fracture. It was concluded that early closed reduction followed by open anatomic reduction with removal of all loose fragments of bone and cartilage and restoration of stability by internal fixation of the fracture of the acetaulum offers the best prognosis.
- 340 View
- 0 Download

- Conservative Treatment of Ligamentous Injury of Knee in Head Trauma Patients
- Joon Young Kim, Young An Choi, Young Chul Choi, Bo Seok Kong
- J Korean Soc Fract 1989;2(1):42-48. Published online June 30, 1989
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1989.2.1.42
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Operative treatment has been used in unstable ligamentous imjury of knee joint. We experienced three cases of ligamentous injury of knee that was accompained with head trauma and other organ injury. Despite of sugical candidate, we did only conservative treatment due to poor general condition and difficulty of anesthesia. The result was realtively better than we expected. We reported these cases.
- 373 View
- 0 Download

- Popliteal Artery Injuries Associated with Trauma Around the Knee
- Myung Chul Yoo, Chung Soo Han, Kye Lim Lee, Moon Hwan Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 1989;2(1):34-41. Published online June 30, 1989
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1989.2.1.34
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Between Jan. 1980 and Dec. 1987, 47 cases in 44 patients with politeal artery injury associated with trauma around the knee joint were managed at Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, KMC. Authors analysed the diagonstic methods, operations with its results and prognostic factors, and the results were as follows: 1. The incidence was 3%(44/1473) from Jan. 1980 to Dec. 1987 2. 14 cases of 19 cases, who underwent the vascular surgery, were survived(74%) and further amputations were applied to failed 5 cases. 3. Doppler flowmeter was considered as very useful diagnostic tool because of simplicity, safety, and accuracy, therefore angiography was not necessary in all cases. 4. The length of ischemic time and the amount of associated soft tissue damage were considered as important prognostic factors. 5. Vein graft was considered as good operative technique, but thrombectomy alone was not enough method for politeal artery injury. 6. ligament repair was not always necessary in treatment of popliteal artery injury associated dislocation of knee. 7. Prophylatic decompression was necessary in all cases after vascular surqery and fibulectomy fasciotomy was considered as outstanding technique.
- 351 View
- 0 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


