Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Articles
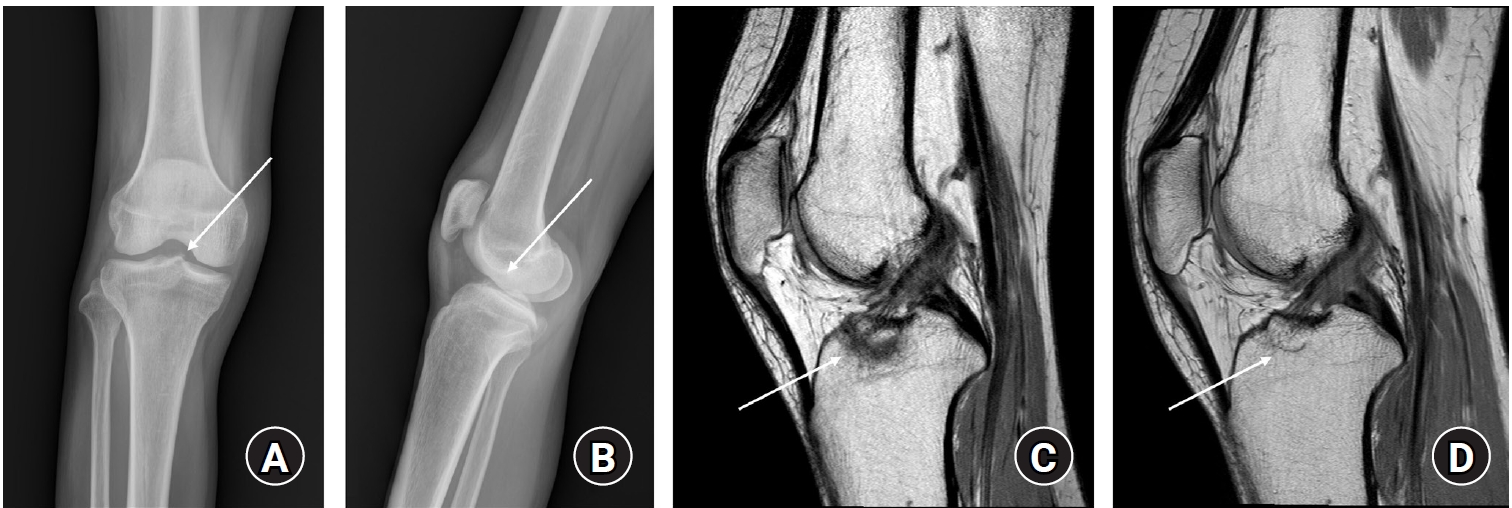
- Treatment of avulsion fractures around the knee
- Jeong-Hyun Koh, Hyung Keun Song, Won-Tae Cho, Seungyeob Sakong, Sumin Lim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):63-73. Published online March 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00073
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fractures of the knee occur when tensile forces cause a bone fragment to separate at the site of soft tissue attachment. These injuries, which frequently affect adolescent athletes, can involve the cruciate and collateral ligaments, arcuate complex, iliotibial band, and patellar and quadriceps tendons. Radiographs aid in the initial diagnosis, while computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging facilitate a comprehensive evaluation of injury severity and concomitant damage. Specific avulsion fracture types include: anterior cruciate ligament avulsions (tibial site, Meyers and McKeever classification), posterior cruciate ligament avulsions (tibial attachment, Griffith's classification), Segond fractures (anterolateral complex injury), iliotibial band avulsions, medial collateral ligament avulsions (reverse Segond, Stieda fractures), arcuate complex avulsions ("arcuate sign"), medial patellofemoral avulsions (patellar dislocations), and patellar/quadriceps tendon avulsions. The treatment depends on the fracture location, displacement, and associated injuries. Non-displaced fractures can be managed conservatively, while displaced fractures or those with instability require surgical reduction and fixation. Prompt recognition and appropriate intervention prevent complications such as deformity, nonunion, malunion, and residual instability. This review provides an overview of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management of knee avulsion fractures to guide clinical decision-making.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
Jae-Ang Sim, Chul-Ho Kim, Ji Wan Kim
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(3): 152. CrossRef
- Lateral marginal fractures of the patella and patellofemoral pain
- 18,942 View
- 205 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Treatment of Avulsion Fractures around the Knee
- Sumin Lim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(2):117-124. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.2.117
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fractures are common in athletes and result from high-impact or sudden, forceful movements involving the separation of a bone fragment at the ligament or tendon attachment site. The key focus areas include the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments, medial collateral ligament, anterolateral complex, arcuate complex, medial patellofemoral ligament, patellar tendon, and quadriceps tendon. Diagnostic approaches combine radiography with advanced imaging techniques, such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, to elucidate the extent of injury and guide treatment decisions. Treatment ranges from conservative management for non-displaced fractures to surgical intervention for displaced fractures, with strategies customized based on the specific ligament involved and the nature of the fracture.
- 1,316 View
- 10 Download

- Avulsion Fractures in the Ankle and Foot
- Gyeong Hoon Lim, Jae Won Kim, Sung Hyun Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(2):102-116. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.2.102
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An avulsion fracture occurs when a muscle-tendon unit attached to a bone produces sufficient force to tear a fragment of the bone. If not treated properly, this injury can lead to deformity, nonunion, malunion, pain, and disability. Although avulsion fractures around the foot and ankle can occur anywhere there are tendon and ligament attachments, they are common in the anterior talofibular ligament, anterior-inferior tibiotalar ligament, calcaneal tuberosity, the base of the fifth metatarsal, and navicular bone. The optimal treatment for each fracture depends on the location and severity of the fracture. Conservative treatment involves limiting weight bearing for a period, splint immobilization, and using various orthoses. Surgical treatment is usually reserved for cases of severe displacement or when nonsurgical treatment has failed. The goals of surgery include reduction of the fracture fragment, prevention of nonunion or malunion and soft tissue injury, and early return to function. The decision for each treatment modality may depend on the patient demographics or preferences and the surgeon experience. This review summarizes previous and current views on the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of common avulsion fractures to guide the treatment and diagnosis.
- 2,095 View
- 48 Download

Case Reports
- Avulsion Fracture of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament from Femoral Insertion Occurred in a Patient with Residual Poliomyelitis: A Case Report
- Wonchul Choi, Taesup Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(4):149-153. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.4.149
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fracture of the posterior cruciate ligament from its femoral insertion is quite rare, particularly in adults, and the treatment guidelines have not been established. A 68-year-old female patient with residual poliomyelitis presented with an avulsion fracture of the femoral insertion of the posterior cruciate ligament after a falling accident and was treated with arthroscopic headless compression screw fixation and pull-out suture of the avulsed ligament. We report this case with a relevant discussion of this type of injury.
- 398 View
- 0 Download

- Pediatric Cartilaginous Tibia Eminence Fracture Overlooked on Plain Radiograph: A Report of Two Cases
- Seong Eun Byun, Yunseong Choi, Wonchul Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2017;30(1):29-34. Published online January 31, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2017.30.1.29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In children with open physis, avulsion fracture of the tibia eminence, as an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury, is more commonly observed than an ACL rupture. Pure cartilaginous avulsions of the ACL tibia insertion seldom occurs. In such case, cartilaginous lesion is frequently overlooked or misdiagnosed on plain radiograph and may result in a less favorable treatment outcome. We report two cases of cartilaginous tibia eminence fractures of the children that were initially overlooked from plain radiographs, and then diagnosed by magnetic resonance imaging, which was ultimately treated by arthroscopyassisted headless compression screw fixation.
- 494 View
- 4 Download

- Avulsion of the Femoral Attachment of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Associated with Ipsilateral Femoral Shaft Fracture in Skeletally Mature Patient: A Case Report
- Seong Eun Byun, Taesup Kim, Bang Hyun Kim, Jae Hwa Kim, Soo Hong Han, Wonchul Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(3):200-205. Published online July 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.3.200
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fracture at the femoral attachment of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is very rare and has been reported mostly in skeletally immature patients. Authors experienced a case of avulsion fracture at the femoral attachment of ACL in a skeletally mature, a 21-year-old male associated with ipsilateral femoral shaft fracture. Here, authors report on the case with a literature review. Care should be taken because an avulsion fracture at the femoral attachment of ACL can be accompanied by ipsilateral femoral shaft fracture in skeletally mature patients.
- 451 View
- 0 Download

Review Article
- Diagnosis and Management of Ligament Injuries of the Wrist
- Ki Tae Na, Joo Yup Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2016;29(2):160-170. Published online April 30, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.2.160
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The wrist joint is formed by the distal end of the radius and ulna proximally, and eight carpal bones distally. It has many ligaments to maintain stability of the complex bony structures. The incidence of ligament injuries of the wrist has increased due to sports activities. However, diagnosis and management of these injuries are sometimes difficult because of the anatomic complexity and variable injury patterns. Among them, scapholunate ligament injury and triangular fibrocartilage tears are the two most common injuries resulting in chronic disabling wrist pain. Thorough understanding of the wrist anatomy and physical and radiologic examination is mandatory for proper diagnosis and management of these conditions. This article will briefly discuss the wrist joint anatomy and biomechanics, and review the diagnosis and management of the scapholunate ligament injury and triangular fibrocartilage injury.
- 1,074 View
- 16 Download

Original Articles
- Concomitant Carpal Injuries in Distal Radius Fractures: Retrospective Analysis by Plain Radiographs and Computed Tomography
- Chul Hyun Cho, Eun Seok Son
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(1):1-7. Published online January 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.1.1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the incidence and characteristics of concomitant carpal bone fractures and ligament injuries and to analyze risk factors for carpal injuries in patients with distal radius fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 362 patients with 379 distal radius fractures were reviewed retrospectively. Associated carpal bone fractures and ligament injuries were evaluated by plain radiographs and computed tomography at the time of initial trauma. Correlation between associated carpal injuries and various parameters was also analyzed.
RESULTS
Of 379 distal radius fractures, 39 cases (10.3%) had one or more carpal bone fracture and 40 cases (10.6%) had carpal ligament injuries. Overall, carpal injuries occurred in 59 cases (15.6%) distal radius fractures. Associated carpal ligament injuries showed correlation with young age and associated carpal bone fractures showed correlation with AO type B distal radius fractures. Carpal injuries including fracture and ligament injury showed correlation with male, high energy trauma, or associated injuries beyond wrist.
CONCLUSION
The incidence of concomitant carpal injuries in patients with distal radius fractures is relatively high. Concomitant carpal injuries were more common in young age, male, high energy trauma, AO type B distal radius fractures, or associated injuries beyond wrist. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Korean Medicine Treatments for the Angular Deformity of Wrist Fracture with Disuse Osteopenia: A Case Report
Myung Jin Oh
Korean Journal of Acupuncture.2018; 35(4): 234. CrossRef - Comparison of Distal Radius Fractures with or without Scaphoid Fractures
Jin Rok Oh, Dong Woo Lee, Jun Pyo Lee
Journal of the Korean Society for Surgery of the Hand.2016; 21(1): 23. CrossRef
- Korean Medicine Treatments for the Angular Deformity of Wrist Fracture with Disuse Osteopenia: A Case Report
- 962 View
- 18 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Tension Band Wiring for Distal Clavicle Fracture: Radiologic Analysis and Clinical Outcome
- Seong Cheol Moon, Chul Hee Lee, Jong Hoon Baek, Nam Su Cho, Yong Girl Rhee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(2):127-135. Published online April 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.2.127
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the radiologic and clinical outcomes after tension band wire fixation of Neer type II distal clavicle fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty-six patients with Neer type II distal clavicle fractures who underwent tension band wire fixation from March 2002 to May 2011 were included in the study. Fifteen cases were classified as Neer type IIa and 11 cases as type IIb. The postoperative mean follow-up period was 14.3 months. Clinical and radiologic evaluation was performed at two weeks, six weeks, three months, six months, and 12 months postoperatively.
RESULTS
Bony union on X-rays was observed at an average of 11.7 weeks (range 8-20 weeks) postoperatively. The overall visual analogue scale score for pain was 1.23+/-2.75 postoperatively. The overall postoperative University of California at Los Angeles score increased to 33.5+/-2.15 from the preoperative score of 21.6+/-1.91 (p<0.05).
CONCLUSION
Among various methods of treatment for Neer type II distal clavicle fracture, K-wire and tension band fixation was used and relatively satisfactory radiological and clinical results were obtained. This surgical method yields excellent clinical results, owing to its relatively easy technique, fewer complications, and allowance of early rehabilitation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical and Radiologic Outcomes of Acute Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation: Comparison of Kirschner's Wire Transfixation and Locking Hook Plate Fixation
Yong Girl Rhee, Jung Gwan Park, Nam Su Cho, Wook Jae Song
Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow.2014; 17(4): 159. CrossRef
- Clinical and Radiologic Outcomes of Acute Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation: Comparison of Kirschner's Wire Transfixation and Locking Hook Plate Fixation
- 893 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Surgical Management of Comminuted Avulsion Fracture of the Proximal Fibula with Lateral Collateral Ligament Injury: Technical Note
- Jong Min Kim, Byeong Mun Park, Sang Hoo Lee, Seung Ju Jeon, Jun Beum Shin, Kyeong Seop Song
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(1):77-80. Published online January 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.1.77
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Anteromedial force to the knee in an extended position can cause an avulsion fracture of the proximal fibula with combined injuries to the posterolateral ligaments. Avulsion fractures of the proximal fibula are rare and current management of these fractures is based on few descriptions in literature. Various surgical methods of fixation for these fractures have been reported, but there is still no standard treatment modality. Anatomic reduction of these fractures is technically difficult, and failure of reduction may cause posterolateral instability, secondary arthritis and other complications. We present our experience with two such cases of comminuted avulsion fractures of the proximal fibular with posterolateral ligament ruptures surgically fixated with a locking compression hook plate and non absorbable sutures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fixation of fibular head avulsion fractures with the proximal tibiofibular screw: Technique guide and clinical experience
Ryan A. Paul, Shu Yang Hu, Ananya Pathak, Ryan Khan, Daniel B. Whelan
Trauma Case Reports.2025; 57: 101175. CrossRef - Treatment of avulsion fractures around the knee
Jeong-Hyun Koh, Hyung Keun Song, Won-Tae Cho, Seungyeob Sakong, Sumin Lim
Journal of Musculoskeletal Trauma.2025; 38(2): 63. CrossRef - Treatment of Avulsion Fractures around the Knee
Sumin Lim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2024; 37(2): 117. CrossRef
- Fixation of fibular head avulsion fractures with the proximal tibiofibular screw: Technique guide and clinical experience
- 1,273 View
- 27 Download
- 3 Crossref

Original Article
- Related Factors of Ligamentotaxis with Posterior Instrumentation for the Surgical Treatment of Thoracolumbar Bursting Fracture
- Sang Bum Kim, Taek Soo Jeon, Seung Hwan Kim, Han Chang, Cheol Mog Hwang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(2):213-219. Published online April 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.2.213
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To investigate factors influencing the amount of indirect reduction by ligamentotaxis according to timing of surgery, extent of surgery, and characteristics of fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed 22 cases of thoracolumbar fracture which had been performed posterior instrumentation and fusion using pedicle screw system. We divided patients into each group according to timing of surgery, number of fusion segment, insertion of screw on fractured vertebra, and rupture of posterior ligament complex, and Denis type. We measured changes of kyphotic angle, anterior vertebral height and wedge angle on plain radiographs, and we compared spinal canal area before and after operation using computed tomographic scans.
RESULTS
Kyphotic angle, anterior vertebral height, wedge angle, and area of spinal canal showed significant improvement postoperatively. The wedge angle improved significantly operated within 3 days after injury, however, kyphotic angle and anterior vertebral height had no correlation with variable factors except the rupture of posterior ligament complex. The amount of restoration of spinal canal also affected only by rupture of posterior ligament complex.
CONCLUSION
There is little relationship between timing of surgery and canal restoration, so we cannot conclude that prompt operation helps reduction of narrowed spinal canal. Otherwise narrowed spinal canal had much less restored by ligamentotaxis when there were rupture of posterior ligament complexes.
- 471 View
- 2 Download

Case Reports
- Bilateral PCL Avulsion Fracture from Tibial Attatchment Site in a 16-years-old Male : A Case Report
- Hee Gon Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(3):189-192. Published online July 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.3.189
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture is occurred by high energy trauma, usually in motor vehicle accident or sports injury. Bilateral posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture is not yet reported in Korea. Authors report a case of bilateral posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture in 16-years-old man treated with anatomical reduction and internal fixation with a review of literature.
- 384 View
- 1 Download

- Irreducible Dislocation of the Interphalangeal Joint of the Great Toe with Lateral Collateral Ligament Entrapment: A Case Report
- Duke Whan Chung, Bi O Jeong
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(2):110-113. Published online April 30, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.2.110
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Dislocations of the interphalangeal joint of the great toe that are irreducible are very rare. Invagination of the plantar plate or the sesamoid bone into the IP joint, which prevents reduction. To our knowledge, however, dislocations of the IP joint of the great toe that were irreducible because of lateral collateral ligament entrapment, not invagination of the plantar plate or the sesamoid bone, have not been reported by any English literature. We report a 29-year-old ballet dancer who sustained an irreducible dislocation of the interphalangeal joint of the great toe owing to lateral collateral ligament entrapment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Open Reduction of a Dislocation of the Interphalangeal Joint of the Great Toe Neglected for 6 Weeks
Jae Kwang Kim, Rag-Gyu Kim
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2011; 46(5): 426. CrossRef
- Open Reduction of a Dislocation of the Interphalangeal Joint of the Great Toe Neglected for 6 Weeks
- 986 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- Comparison of the Surgical Treatment Results of Avulsion Fracture of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament between Children and Adults
- Eun Kyoo Song, Sang Jin Park, Keun Bae Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(2):196-201. Published online April 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.2.196
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To compare the clinical and radiological results after surgical treatments of the avulsion fractures of ACL between children and adults.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
40 cases (18 cases of children, 22 cases of adults), who underwent surgical treatments after avulsion fractures of the ACL and followed up more than one year, were enrolled. Fractures were classified by modified Meyers & McKeever criteria. Range of motion, LK score, Lachman test, Pivot-Shift test, quadriceps muscle atropy and Telos® stress arthrometer were compared.
RESULTS
The types of fracture in children were categorized into 8 cases of type II, 10 cases of type III, and 2, 15, 5 cases of type II, III, IV each in adult group. Mean LK score showed significant difference between 99.3 points in children and 89.5 points in adults (p<0.05). In addition, accompanied injuries and the high degree of fracture leaded low LK score. However, there was no significant difference in range of motion, Lachman test and Pivot-Shift test. Anterior laxity by Telos® device showed an average of 2.0 mm in children, 2.5 mm in adults (p>0.05).
CONCLUSION
Children group showed better treatment results of avulsion fracture of ACL. Higher incidence of type II fractures and less combined injuries considered to be factors for better results.
- 511 View
- 1 Download

- Thoracolumbar Fracture with Posterior Ligament Complex Injury
- Won Ju Shin, Deuk Soo Jun, Young Do Koh, Jea Yoon Cho
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(2):265-270. Published online April 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.2.265
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical features and radiographical landmarks of patients who has a thoracolumbar fracture combined with posterior ligament complex injury retrospectively.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The preoperative plain radiographys, axial CT, MRI and medical records of 27 patients were reviewed who were confirmed the posterior ligament complex injury in operation from January, 2002. to December, 2004.
RESULTS
The patients were from 15 years to 75 years of age (mean 39.1 years), 20 males and 7 females. The mechanisms of injury were 17 falls from a height, 7 traffic accidents and 3 direct blow injuries. There were 17 cases (63%) in thoracolumbar transitional zone, such as 11 cases in T11-T12, 6 cases T12-L1. There were 9 cases of compression fracture and 18 cases of burst fracture according to the shape of fractured vertebra. In the plain radiograph, the degree of kyphotic angle was between 6~49 degrees (mean 22 degrees), anterior vertebral height loss was 7~70% (mean 39%), and posterior vertebral height loss was 0~8% (mean 3%). 21 cases (78%) were the anterior vertebral height loss below 50%, 23 cases (85%) were the degree of kyphotic angle below 30 degrees. Neurological deficits were not registered. 23 cases (85%) were positive in MRI and 24 cases (89%) were positive in direct focal tenderness in the view of posterior ligament complex injury. Conclusions: The posterior ligament complex injury is common finding of the thoracolumbar fracture. The high resolution MRI findings and direct focal tenderness are very importance in identifying the posterior ligament complex injury that is important prognostic factor particularly in mild anterior vertebral height loss and mild kyphotic angle in the plain radiograph.
- 419 View
- 0 Download

- Result of Wolter Plate Fixation for the Treatment of Dislocation of Acromioclavicular Joint and Clinical Importance of Coracoclavicular Ligament Repair
- Jang Suk Choi, Ki Young Kim, Kyong Chil Chung, Heui Chul Gwak, Dong Jun Ha, Kyoung Whan Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(1):41-45. Published online January 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.1.41
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical result of the Wolter plate fixation for the acromioclavicular joint dislocation and the necessity of coracoclavicular ligament repair with the operation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty three patients operated between January 2003 to September 2005 with over 6 months of follow-up period were studied. The Constant-Murley scoring system was administered on 6 months postoperatively and stress films were taken for the surveillance of acromioclavicular joint and coracoclavicular distance after plate removal. All patients were classified into two groups in that coracoclavicular ligament was repaired (10 cases) or not (13 cases) and the clinical indices described above were compared.
RESULTS
With the Wolter plate fixation for the acromioclavicular joint dislocations, 20 cases of Constant-Murley scores were more than 'good' except complicated 3 cases. The scores of the repaired group were 7 cases of excellent, 2 cases of good and 1 case of moderate to poor, and that of not-repaired group were 6 cases, 5 cases and 2 cases respectively. With mean coracoclavicular interspace on x-ray at postoperative 6 months, repaired group showed residual 9% of displacement from initial 194% but not-repaired group showed 28% from initial 188%. There's no statistically significant difference in clinical scores between two group (p=0.072) and neither was residual coracoclavicular interspace displacement (p=0.067).
CONCLUSION
Short term follow-up of Wolter plate fixation for the acromioclavicular dislocation showed acceptable clinical results and there was no statistically significant difference between two groups of repaired coracoclavicular ligaments and not repaired.
- 310 View
- 0 Download

- The Necessity of Deltoid Ligament Repair in Lateral Malleolar Fracture Combined with Medial Clear Space Widening
- Bo Kyu Yang, Sung Ho Hahn, Seung Rim Yi, Young Joon Ahn, Jae Ho Yoo, Min Seok Kim, Byung June Chung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(3):281-285. Published online July 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.3.281
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the necessity of deltoid ligament repair in lateral malleolar fracture associated with medial clear space widening.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The 82 cases of 82 patients received surgical treatment for lateral malleolar fracture with medial clear space widening in our hospital from Jan. 1996 to Feb. 2002. 73 male and 9 female patients were included respectively. Average follow-up period was 13.2 month (12~50). The methods of internal fixation of lateral malleolar fracture were 66 cases by cortical screw, 16 by plate and screws, and 9 by transfixing screw.
RESULTS
Satisfactory reduction was obtained in 65 of 73 cases by only internal fixation of lateral malleolar fracture. Transfixing screw was needed in 8 cases. There was no need for repair of deltoid ligament. In clinical evaluation, no cases of limitation of movement in ankle was seen at final follow-up time. In radiologic evaluation, average medial clear space widening before operation was 5.89 mm (4.5~13 mm) and that of last follow-up time was 2.54 mm (1.5~3.5 mm). 95.2% was above good result.
CONCLUSION
In treatment of unstable lateral malleolar fracture associated with medial clear space widening due to rupture of deltoid ligament, we obtained satisfactory result by accurate anatomical reduction or internal fixation. In these cases, there were no need for repair of deltoid ligament.
- 386 View
- 0 Download

- Bone & Soft Tissue Injuries Diagnosed by Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Thoracolumbar Fractures
- Yong Min Kim, Dong Soo Kim, Eui Seong Choi, Hyun Chul Shon, Kyoung Jin Park, Gi Seok Han, Jae Jung Jeong, Kyoung Il Jeong, Yung Sung Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(2):184-190. Published online April 30, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.2.184
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To assess diagnostic efficacy of the MRI in thoracolumbar fractures, especially in changes of bone and soft tissue which cannot be documented by other diagnostic tools.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Among 85 patients managed for thoracolumbar fractures between January 1997 and June 2003, MRI was performed in 30 patients to get more informations. Plain X-ray, CT and MRI of these cases were reviewed retrospectively by two orthopaedic spine surgeons and one radiologist to investigate the informations which only MRI could afford.
RESULTS
14 (46.7%) among 30 patients had occult fractures of vertebrae other than main fracture which had not been diagnosed as fractured. Besides 6 patients who showed distraction of posterior structure on plain X-ray, injury of posterior ligament complex was confirmed by MRI in 12(40%) patients. Additionally, MRI visualized other soft tissue injuries such as intramuscular and subcutaneous hematoma, changes of the spinal cord and intervertebral disc. In 16 among 30 patients, informations achieved from MRI were the most important factors in deciding treatment modality.
CONCLUSION
MRI seems to be efficient in visualizing not only soft tissue injury such as ligament but also occult fractures of additional vertebra in thoracolumbar fractures, therefore MRI seems to be an important diagnostic tool in decision of treatment modalities, especially in cases of uncertain stability. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Measurement Discrepancy of Sagittal Parameters between Plain Radiography and 3D Computed Tomography in Thoracolumbar and Lumbar Fractures
Dong-Soo Kim, Yong-Min Kim, Eui-Sung Choi, Hyun-Chul Shon, Kyoung-Jin Park, Byung-Ki Cho, Ji-Kang Park, Hyun-Cheol Lee
Journal of the Korean Orthopaedic Association.2012; 47(3): 198. CrossRef - Relationship between Lamina Fractures and Dural Tear in Low Lumbar Burst Fractures
Ki-Chan An, Dae Hyun Park, Yong-Wook Kwon
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(3): 256. CrossRef
- Measurement Discrepancy of Sagittal Parameters between Plain Radiography and 3D Computed Tomography in Thoracolumbar and Lumbar Fractures
- 716 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- MRI Findings of Posterior Ligament Complex Injury in Thorcolumbar Bursting Fractures
- Young Do Koh, Yeo Heon Yun, Hoon Jeong
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(4):541-547. Published online October 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.4.541
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To investigate the MR findings of structures injured in the burst fractures of thoracolumbar spine.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty-one patients who had thoracolumbar burst fractures with posterior ligament complex injury on MRI were studied. For the evaluation of stability of fractures, we used the scheme described by Oner et al. We identified the state of posterior ligament complex on surgery.
RESULTS
The MRI findings of ALL were state 1 in four, state 2 in fourteen, and state 3 in three. Those of PLL were state 1 in twelve, state 2 in six, and state 3 in three. The findings of posterior ligament complex were state 2 in one, state 3 in three, and state 4 in seventeen. The endplate state 1 was in four, state 2 in six, state 3 in seven, and state 4 in four. The disc state 1 was in twelve, state 2 in six, state 3 in two, state 4 in one. The vertebral body involvement state was 1 in four, state 2 in nine, and state 3 in eight. The injuries of posterior ligament complex were confirmed intraoperatively in all twenty-one patients.
CONCLUSION
We recommend the use of MRI to evaluate stability of fractures and state of posterior ligament complex in thoracolumbar burst fractures.
- 420 View
- 1 Download

- Treatment of Distal Clavicle Fractures with Coracoclavicular ligament Injury
- Nam Yong Choi, Suk Ku Han, Seong Jin Park, Ki Ho Na, Young Hun Kim, Hyun Seok Somg, Yong Jin Kwon
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(1):21-27. Published online January 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.1.21
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the radiological and clinical results of the treatment of distal clavicular fractures with coracoclavicular ligament injury by coracoclavicular fixation with plating or repair of coracoclavicular ligament.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixteen cases with minimum six months of follow-up were included in our study. Male was twelve and average age was 43(28-80). Ten cases of Craig type 2 were treated with coracoclavicular screw fixation with plating. Six cases of Craig type 5 were treated with coracoclavicular screw fixation with repair of coracoclavicular ligament. The radiologic assessment including coracoclavicular distance and union time and the clinical assessment including range of motion and degree of pain were evaluated.
RESULTS
Fifteen cases were united, but one case developed osteomyelitis and nonunion. Full range of motion was achieved in fifteen cases at last follow-up. Average coraco- clavicular distance compared to contralateral site in AP view was 2.1 mm increase in patients with plate fixation and 1.3 mm increase in patients with ligament repair. Average union time was 14.3 weeks and little differenece was noted between two groups(P>0.05).
CONCLUSION
Coracoclavicular screw fixation with plating or repair of coracoclavicular ligament were a useful method to treat distal clavicular fractures combined with coracoclavicular ligament injury.
- 437 View
- 3 Download

- Reconstruction of Medial Collateral Ligament in Old Posterior Dislocation of the Elbow
- Sang Soo Lee, Ho Yeun Hwang, Dong Hee Lee, Il Hyun Nam, Sang Un Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(3):576-583. Published online July 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.3.576
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate and analyse the operative results of reconstruction of medial collateral ligament(MCL) in old posterior dislocation of the elbow.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Nine patients (from 1989 to 1999) with old posterior dislocation of the elbow treated by operation were reviewed. We analysed the pattern of dislocation, associated injury, method of operation, complication and functional results. All patients were treated with open reduction. Reconstruction of MCL was undertaken in three patients of nine.
RESULTS
All nine patients who had underwent open reduction were improved in the flexion-extension motion of elbow. Three patients of nine underwent reconstructive surgery of MCL were much improved in the flexion-extension motion. But there is no differences in improving the pronation-supination motion between of them(P>0.05, ttest).
CONCLUSION
Precise understanding of MCL anatomy and appropriate intraoperative technique are mandatory. We achieved much more range of motion in the cases of reconstruction and early motion rather than those of immobilization for 3 weeks with K-wire. We believe reconstruction of MCL is a useful addition to treatment options for old elbow dislocation of elbow.
- 408 View
- 0 Download

- Clinical Experiences of the Femoral Unicondylar Fractures
- Ryuh Sup Kim, Suk Myun Ko, Kyu Jung Cho, Dong Hun Choi, Hyun Woo Park
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(3):479-487. Published online July 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.3.479
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The femoral unicondylar fractures occur less frequently than the supracondylar or intercondylar femoral fractures. We document the problems and results in the treatment of these fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eleven patients with minimal follow-up peroid of 12 months were included. In the methods of treatment, the operation with by closed or open reduction and internal fixation with screws was used for 7 cases, the conservative treatment for 4 cases. The therapeutic outcomes were rated by the Lysholm knee scoring scale.
RESULTS
The concomitant injuries including neurovascular, collateral or cruciate ligaments and capsular structures of knee to ipsilateral extremity were frequent events. The therapeutic outcomes were significantly affected by associated injuries. The only 5 cases had satisfactory result by the Lysholm knee scoring scale.
CONCLUSION
These injuries have been considered to be the result of high-energy trauma on flexed knee. The open reduction and internal screw fixation of the femoral unicondylar fractures are necessary for good results because those are unstable and easily displaced. The associated disruption of the cruciate ligament was frequently associated injury and, significantly affected to the therapeutic outcome.
- 380 View
- 0 Download

- Knee Fractures and Ligament Injuries Associated with Ipsilateral Femoral Shaft Fractures: Mechanism of Injury, Site of th Knee Fracture and Ligament Injury
- Dong Ju Chae, Phyl Hyun Chung, Won Suk Chae
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(2):230-235. Published online April 30, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.2.230
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
: To establish the incidence and type of knee fractures, injury of knee ligament associated with ipsilateral femoral shaft fractures. What is the most common mechanism of these combined injuries? MATERIALS AND METHODS : From March 1995 to February 1999, evaluation of one hundred and twenty consecutive patients with fracture of the femoral shaft showed fractures and injuries of the ligaments of the ipsilateral knee in thirty-five(29%) of them. Of those thirty-five, nineteen patients had injured their knees and femoral shaft fractures by the dashboard injury. Twelve injuries were caused in a motor cycle accident, and two patients occurred in pedestrians struck by cars. Two injuries were caused by falls.
RESULTS
: There were twenty fractures of th knee and fifteen injuries of the ligament. Seventeen of the twenty fractures were in the patella, two in the bicondyle of the proximal tibia and one in the lateral condyle of the proximal tibia. Eleven of seventeen fractures of the patella were open fractures. Of fifteen injuries of the ligament, there were six posterior cruciate ligament tears (including 2 partial tears and 1 avulsion fracture), three posterior cruciate ligament tears with medial or lateral collateral ligament disruption , three anterior cruciate ligament tears(2 tibial spine fractures and 1 partial tear), two lateral collateral ligament disruptions and one medial collateral ligament tear. The locations of femoral shaft fracture were proximal in four patients, middle in thirty, and distal in one patient.
CONCLUSION
: We conclude that there is a high incidence of ipsilateral fracture of the patella and posterior cruciate ligament tears in patients with femoral shaft fractures. The dashboard injury is the most common mechanism of the ipsilateral knee fractures and ligament tears with femoral shaft fractures.
- 423 View
- 2 Download

- Treatment of Avulsion Fracture of posterior Cruciate Ligament from Tibial Attachment: Retrospective Study
- Moon Jib Yoo, Suk Joo Lyu, Kwang Ho Jin, Myung Ho Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1999;12(3):607-613. Published online July 31, 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1999.12.3.607
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
If PCL injury is not treated properly, it may result in progressive instability and functional disability, ultimately degenerative changes of the knee joint. So, we classified fracture type according to extent of displacement and comminution. We will investigate the result and prognosis of operative treatment, and fracture type, associated injuries, and fixation device affect the result. Finally we will ascertain the effectiveness of MRI. MATERIAL AND METHODS: 15 patients were treated in our hospital during the period september 1995 to july 1998. All of them were male. 14 of the 15 patients were treated operatively and 1 patient conservatively. The follow-up period after operative treatment varied from 9 to 30 months.
RESULTS
The roentgenograms showed union in all patients. There was subjective satisfaction in 11 of 15 patients. According to the measurement using objective device(KT-2000), in 12 patients, posterior displacement of tibia was less than 2mm, and in 3 patients, less than 4mm. According to Lysholm and Gillquist scoring scale, 11 patients were excellent, 3 patients were good, and 1 patient was fair. The fracture type and fixation device exerts no effect on the results, while associated injury around the knee joint had significant effect on the results.
CONCLUSION
Firstly, In avulsion fracture of PCL from tibial attachment, we were able to obtain satisfactory result by operative treatment using the small curvilinear posterior incision. Secondly, By using MRI, we were able to classify the fracture type more exactly and also find associated soft tissue injuries on the traumatized knee joint. As a result, MRI was quite helpful in determining the treatment and prospection of prognosis. Thirdly, The type of device had no effects on the results, no need of removal of fixation devices. Finally, Fixation was made possible by small curvilinear skin incision.
- 511 View
- 0 Download

- Injuries of the Knee Associated with Fractures of the Tibial Shaft
- Kwang Won Lee, In Sung Hwang, Seung Hun Lee, Tae Gyoo Ahn, Ha Yong Kim, Whoan Jeang Kim, Won Sik Choy
- J Korean Soc Fract 1999;12(2):277-283. Published online April 30, 1999
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1999.12.2.277
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Two hundred and seventeen consecutive patients with two hundred and twenty five diaphyseal tibia fractures were retrospectively reviewed to evaluate the frequencies, types and the results of treatments for the associated ipsilateral knee ligaments and menisci injuries from May 1993 to Feb 1997 at Eulji Medical College Hospital. Average follow-up period was 41 months(20~65 months). Thirteen patients with knee injuries(5.8%) were diagnosed by stress X-ray & MRI evaluation and confirmed by arthroscopic examination. Eleven patients(84.6%) were diagnosed as having a ligament or meniscus injury at the time of initial management. The posterior cruciate ligament(PCL) was injured in eight patients(50%); the anterior cruciate ligament(ACL), in three; the medial collateral ligament, in three; the lateral collateral ligament, in two: the medial meniscus, in two; and the lateral meniscus, in two. There was no relationship between specific ligament damage and the cause of the injury or level of fracture. Collateral ligament injuries, two ACL, and four PCL injuries were treated conservatively and one PCL injuries were treated with pull-out suture technique and another four PCL injuries were treated with reconstruction using bone-patella tendon-bone. One ACL injury was treated with reconstruction using semitendinosus tendon. As evaluated by the method of HSS knee score, there were seven(53.9%) excellent, four(30.8%) good, and two fair(15.3%). On the basis of the results of this study, we believe that, after stabilization of a fracture of the tibial shaft, it is essential to examine the knee throughly to identify any associated ligamentous injuries.
- 380 View
- 2 Download

- Iigament Injuries of the Knee Joint Combined with Ipsilateral Femoral Shaft Fracture
- Jin Hyung Sung, Choang Whan Han, Jae Duk Ryu, Weon Jin Cha, Jin Young Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1998;11(3):509-513. Published online July 31, 1998
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1998.11.3.509
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Most fractures of the shaft of the femur are caused by high-energy trauma. It would be expected that in many cases the ipsilateral knee ligaments are subjected to severe stress. In these days, early diagnosis and proper treatment of combined ligament injury in ipsilateral femoral shaft fracture become to be important and are possible by arthroscope and MRI. We retrospectively reviewed a series of 97 patients with 97 fractures of the femoral shaft from March 1995 to December 1997. demonstrable ipsilateral knee ligament laxity was present in 10(11.3 per cent) of these patients. There were 7 males and 8 left femur fractures. Eight of them were injured by traffic accident. Ten patients were followed for an average months. PCL injuries were five cases and ACL and MCL injuries were two cases each and posterolateral instability was one case. Early diagnosis was possible in MCL and ACL cases but diagnosis was dilayed to average 10 months post-accidentally in PCL injuries. MCL injuries and one ACL injuries were treated conservatively and one ACL and one PCL avulsion fracture were treated with pull-out suture technique and another 4 PCL injuries were treated with reconstruction using bone patella tendon bone, From this study, we advocate careful asessment of the knee, especially PCL injury in all cases of fracture of the femur caused by high-energy trauma.
- 375 View
- 0 Download

- Surgical Treatment of Acromioclayicular Joint Dislocation with Coracoclavicular Ligament Reconstruction using Coracoacromial Ligament
- Seung Rim Park, Hyoung Soo Kim, Joon Soon Kang, Woo Hyung Lee, Joo Hyung Lee, Min Seon Rim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1997;10(4):949-955. Published online October 31, 1997
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1997.10.4.949
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Several treatment methods for complete acromioclavicular(AC) joint dislocation have been recommended. This study was performed to evaluate the results of the injuries that had been treated operatively with Bosworth technique combined with coracoclavicular ligament reconstruction using coiacoacromial ligament. Between September 1992 and October 1995, 19 cases were treated with this method. We made an assessment of the results suggested by Taft. Subjectively, fifteen patients had no pain or stiffness. 17 patients had normal strength and full range of motion objectively. On the roentgenographic bases, 16 cases showed normal findings and one showed the subluxation of the AC joint. The overall Taft score was 10.8 points and 84 % of the patients showed good or excellent results. The advantages of this method include anatomical reduction of the AC joint and early motion of shoulder. Ligament reconstruction enables early removal of the lag screw which precludes joint stiffness and metal problems. We conluded that this method was a good surgical method for complete AC joint dislocation.
- 384 View
- 0 Download

- Change of Canal Compromise After Ligamentotaxis in Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture
- Kyu Jung Cho, Min Suk Yang
- J Korean Soc Fract 1996;9(3):759-766. Published online July 31, 1996
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1996.9.3.759
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Twenty-one patients with burst fracture of the thoracolumbar spine were treated by posterior pedicle screw instrumentation and fusion. We assessed canal compromise using CT fcan preoperatively and its restoration shortly after instrunientation lot confirmation of effect of lisamentotafis. The amount of neurologic recovery in each patient was compared to the final area of the spinal canal. The mean initial canal compromise was 42.6% and this was reduced to 16.2% postoperatively. The mean sagittal diameter was 10.2mm preoperatively & 12.9mm postoperatively. We achieved a mean reduction of canal compromise of 62%. A significant correlation between preoperative canal compromise and amount of restoration, or severity of neurologic deficit could not be established. Ligamentotaxis by pedicle screw instrumentation could effectively decompress the canal in thoracolumbar burst fracture.
- 432 View
- 0 Download

- The treatment of acromiclavicular ligament injury using coracoacrom ial ligament transfer with acromial bone block report of fourcases
- Duck Yun Cho, Jai Gon Seo, Eung Ha Kim, Eun Sung Koh
- J Korean Soc Fract 1992;5(1):22-27. Published online May 31, 1992
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1992.5.1.22
- 455 View
- 1 Download

Case Report
- Treatment of Old Distal Radioulnar Dislocation: A Preliminary Report
- Kwon Ick Ha, Sung Ho Hahn, Min Young Chung, Bo Kyu Yung, Seung Rim Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 1990;3(1):10-15. Published online May 31, 1990
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1990.3.1.10
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Dislocations of the distal radioulnar joint without fracture are more common than would be expected from the literature and most of these injuries are not diagnosed when seen initially. Several chronic problems may befall the distal radioulnar joint-loss of forearm rotation, chronic pain and arthritis, and a great many surgical procedures have been devised to relieve them. Six patients were treated with resection of ulnar head (Darrach Operation)in 3 cases, ligamentous stabilization(Hui and Linscheid Operation)in 3 cases, and we found more satisfactory results in the latter.
- 425 View
- 0 Download

Original Article
- Conservative Treatment of Ligamentous Injury of Knee in Head Trauma Patients
- Joon Young Kim, Young An Choi, Young Chul Choi, Bo Seok Kong
- J Korean Soc Fract 1989;2(1):42-48. Published online June 30, 1989
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1989.2.1.42
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Operative treatment has been used in unstable ligamentous imjury of knee joint. We experienced three cases of ligamentous injury of knee that was accompained with head trauma and other organ injury. Despite of sugical candidate, we did only conservative treatment due to poor general condition and difficulty of anesthesia. The result was realtively better than we expected. We reported these cases.
- 373 View
- 0 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


