Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
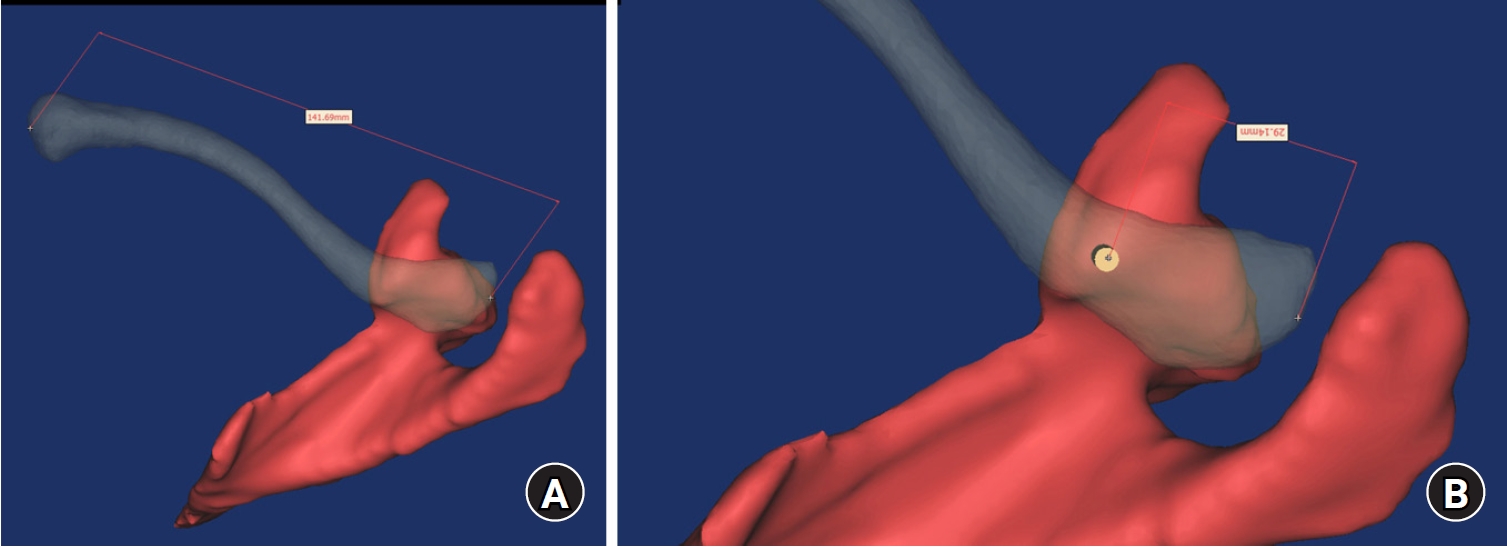
- Computational simulation of coracoclavicular screw insertion through the superior distal clavicular plate for clinical applications in Korean cadavers
- Hyung-Lae Cho, Ji Han Choi, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):143-151. Published online July 22, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00122
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The study was conducted to determine the practical area for inserting the coracoclavicular (CC) screw through the plate by analyzing three-dimensional (3D) shoulder models featuring virtually implanted, actual-size plates and screws.
Methods
Ninety cadaveric shoulders (41 males and 49 females) underwent continuous 1.0-mm slice computed tomography scans. The data were imported into image-processing software to generate a 3D shoulder model, including the scapula and clavicle. The overlapping area between the clavicle and the horizontal portion of the coracoid process (horizontal portion_CP) was analyzed in the cranial view. A curved pelvic recon plate was virtually placed on the upper surface of the distal clavicle, and an actual-size (3.5 mm) CC screw was inserted through the plate.
Results
The distal clavicle directly overlapped with the horizontal portion_CP in the vertical direction. The overlapping area was sufficient to place the 3.5 mm and 4.5 mm-sized screws. In all shoulder models, the CC screw could be inserted through the plate into the vertical direction, with an average length of 35.5 mm (range, 26.2–62.5 mm; standard deviation, 1.2 mm). In 87 models, the CC screw was inserted through the third hole from the lateral end of the plate. Two models were inserted through the second hole, and one model through the fourth hole.
Conclusions
The upper surface of the clavicle has sufficient overlapping area to place CC screws through the plate in the vertical direction in the corresponding hole. Supplemental CC screw fixation through the plate can be performed without additional or special equipment. Level of evidence: IV
- 670 View
- 22 Download

- Three-Dimensional Analysis of the Morphological Features in the Femur of Atypical Fracture and Practical Implications of Intramedullary Nailing
- Yong Uk Kwon, Kyung-Jae Lee, Joo Young Choi, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(2):87-95. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.2.87
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study analyzed the morphological features of the contralateral femur without an atypical fracture by constructing a three-dimensional model with an actual size medullary canal.
Materials and Methods
Lateral and anterior bowing of the shaft were measured for 21 models, and the shape of the medullary canal was analyzed. To eliminate the projection error, the anteroposterior (AP) femur was rotated internally to the extent that the centerline of the head and neck, which is the ideal position of cephalomedullary nail screw, was neutral, and the lateral femur matched the medial and lateral condyle exactly.
Results
The lateral bowing and anterior bowing was an average of 5.5° (range, 2.8°-10.7°; standard deviation [SD], 2.4°) and 13.1° (range, 6.2°-21.4°; SD, 3.2°), respectively. In the area where lateral bowing increased, the lateral cortex became thicker, and the medullary canal was straightened. On the lateral femur, the anterior angle was increased significantly, and the diameter of curvature averaged 1,370.2 mm (range, 896-1,996 mm; SD, 249.5 mm).
Conclusion
Even if the anterolateral bowing increases in the atypical femur, the medullary canal tends to be straightened in the AP direction. So, it might be considered as a reference to the modification of an intramedullary nail to increase the conformity.
- 483 View
- 5 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 First
First Prev
Prev


