Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
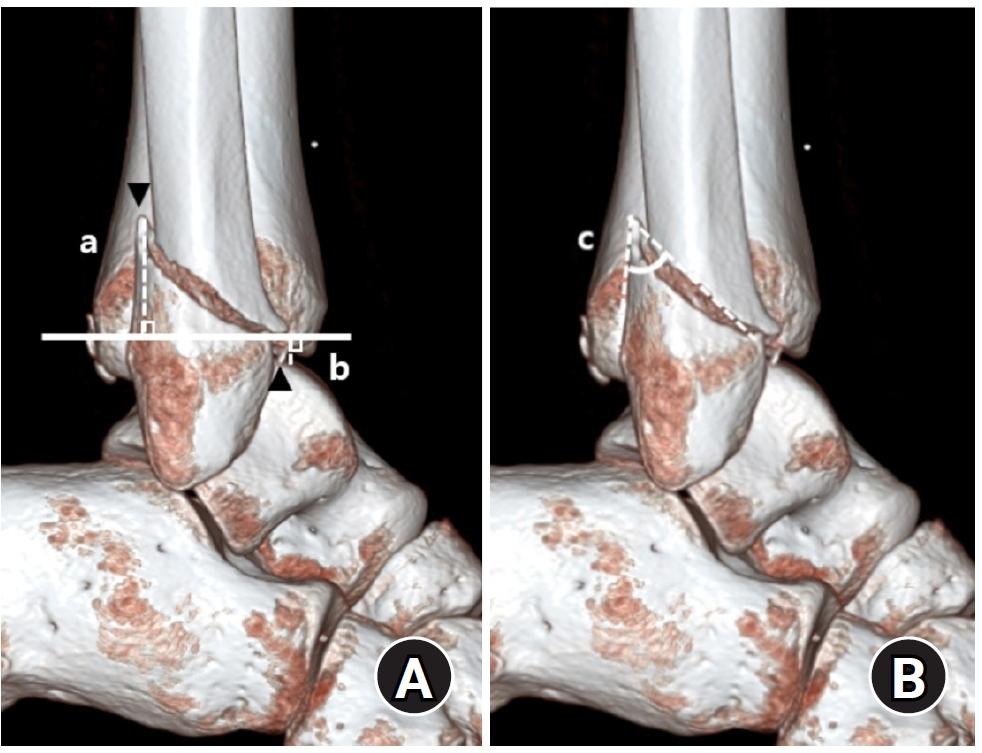
- Relationship of lateral malleolar fracture patterns to posterior malleolar fracture morphology in supination-external rotation ankle fractures in Korea: a retrospective cohort stduy
- Jong-Eun Kim, Chan-Jin Park, Jun-Young Lee, Keun-Bae Lee, Gun-Woo Lee
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):212-220. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00234
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Posterior malleolar fractures frequently accompany rotational ankle fractures. However, the morphological relationship between lateral and posterior malleolar fractures in supination-external rotation (SER) ankle fractures remains unclear. This study aimed to classify lateral malleolar fracture patterns in SER type 3 and 4 ankle fractures and investigated their associations with posterior malleolar fracture morphology.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 132 patients with SER type 3 or 4 ankle fractures and concurrent posterior malleolar fractures between January 2016 and December 2021. Lateral malleolar fractures were categorized as fibular fractures extending <4.5 cm proximal to the ankle joint (102 ankles) or fibular fractures extending ≥4.5 cm proximal to the ankle joint (30 ankles) based on posterior cortex height measured using three-dimensional computed tomography (3D-CT). Posterior malleolar fracture morphology was assessed using the Haraguchi and Bartonicek classifications. Quantitative parameters—including fracture height, angle, and articular involvement—were analyzed using 3D-CT imaging.
Results
Fibular fractures extending ≥4.5 cm proximal to the ankle joint were associated with a significantly higher frequency of Haraguchi type II and Bartonicek types 3 and 4 posterior malleolar fractures. This group also exhibited greater articular involvement (19.2% vs. 12.0%) and posterior cortical height (55.4 mm vs. 24.8 mm) compared to the <4.5 cm group (all P<0.001).
Conclusions
In SER type 3 and 4 ankle fractures, a fibular fracture extending ≥4.5 cm proximal to the ankle joint may be associated with posterior malleolar fractures exhibiting greater articular involvement and medial extension. Preoperative evaluation of the lateral malleolar fracture pattern may provide useful insights into posterior malleolar morphology and assist in surgical planning. However, these findings should be interpreted with caution due to inherent study limitations. Level of evidence: IV
- 982 View
- 20 Download

- Analysis for the Factors Influencing Bone Union in Segmental Tibial Shaft Fractures Treated with Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing
- Kyung Jin Song, Kwang Bok Lee, Byung Yun Hwang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(2):153-159. Published online April 30, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.2.153
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To find the factors influencing bone union in segmental tibial shaft fractures treated with interlocking intramedullary nailing, and to find the special attentions during operation based on this factors.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This retrospective study made to investigate the medical records and plain radiograms of 32 patients who treated with interlocking intramedullary nailing. We statistically analyzed the correlation between bone union time and factors influencing bone union, including fracture site, fracture pattern, Melis type, open fracture, nail diameter, reaming, postoperative gap, postoperative angulation.
RESULTS
The factors that showed the significant difference statistically were fracture site, Melis type, open fracture, postoperative gap, postoperative angulation. The factors that showed no significant difference statistically were fracture pattern, nail diameter, reaming.
CONCLUSION
We recommend that surgeons should be considered the site and type, open fracure in preoperative stage. During operation, try to reduce it accurately without angulation and gap if possible. And so, the careful planing of treament can be expected with a high rate of union and a low rate of complication. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Outcomes and Analysis of Factors Affecting Bone Union after Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing in Segmental Tibia Fractures
Sang Soo Park, Jun-Young Lee, Sang-Ho Ha, Sung-Hae Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2013; 26(4): 275. CrossRef
- Outcomes and Analysis of Factors Affecting Bone Union after Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing in Segmental Tibia Fractures
- 547 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


