Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Comparative results of the femoral neck system versus the dynamic hip screw for stable femoral neck fractures in older adults in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
- Byung-Chan Choi, Byung-Woo Min, Kyung-Jae Lee, Jun-Sik Hong
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):203-211. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00276
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
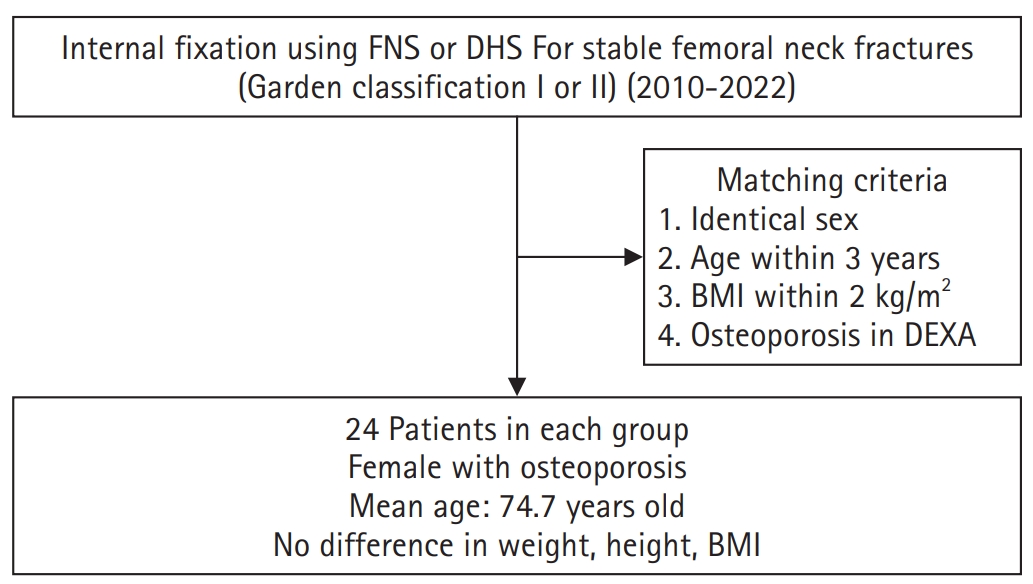
This study aimed to compare the clinical and radiological outcomes of the femoral neck system (FNS) and the dynamic hip screw (DHS) for the internal fixation of stable femoral neck fractures in older adults.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study included 48 matched older adult patients based on sex, age, BMI, and osteoporosis status, who had undergone internal fixation with either FNS or DHS for stable femoral neck fractures between January 2010 and December 2022. To minimize selection bias, a 1:1 case-control matching was performed based on sex, age, body mass index (BMI), and the presence of osteoporosis. A total of 48 patients (24 in each group) were included. We compared perioperative data (operation time, hemoglobin change, transfusion rate), functional outcomes using the Koval score, and radiological outcomes, including union rate, femoral neck shortening, and complication rates.
Results
The mean operation time was significantly shorter in the FNS group than in the DHS group (60.9 minutes vs. 70.8 minutes; P=0.007). There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in the union rate (87.5% in FNS vs. 95.8% in DHS), femoral neck shortening, final Koval score distribution, or overall complication rates (12.5% in both groups).
Conclusions
For treating stable femoral neck fractures in older adults, the FNS demonstrated comparable clinical and radiological outcomes to the DHS, with the distinct advantage of a shorter operation time. While these findings suggest that the FNS is a promising and safe alternative that may reduce the surgical burden, definitive conclusions are precluded by the small sample size, warranting further research to corroborate these results. Level of evidence: IV.
- 133 View
- 4 Download

- Risk factors of surgical complications after use of the femoral neck system: a random forest analysis
- Chul-Ho Kim, Hyun-Chul Shon, Han Soul Kim, Ji Wan Kim, Eic Ju Lim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):160-167. Published online July 23, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00157
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The femoral neck system (FNS), a novel fixation device for managing femoral neck fractures (FNFs), has gained popularity in recent years. However, analyses of the surgical complications and reoperation risks associated with the use of FNS remain limited.
Methods
This retrospective observational study analyzed 57 patients who had undergone FNS fixation for FNF at two university hospitals between July 2019 and February 2024. Demographic, perioperative, and outcome variables, including age, sex, fracture classification (Garden, Pauwels, and AO), implant characteristics, tip-apex distance (TAD), neck shortening, and neck-shaft alignment, were analyzed. In addition to univariate analysis, a machine learning analysis was conducted using a random forest classifier with stratified sampling (80% training, 20% testing). The accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and area under the receiver’s operating curve were calculated to assess model performance.
Results
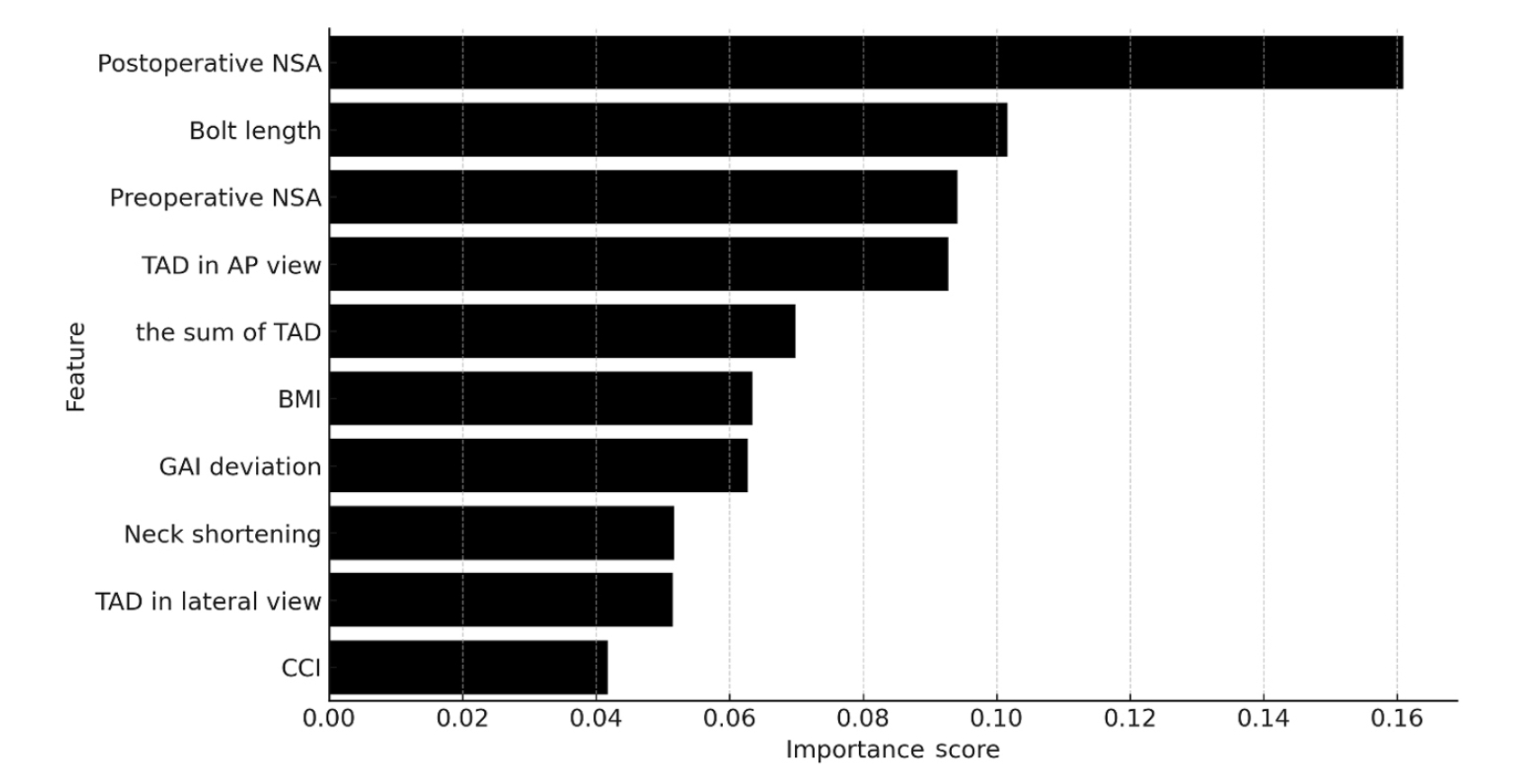
Ten patients experienced osteonecrosis of the femoral head (n=6), implant cut-out or penetration (n=3), and peri-implant fracture (n=1). Univariate analysis revealed that the TAD in the complication group was significantly shorter than that in the control group (12.1 vs. 16.7 mm; P=0.012). Additionally, neck shortening in the complication group was greater than that in the control group (4.9 vs. 2.3 mm; P=0.011). The random forest model achieved an accuracy of 83.3% and identified postoperative neck-shaft angle (NSA) as the most important predictor of complications (feature importance, 0.161), followed by bolt length (0.102) and preoperative NSA (0.094).
Conclusions
Risk factor analysis conducted using a random forest model identified postoperative NSA as the most important feature associated with postoperative complications following FNS. Therefore, care should be taken to normalize the postoperative NSA during FNF surgery. Level of Evidence: III.
- 520 View
- 24 Download

Review Article
- Pediatric Femoral Neck Fracture
- Joo Hyung Han, Hoon Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(1):34-43. Published online January 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.1.34
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pediatric femoral neck fracture is an uncommon injury with a high complication rate, regardless of the appropriate diagnosis and management. The bony anatomy and blood supply of the proximal femur in a skeletally immature patient differ from those in adult patients. Generally, these fractures result from high-energy trauma, but pathologic hip fractures also occur, usually from low-energy trauma. Pediatric femoral neck fractures are categorized using the Delbet classification system. This classification guides management and aids clinicians in determining the risk of avascular osteonecrosis. The ideal surgical treatment is determined by the fracture type and the age of the patient. Reduction, which is achieved using a closed or open procedure, combined with stable fixation and/or cast immobilization, is recommended for most of these fractures. Anatomical reduction within 24 hours from the injury may result in a good surgical outcome. Although the effects of capsular decompression after reduction and fixation have not been established, decompression is easy to perform and may reduce the risk of avascular necrosis. Despite appropriate management, osteonecrosis can occur after all types of pediatric femur neck fractures. Other complications include coxa vara, nonunion, and premature physeal arrest.
- 700 View
- 16 Download

Original Articles
- Complications and Affecting Factors for Intracapsular Femoral Neck Fractures Treated by Multiple Pinning
- Sung Jung Kim, Shin Yoon Kim, Gi Bong Cha, Chang Wug Oh, Il Hyung Park, Joo Chul Ihn
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(2):201-208. Published online April 30, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.2.201
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To investigate the relationship between the complications of intracapsular femoral neck fractures treated by multiple pinning and several affecting factors.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixty-eight patients with intracapsular femoral neck fractures were treated by multiple pinning from March 1993 to January 2000 and followed at more than one year. Relationship between the complications such as failure of union, collapse of femoral head due to osteonecrosis of femoral head and several affecting factors including displacement of fracture according to Garden stage, state of reduction, position of screws, time interval from injury to operation, and fracture level were analyzed. The Fisher exact test, chi-square test, and multivariate logistic regression analysis were used to find the relevant factors influencing incidence of complications. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
RESULTS
Position of screw was the most important single factor affecting the results of treatment of intracapsular femoral neck fracture (p=0.046). Moreover, the Garden stage and position of screw were revealed affecting the incidence of complications together with other factors (each p value was 0.028 and 0.027).
CONCLUSION
We considered that satisfactory position of screw was important to reduce complications after multiple pinning for intracapsular femoral neck fracture. And the results of operation also seemed to closely relate with multiple factors including Garden stage and status of reduction. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Factors Predicting Complications after Internal Fixation of Femoral Neck Fractures
Tae-Ho Kim, Jong-Oh Kim, Sung-Sik Kang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(2): 79. CrossRef
- Factors Predicting Complications after Internal Fixation of Femoral Neck Fractures
- 280 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Treatment of Femoral Neck Fractures in the Elderly Patiene
- Chung Nam Kang, Kwon Jae Roh, Yeo Hon Yun, Dong Jun Kim, Cheol Min Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1995;8(1):61-67. Published online January 31, 1995
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1995.8.1.61
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We analyzed 41 femoral neck fractures in 40 elderly patients aged over 65 years. All of them were treated by surgery and followed for average 22 months (range, 14 to 52 months) at the Ewha Womans University Hospital from 1988 to 1992. Of these, 15 cases were treated with internal fixation and 26 cases with endoprosthetic or total hip replacement arthroplasty For the level of fractures the most common features were subcapital, that were moderately to severely (Gardens stage III or IV) displaced. In the internal fuation group the results were unsatisfactory in the cases of subcapital type, moderate to severe (Gardens stage III or IV) displacement, Pauwels type III and those with osteoporosis (below stage III in Singh index). Our short term follow-up results showed that the prosthetic replacement group were generally superior in that they were not affected by the types of fractures and the degree of osteoporosis.
- 171 View
- 0 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA

 First
First Prev
Prev


