Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
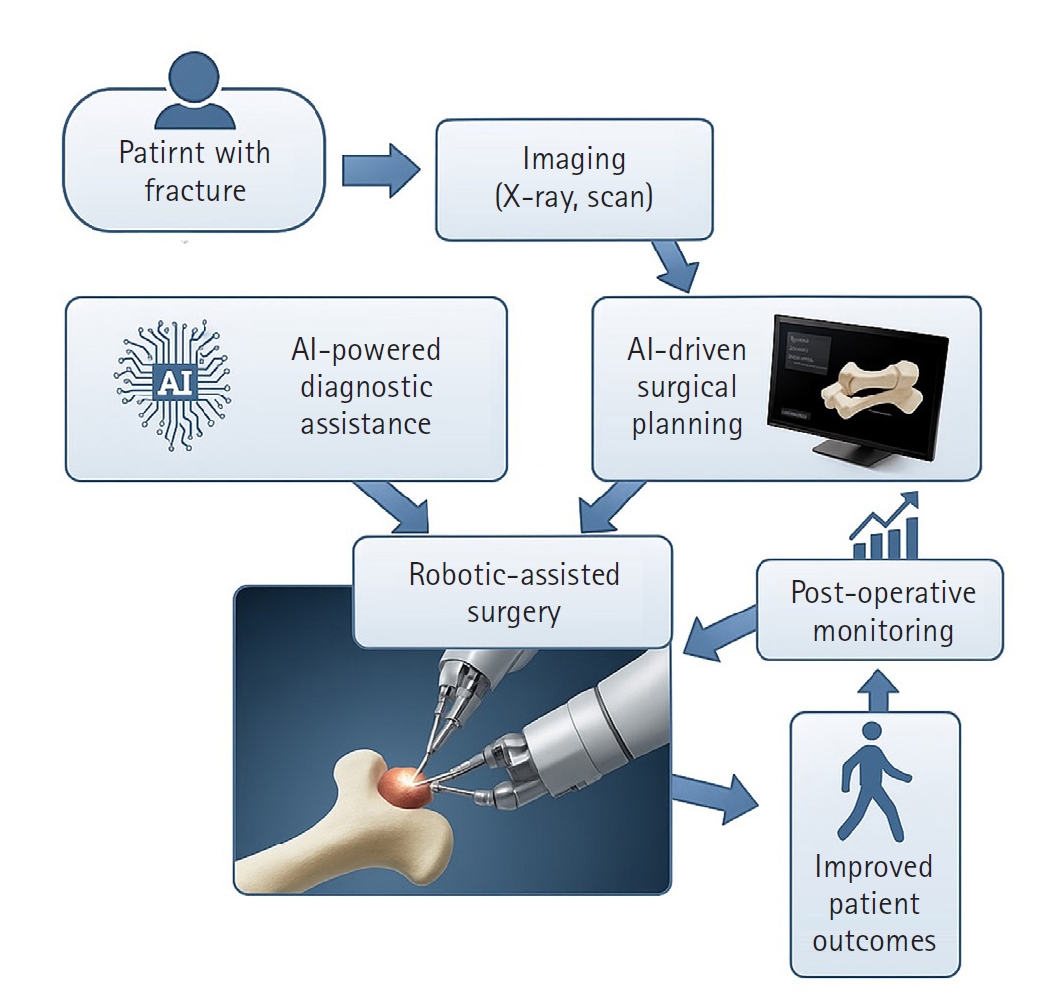
- Innovative applications of artificial intelligence in orthopedics focusing on fracture and trauma treatment: a narrative review
- Chul-Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):178-185. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00283
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Artificial intelligence (AI) is bringing about transformative changes in orthopedic surgery, with its potential being particularly prominent in the field of fracture and trauma treatment. This review explores the current applications and future prospects of AI-driven surgical planning and simulation, robot and image-based navigation surgery, and image-assisted diagnostic technologies. Robotic assistance in orthopedic surgery, which was initially applied to improve accuracy in component implantation for knee and hip arthroplasty and to achieve high precision in spinal screw placement, has recently expanded its use to include accurate, minimally invasive reduction of pelvic fractures. In diagnostics, AI aids in the early prediction and classification of ambiguous fractures in various anatomical regions—for example, detecting shoulder or hip fractures, identifying incomplete atypical femur fractures, and classifying femoral neck fractures—through X-ray image analysis. This improves diagnostic accuracy and reduces medical costs. However, significant challenges remain, including high initial costs, steep learning curves, a lack of long-term studies, data bias, and ethical concerns. Continued research, interdisciplinary collaboration, and policy support are crucial for the widespread adoption of these technologies.
- 968 View
- 2,147,483,661 Download

Original Articles
- Risk Factors of Fixation Failure in Femoral Neck Fractures
- Sung Hyun Yoon, Kyu Beom Kim, Hyung Jun Lee, Kyung Wook Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(4):118-124. Published online October 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.4.118
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Internal fixation after a femoral neck fracture (FNF) is one of the conventional treatment options for the young and active elderly patients. However, fixation failure of internal fixation is a probable complication. The treatment of fixation failure after a primary internal fixation of the FNF remains a challenge.
Materials and Methods
Between July 2002 and March 2017, 83 patients who underwent internal fixation after FNF were retrospectively analyzed. Radiological assessments, including Pauwels’ angle, fracture level, reduction quality, and bone union, were measured, preoperatively and postoperatively. Moreover, intraoperative variables such as time to surgery, surgical time, and estimated blood loss were also evaluated.
Results
The patients were divided into the fixation failure and the non-failure groups. Among the 83 patients, 17 cases (20.5%) of fixation failure after the primary internal fixation of the FNF were identi-fied. When comparing the two groups according to the radiographic data, Pauwels’ angle and the reduction quality based on Garden’s angle showed significant differences (p<0.001). Moreover, when comparing the intraoperative variables, unlike the surgical time and estimated blood loss, significant differences were noted in the time interval from injury to surgery and specifically in whether the surgery was performed within 12 hours after injury (p<0.001).
Conclusion
Pauwels’ angle, reduction quality, and time to surgery are the major factors that can predict the possibility of internal fixation failure of the FNF. Early and accurate anatomical reduction is needed to decrease complications after the internal fixation of the FNF.
- 2,637 View
- 37 Download

- Outcomes of Minimally Invasive Surgery in Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures: Sanders Type III, Joint Depressive Type Calcaneal Fracture
- Je Hong Ryu, Jun Young Lee, Kang Yeol Ko, Sung Min Jo, Hyoung Tae Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(3):85-94. Published online July 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.3.85
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
To evaluate the radiologic and clinical outcomes of a minimally invasive technique using the tarsal sinus approach in the management of Sanders type III, joint depressive type calcaneal fractures.
Materials and Methods
Between July 2011 and September 2019, data of 29 patients who underwent a minimally invasive procedure with the sinus tarsi approach for Sanders type III joint depressive intra-articular calcaneal fractures, and were followed up for more than 1 year were analyzed. We evaluated the radiologic outcomes by assessing the radiologic parameters (Böhler angle, Gissane angle, calca-neal length, calcaneal height, calcaneal width). We also evaluated the clinical outcomes based on the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) ankle-hindfoot score and the complications associated with the technique.
Results
The radiological results showed an improvement in the Böhler angle from 2.5° to 18.6° and the Gissane angle from 132.4° to 119.1° after the operation. The mean AOFAS score during the clini-cal evaluation was 79.5. We observed 13 cases of posttraumatic arthritis, 1 case of subtalar arthrodesis, and no case of wound complication.
Conclusion
Minimally invasive technique for Sanders type III joint depressive calcaneal fractures resulted in relatively satisfactory radiologic and clinical outcomes. Open reduction and internal fixation through the sinus tarsi approach reduce complications including wound problems. This approach offers satisfactory results without long-term complications.
- 564 View
- 2 Download

- Comparison of Surgical Outcomes for Lisfranc Joint Injuries: Dorsal Bridge Plating versus Transarticular Screw versus Combination
- Ba Rom Kim, Jun Young Lee, Sung Hun Yang, Seung Hyun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(1):17-24. Published online January 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.1.17
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
In Lisfranc joint injury, the traditional treatment has been open reduction and internal fixation with a transarticular screw. Despite this, additional complications, such as damage to the articular surface and breakage of the screw, have been reported. Therefore, this study compared the clinical and radiological outcomes of dorsal bridge plating with those of transarticular screws and combination treatment in Lisfranc joint injury.
Materials and Methods
Among the 43 patients who underwent surgical treatment due to Lisfranc joint injury from June 2015 to March 2021, 40 cases followed for more than six months after surgery were analyzed, excluding three patients: one lost to follow-up, one had to amputate, and one expired. The radiological parameters were measured using the Wilppula classification in the last follow-up. The clinical outcomes were evaluated using the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) midfoot score.
Results
The AOFAS midfoot score, according to the surgical method, was significantly higher in the dorsal bridge plating (p=0.003). The radiological outcomes showed significantly better anatomical reduction when dorsal bridge plating was used (p=0.040). According to the Wilppula classification, the AOFAS midfoot score improved as the quality of anatomical reduction improved (p=0.018). Finally, the AOFAS midfoot score decreased as the number of column fixations increased (p=0.002). There were two complications: screw breakage in dorsal bridge plating and superficial skin necrosis in the combination treatment. Skin defects caused by necrosis improved after negative pressure wound therapy and split-thickness skin graft.
Conclusion
In treating Lisfranc joint injuries, open reduction and internal fixation by dorsal bridge plating can be an appropriate treatment option. Nevertheless, studies, such as long-term follow-up research, on complications, such as osteoarthritis, will be needed.
- 764 View
- 10 Download

Review Article
- Treatment of Scaphoid Fractures and Nonunions
- Wan-Sun Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(4):182-189. Published online October 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.4.182
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A scaphoid fracture is one of the most common types of wrist fractures, and if treatment is delayed, there is a high possibility of nonunion due to anatomical factors such as limited blood supply to the injured bone. Therefore, it is important to suspect a scaphoid fracture based on the mechanism of wrist injury and physical examination of the patient. A computed tomography scan or magnetic resonance imaging can also aid early diagnosis of the fracture. Stable acute fractures can be treated conservatively, but unstable fractures require surgical treatment, and percutaneous screw fixation is usually performed. Nonunions require bone grafts and are treated with non-vascularized bone grafts and screw fixation. However, if the nonunion is located at the proximal pole, a vascularized bone graft may be considered because there is a possibility of avascular necrosis. Pedicled vascularized and free vascularized medial femoral condyle bone grafts are mainly used in such cases. The treatment of a proximal pole nonunion with impaired blood flow remains controversial. There are conflicting opinions on whether a nonvascularized bone graft is sufficient or whether a vascularized bone graft is necessary.
- 692 View
- 6 Download

Original Article
- Assessment of Noncontiguous Posterior Malleolar Fractures in Distal One-Third Tibia Shaft Fractures with Proximal Fibula Fractures
- Dae-Geun Kim, Byung Hoon Kwack
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(3):103-108. Published online July 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.3.103
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Posterior malleolar fractures after intramedullary nail surgery rarely occur in distal tibia shaft fractures. The importance of preoperative ankle evaluation in preventing these fractures is also common knowledge. There are no studies in the literature on posterior malleolar fractures in distal onethird tibia shaft fractures except for distal metaphyseal tibia fractures to the best of our knowledge. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the incidence and radiological features of posterior malleolar fractures in distal one-third tibia shaft fractures with proximal fibula fractures.
Materials and Methods
Thirty-one patients diagnosed with distal one-third tibia shaft fractures with proximal fibula fractures from January 2016 to May 2021 were retrospectively reviewed. With the aid of plain radiographs and computed tomography (CT) scans, the fracture patterns of the tibia and fibula were classified according to the AO Foundation/Orthopedic Trauma Association (AO/OTA) classification, and posterior malleolar fractures were identified. The fracture pattern was classified according to the Haraguchi classification, and the angle between the bimalleolar axis and the posterior malleolar fracture line was measured when there was a posterior malleolar fracture.
Results
Out of the 31 distal one-third tibia shaft fractures with proximal fibula fractures, 16 cases (51.6%) had noncontiguous posterior malleolar fractures that were confirmed on a CT scan, while 3 cases (18.8%) were visible on initial plain radiographs. There was no statistically significant variation seen in the presence of a posterior malleolar fracture in the tibia (p=0.15) and fibula (p=0.87) fractures. According to the Haraguchi classification, there were 15 posterolateral-oblique fractures (Type I) and 1 medial-extension fracture (Type II), and the mean angle was 24.5°.
Conclusion
Noncontiguous posterior malleolar fractures occurred in approximately half of the distal one-third tibia shaft fractures with proximal fibula fractures, and a CT scan was considered necessary to diagnose posterior malleolar fractures before surgery
- 577 View
- 11 Download

Case Reports
- Rare Experience of Bilateral Femoral Neck and Shaft Fractures - A Case Report -
- DaeHyun Choe, Jae-Ho Lee, Ki-Chul Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(3):154-158. Published online July 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.3.154
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ipsilateral fractures of the femoral neck and shaft are relatively common injuries and accompany 2% to 9% of all femoral shaft fractures. On the other hand, it is extremely rare for these injuries to occur bilaterally. This paper reports the authors’ experience of a case with bilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures. The patient sustained multiple injuries, including liver laceration with hemoperitoneum, bilateral open fractures of the tibia, and bilateral femoral neck, and shaft fractures caused by a high-speed motor vehicle accident. Under the circumstances, damage-control orthopedic principles were applied, and external fixators were initially placed. After the patient’s general condition showed improvement, both femurs were fixed with a reconstruction nail. Fracture healing was achieved without complications, such as avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Despite the rare occurrence, this paper describes this case because these injuries must be managed with meticulous attention.
- 536 View
- 8 Download

- Heterotrophic Ossification after Aggressive Rehabilitation in Patients with Trauma: A Case Report
- Jae Ang Sim, Yong Cheol Yoon, Seung Hyun Baek
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(1):32-37. Published online January 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.1.32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Heterotrophic ossification (HO) is a reactive disease presenting the formation of mature lamellar bone in soft tissues. It is known to occur following surgery, soft tissue injury, or central nervous system anomalies. However, a definite cause has not yet been clearly addressed. During the process of approach, reduction, and fixation while conducting surgeries, partial injury of soft tissue is inevitable. Additionally, secondary injuries may be caused during the active and passive range of motion exercises that should be done for the recovery of joint motion after surgery. The authors experienced cases of HO that may occur during surgery and rehabilitation after surgery. The authors recognized that special care is required for patients complaining of severe pain during the early stage of rehabilitation immediately after surgery. This study aimed to reaffirm the principles of fracture treatment by reviewing the cases and to investigate the occurrence of HO after fracture surgery.
- 680 View
- 1 Download

Original Article
- Clinical Outcomes of Minimally Invasive Surgery in Sanders Type IV Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures
- Jun Young Lee, Hyunwoong Jang, Young Wook Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(4):181-187. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.4.181
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study evaluated the radiologic and clinical results in patients who underwent minimal invasive surgery using sinus tarsi approach in Sanders type IV calcaneal fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This retrospective study evaluated 13 cases of Sanders type IV calcaneus fractures that were treated by minimal invasive surgery using the sinus tarsi approach from July 2012 to April 2017. Further, these cases could be followed up for more than 12 months. Bone union, radiologic parameters such as Böhler's angle, Gissane's angle, calcaneal height, length, and width, the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) ankle-hindfoot score, and the postoperative complications were evaluated.
RESULTS
Bony union was achieved in all the cases at the final follow up, and the mean union time was 5.5 months. One patient underwent reoperation for a surgical site infection, six patients had post traumatic arthritis, and two of them underwent subtalar joint fusion. The mean AOFAS ankle-hindfoot score was 81.2. At the final follow-up, the mean values of Böhler's angle and Gissane's angle were 20° and 119.8°, respectively, and the mean values of the calcaneus height, length, and width were 46.8 mm, 81.8 mm, and 45.6 mm, respectively.
CONCLUSION
Minimal invasive surgery using the sinus tarsi approach for Sanders type IV calcaneal fracture resulted in satisfactory anatomic reduction and stable fixation, and satisfactory clinical and radiologic results were obtained in most of the patients. Minimal invasive surgery is thought to reduce the soft tissue-related complications as compared to surgery using the extensile lateral approach.
- 1,034 View
- 16 Download

Review Article
- Surgical Treatment for Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures
- Chul Hyun Park, Oog Jin Shon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(3):221-231. Published online July 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.3.221
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Calcaneal fractures are the most common type of tarsal fracture, and comminuted and bursting fractures are common due to the anatomic characteristics of the calcaneus. Assessment and treatment of calcaneal fractures has improved significantly over time. Despite advancements in surgical techniques and equipment, these fractures remain difficult to treat. In this review article, the physiopathology, classification, and surgical treatments of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures are updated.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current Treatment of Calcaneal Fractures and Dislocation
Dae Jin Nam, Sung Hyun Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2022; 35(2): 74. CrossRef
- Current Treatment of Calcaneal Fractures and Dislocation
- 1,289 View
- 17 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- Comparison of Quality of Life between Before and After Orthopaedic Implant Removal Surgery
- Sang Bong Ko, Seung Bum Chae
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(2):101-106. Published online April 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.2.101
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to determine whether or not a patient's results are improved after removal of an internal fixative from a patient with no related symptoms.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This prospective study included 87 patients who agreed to participate in the study and satisfied the criteria for selection and exclusion of patients who underwent the operation for removal of internal fixative due to broken bones from March 1st, 2004 to December 31st, 2011 at Daegu Catholic University Medical Center. The average replication period was 27 months (12-64 months) and the average age at the time of the operation for removal was 41.5 years (21-75 years) for 55 males and 32 females. The quality of life for all patients was evaluated using Short Form 36 (SF-36) surveys before the operation for removal and after a minimum of one year.
RESULTS
After an orthopedic operation for removal of internal fixative, physical health status showed statistically significant improvement (p=0.001); however mental health status did not (p=0.411). A satisfaction test for the subjective surgery written by patients indicated an improvement of subjective health status in 52.9% after the surgery for removal but with no difference in 29.9% compared to preoperation.
CONCLUSION
In case of an operation for removal of internal fixative for patients with no related symptoms with internal fixatives used for treatment of fractures showing agglutination opinions, an improvement was observed in physical health status, not in mental health status. When surgery for removal of internal fixative is performed for patients without related symptoms, consideration that subjective satisfaction of patients shows an improvement only in 52.9% will be helpful.
- 727 View
- 6 Download

- Modified Phemister Technique with Mersilene Tape Augmentation in the Acute Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation
- Hyun Dae Shin, Kwang Jin Rhee, Young Mo Kim, Kyung Cheon Kim, Choong Hui Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(2):83-88. Published online April 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.2.83
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To find out the consequences of the surgical treatment of acromioclavicular joint dislocation, using modified Phemister technique with Mersilene tape augmentation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We chose 26 patients who were able to follow up 1 year or more among the patients who were diagnosed as acromioclavicular joint dislocation in our hospital through February 2001 to March 2003 and took modified Phemister surgery with Mersilene tape augmentation. Patients with clavicle fracture were excluded. Evaluation of the surgical results was done with the condition or pain, function, range of motion by using Imatani evaluation system, and preoperative, postoperative and last follow up radiographs.
RESULTS
Most of the cases showed satisfactory result. Clinical evaluations were 16 excellent (62%), 10 good (38%), radiological evaluations were 14 excellent (54%), 10 good (38%), 2 fair (8%), and no poor group. On the final follow up six cases showed vertical translation, but none had clinical symptoms. Seven cases showed a little inflammation at where pin were inserted, but after the removal of the pin, the inflammation was gone.
CONCLUSION
The modified Phemister surgery for acromioclavicle dislocation is simple, but we can obtain strong fixation, and there is no burden of the removal of the metal plate, or complication of re- dislocation after the removal of the pin, so it is thought as a very effective surgery.
- 457 View
- 3 Download

- Development and Accuracy Test of a Robot-arm Type Image-guided Surgery System for Percutaneous Screw Fixation of the Sacro-iliac Joint
- Jin Sup Yeom, Won Sik Choy, Hayong Kim, Jong Won Kang, Kwang Won Lee, Whoan Jeang Kim, Jae Hoon Ahn, Seong Kyu Park, Jong Hwa Won, Hyungmin Kim, Namkug Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(2):191-197. Published online April 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.2.191
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To develop a robot-arm type image-guided surgery system for percuatneous screw fixation of the sacro-iliac joint and to evaluate its accuracy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We have developed an image-guided surgery system using a three-dimensional digitizer (Microscribe 3-D G2, Immersion, USA) and a personal computer. The registration error and target localization error at fiducial registration were measured 30 times for each using a phantom made with plastic pelvic bone model (Sawbones, USA). Sixteen 6.5 mm cannulated screws were inserted into four plastic bone models, and the accuracy was evaluated.
RESULTS
The target localization error was 1.46+/-0.47 mm while the registration error was 0.73+/-0.23 mm. All of the 16 screws were inserted well across the sacro-iliac joint, and there was neither cortical breach nor collision between screws or washers.
CONCLUSION
The accuracy of the developed system was similar to that of optical tracker-based navigation systems, and its helpfulness and usefulness was proven with simulation surgery using plastic bone models.
- 420 View
- 0 Download

- Development of a Computer-assisted Surgery System for Screw Fixation of the Sacro-iliac Joint
- Jin Sup Yeom, Won Sik Choy, Ha Yong Kim, Whoan Jeang Kim, Jong Won Kang, Yeongho Kim, Hyungmin Kim, Donghyun Seo, Seok Lee, Jae Bum Lee, Namkug Kim, Cheol Young Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(1):1-7. Published online January 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purposes of this study were to develop a computer-assisted surgery system for percutaneous screw fixation of the sacro-iliac joint and to evaluate its accuracy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We have developed a navigation system composed of an optical tracking device (Polaris, Northern Digital, Canada) and a personal computer. The registration error and target localization error at hybrid registration were measured using a phantom. The errors were measured 30 times for each. Sixteen 6.5 mm cannulated screws were inserted into four plastic bone models (Sawbones, USA), and the accuracy was evaluated.
RESULTS
The registration error was 0.76 +/-0.33 mm, and the target localization error was 1.43 +/-0.42 mm. All of the 16 screws were inserted well across the sacro-iliac joint, and there was neither penetration of the cortical bones nor collision between screws or washers.
CONCLUSION
The accuracy of the developed system was similar to existing ones, and its usefulness and helpfulness was proven with screw insertion into plastic bone models.
- 394 View
- 3 Download

- Clinical Evaluation of Antibiotics Prophylaxis Against Infection in Clean Orthopaedic Surgery
- Nam Hyun Kim, Soo Bong Hahn, Hong Jun Park
- J Korean Soc Fract 1995;8(4):815-822. Published online October 31, 1995
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1995.8.4.815
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Prophylactic antibiotic treatment to prevent postoperative wound infection is an appealing routine to the orthopaedic surgeon. But, there has been no adequate guideline of prophylactic antibiotics in the field of ctean orthopaedic surgery. The purpose of this study was to investigate the method of effective administration of antibiotics and the factors affecting the postoperative infection in clean orthopaedic surgery. Two hundred and forty one patients were included in a prospective randomized double-blind trial comparing the efficacy of three days(group 1,42 patients) versus that of five days cefotiam(group II, 199 patients) injection for prophylaxis against wound infection in patients who had an operation using bone plate, Ender of Kiintscher nails, or other internal fixation devides. The two groups were similar in terms of mean age, sex ratio, duration of preoperative hospital stay, underlying risk factors and type of surgical procedure. A wound infection developed in one of the forty-two patients in group I(2.3%) and in nine of 199 patients in group II(4.5%). This difference of infection rate is not stati stically significant(p>O.05). Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis , Klebsiella pneumoniae and Enterobacter aerogenes were the common infecting organisms. And the infection rate in lower extremity operations was higher than that of other regions in the group II (p In conclusion. the recommended method of administration of prophylactic antibiotics in clean orthopaedic surgery to prevent postoperative wound infection is a high dosage injection of antibiotics one hour before surgery, intraoperative infusion of one dosage when the operation lasts more than one hour and then postoperatively within 72 hours. This will reduce the adverse effects of medication and will also reduce the costs.
- 319 View
- 2 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


