Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
- Current concepts in the management of phalangeal fractures in the hand
- Hyun Tak Kang, Jun-Ku Lee
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):109-123. Published online July 22, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00136
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
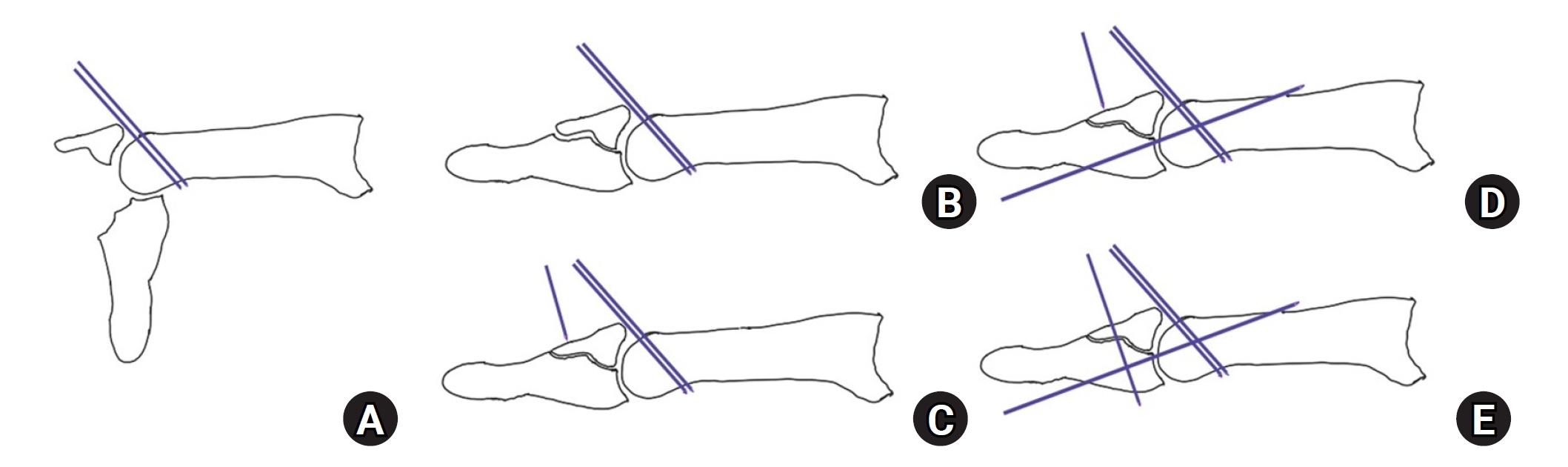
PDF - This review focuses on the treatment of hand fractures based on the anatomical location of the fractured phalanx, excluding the thumb, and examines recent studies on the topic. The main points are as follows: in most cases of hand fractures, conservative treatment should be prioritized over surgical intervention. The three key factors in determining whether surgical treatment is necessary are (1) whether the fracture is intraarticular, (2) the stability of the fracture itself, and (3) the extent of damage to surrounding soft tissues. The primary surgical treatment is closed reduction and Kirschner-wire fixation. The risk of rotational deformity increases with fractures closer to the proximal region. Intra- articular fractures may lead to subsequent stiffness and arthritis; thus, computed tomography is recommended to assess the fracture pattern. Anatomic reduction of intraarticular fragments is required, along with correction of the inherent joint instability. No surgical method has proven to be superior; it is advantageous for the surgeon to choose a surgical approach they are familiar with and confident in, based on the specific fracture and patient factors. Complications in hand fractures are various; the most frequent is stiffness, and nonunion is uncommon. Early joint motion is crucial in minimizing the risk of stiffness.
- 17,301 View
- 378 Download

Original Article
- Computational simulation of coracoclavicular screw insertion through the superior distal clavicular plate for clinical applications in Korean cadavers
- Hyung-Lae Cho, Ji Han Choi, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):143-151. Published online July 22, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00122
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The study was conducted to determine the practical area for inserting the coracoclavicular (CC) screw through the plate by analyzing three-dimensional (3D) shoulder models featuring virtually implanted, actual-size plates and screws.
Methods
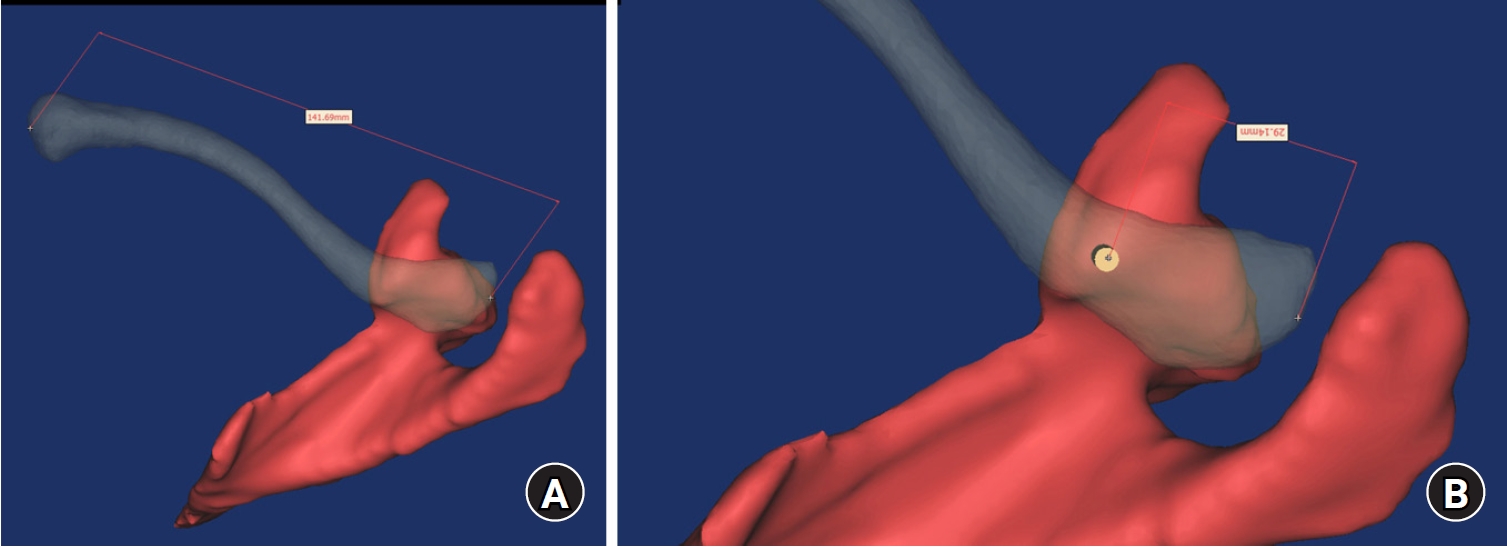
Ninety cadaveric shoulders (41 males and 49 females) underwent continuous 1.0-mm slice computed tomography scans. The data were imported into image-processing software to generate a 3D shoulder model, including the scapula and clavicle. The overlapping area between the clavicle and the horizontal portion of the coracoid process (horizontal portion_CP) was analyzed in the cranial view. A curved pelvic recon plate was virtually placed on the upper surface of the distal clavicle, and an actual-size (3.5 mm) CC screw was inserted through the plate.
Results
The distal clavicle directly overlapped with the horizontal portion_CP in the vertical direction. The overlapping area was sufficient to place the 3.5 mm and 4.5 mm-sized screws. In all shoulder models, the CC screw could be inserted through the plate into the vertical direction, with an average length of 35.5 mm (range, 26.2–62.5 mm; standard deviation, 1.2 mm). In 87 models, the CC screw was inserted through the third hole from the lateral end of the plate. Two models were inserted through the second hole, and one model through the fourth hole.
Conclusions
The upper surface of the clavicle has sufficient overlapping area to place CC screws through the plate in the vertical direction in the corresponding hole. Supplemental CC screw fixation through the plate can be performed without additional or special equipment. Level of evidence: IV
- 670 View
- 22 Download

Review Articles
- How to obtain the desired results from distal tibial nailing based on anatomy, biomechanics, and reduction techniques
- Jungtae Ahn, Se-Lin Jeong, Gu-Hee Jung
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):74-85. Published online March 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00024

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Distal tibial metaphyseal fractures are commonly caused by high-energy injuries in young men and osteoporosis in older women. These fractures should be clearly distinguished from high-energy pilon fractures. Although the optimal surgical intervention methods for distal tibial metaphyseal fractures remain uncertain and challenging, surgical treatments for nonarticular distal tibia fractures can be broadly divided into two types: plate fixation and intramedullary nail (IMN) fixation. Once functional reduction is achieved using an appropriate technique, distal tibial nailing might be slightly superior to plate fixation in reducing postoperative complications. Thus, the surgical strategy should focus on functional realignment and proceed in the following sequence: (1) restoring the original tibial length, regardless of whether fibular fixation is to be done; (2) making the optimal entry point through an anteroposterior (AP) projection based on the overlapping point between the fibular tip and lateral plateau margin; (3) placing Kirschner wires (Ø2.4 mm) as blocking pins (in the AP orientation for coronal control and in the mediolateral [ML] orientation for sagittal control) as close to the upper locking hole as possible without causing further comminution on the concave aspect of the short fragment; and (4) making the the distal fixation construct with at least two ML and one AP interlocking screw or two ML interlocking screws and blocking screws. After the IMN is adequately locked, blocking pins (Ø2.4 mm) need to be replaced by a 3.5 mm screw.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Rigid intramedullary nailing with suprapatellar approach for tibial shaft fractures in adolescents with open physes
Jong Wha Lee, Jae Ho Cho, Tae Hun Kim, Hyung Keun Song, Won-Tae Cho, Seungyeob Sakong, Hyunil Choi, Sumin Lim
Injury.2026; : 113130. CrossRef - Impact of Foot Width on Patient-Reported Outcomes Assessed by 3-Dimensional Foot Morphometry in Hallux Valgus
Jungtae Ahn, Dae-Cheol Nam, Gu-Hee Jung
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.2025; 17(6): 1062. CrossRef
- Rigid intramedullary nailing with suprapatellar approach for tibial shaft fractures in adolescents with open physes
- 2,950 View
- 56 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Atypical femoral fractures: an update
- Won-Tae Cho, Jeong-Hyun Koh, Seungyeob Sakong, Jung-Taek Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):41-52. Published online March 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00031
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
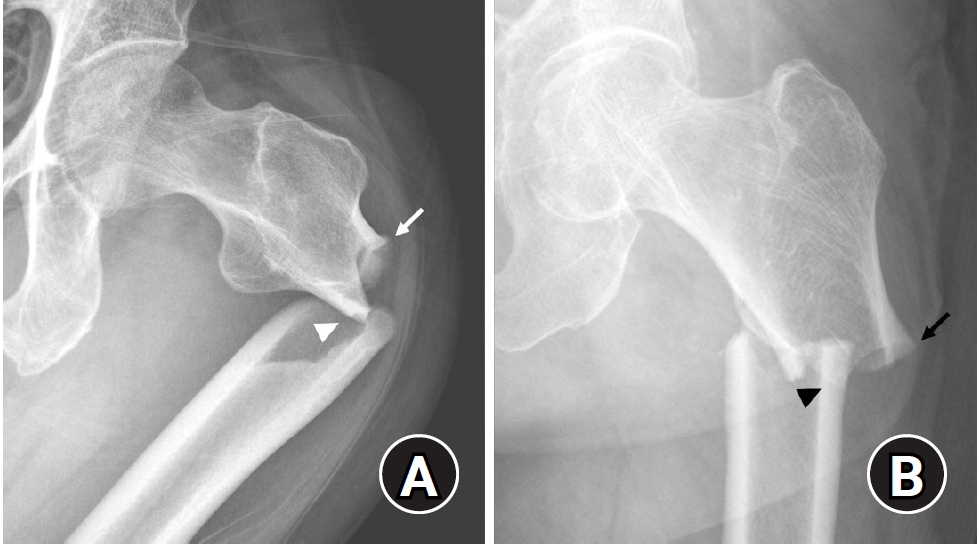
PDF - This narrative review provides an up-to-date overview of atypical femoral fractures (AFFs), emphasizing diagnostic criteria, epidemiology, pathophysiology, risk factors, and evaluation with screening strategies. AFFs are rare but significant complications associated with prolonged bisphosphonate (BP) therapy for osteoporosis. Although the pathogenesis of AFFs has not been fully elucidated, its primary mechanism is thought to involve impaired bone remodeling, leading to unhealed microfractures that progress to stress fractures under repetitive loading. AFFs can occur in various regions of the femur, influenced by femoral geometry and the lower limb axis. Other risk factors include prolonged steroid use, arthroplasty, genetic predispositions, and metabolic bone disorders. The diagnosis of AFFs is based on criteria established by the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. Key radiographic features include lateral cortical transverse fracture lines and localized cortical thickening, typically with minimal or no comminution on the medial cortex. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for screening tests and magnetic resonance imaging as an advanced imaging modality enable the early detection of incomplete fractures. This multi-modal approach facilitates the prompt identification of prodromal cortical changes, reducing the risk of complete fractures in high-risk populations, particularly patients undergoing prolonged BP therapy. Level of Evidence: V
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Atypical Femur Fractures Without Bisphosphonate Exposure (AFFwB): A Retrospective Report of 21 Cases
Lorenzo Lucchetta, Carmelinda Ruggiero, Samuele Berardi, Alice Franceschi, Michele Bisaccia, Giuseppe Rinonapoli
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 15(1): 25. CrossRef
- Atypical Femur Fractures Without Bisphosphonate Exposure (AFFwB): A Retrospective Report of 21 Cases
- 15,016 View
- 410 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Avulsion fractures around the hip joint and pelvis
- Won-Sik Choy, Yonghan Cha, Jung-Taek Kim, Jun-Il Yoo, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):53-62. Published online March 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
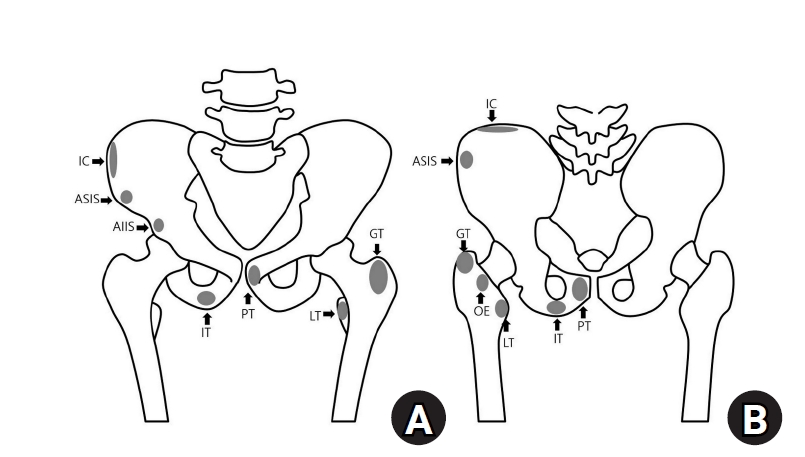
PDF - Avulsion fractures occur when tendons or ligaments are subjected to forces greater than they can withstand at the apophysis or enthesis, regardless of fusion status. The pelvis and hip joint are vulnerable to these injuries due to the diverse muscular structures in these structures, which serve as origins for multiple muscles leading to the lower extremities. Pelvic avulsion fractures commonly affect young athletes, but can also occur in adults. The diagnosis typically involves assessing trauma history, a clinical examination, and radiographic imaging. If the diagnosis is unclear, additional tests such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging may assist in the diagnosis and provide useful information for treatment decisions. While most avulsion fractures respond well to conservative treatment, surgical intervention may be preferred in severe displacements, cases of significant retraction in active athletes, or when a faster recovery is necessary. Chronic or neglected injuries may lead to excessive osseous formation around the pelvis, causing impingement syndromes. Recognizing characteristic radiological findings based on pelvic anatomy helps to make an accurate diagnosis, as chronic injuries can mimic tumors or infectious conditions, necessitating a careful differential diagnosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Avulsion Fracture of the Lesser Trochanter and the Use of Conservative Treatment
Dawid Bartosik, Bartlomiej Cwikla, Anna Kowalczyk, Michalina Loson-Kawalec, Anna Palka-Szymaniec, Bartosz Starzynski, Alina Keska, Jakub Szkuta, Klaudia Wojcik
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Avulsion Fracture of the Lesser Trochanter and the Use of Conservative Treatment
- 9,156 View
- 137 Download
- 1 Crossref

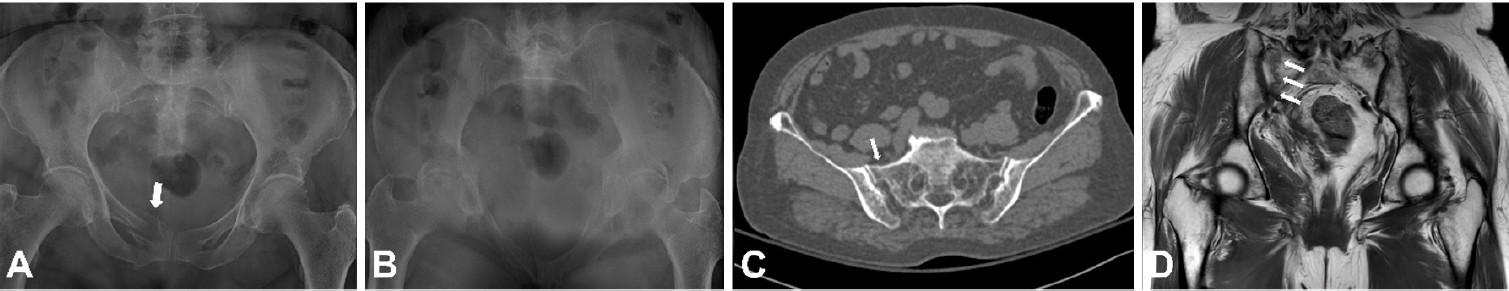
- Easily missed nondisplaced fractures accompanying complete fractures in the lower extremity and pelvis: a narrative review
- Young-Chang Park
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(1):5-12. Published online January 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Nondisplaced fractures accompanying complete fractures are often difficult to detect on plain radiographs or computed tomography scans, posing a diagnostic challenge. The diagnosis of these frequently overlooked injuries can be delayed, potentially leading to suboptimal patient outcomes. This review discusses four commonly missed fracture patterns in the lower extremity and pelvis, including posterior involvement in fragility fractures of the pelvis, intertrochanteric extensions in isolated greater trochanter fractures, ipsilateral femoral neck fractures in high energy femoral shaft fractures, and posterior malleolar fractures in distal spiral tibial shaft fractures. An accurate diagnosis of these accompanying nondisplaced fractures is critical for optimizing surgical outcomes. Surgeons should incorporate thorough preoperative evaluations into their clinical practice to facilitate early detection and appropriate treatment strategies. Prompt identification and comprehensive management remain essential for improving patient outcomes.
- 1,373 View
- 47 Download

Original Article
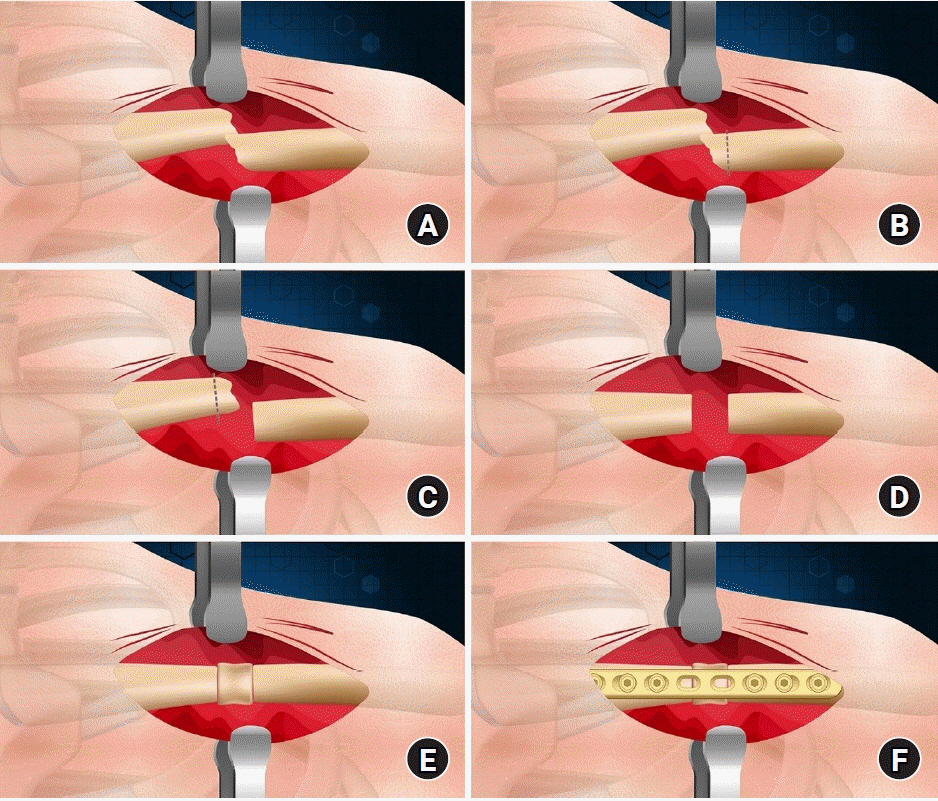
- Interpositional tricortical iliac bone graft in nonunion of midshaft clavicular fractures
- Eun-Seok Son, Bum-Soon Park, Chang-Jin Yon, Chul-Hyun Cho
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(1):23-31. Published online January 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The purpose of this study was to investigate the radiological and clinical outcomes after interpositional tricortical iliac bone graft with plate fixation for the nonunion of clavicle midshaft fractures. Methods: Between 2007 and 2020, 17 cases who were treated by interpositional tricortical iliac bone graft with plate fixation for the clavicle midshaft nonunion combined with bone defect were investigated. The mean age was 53 years (range, 22–70 years). The mean follow-up period was 102.2 months (range, 18–193 months). Serial plain radiographs were used to evaluate radiological outcomes. The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) score, American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons (ASES) score, and Quick-disabilities of the arm, shoulder, and hand (DASH) score were used to evaluate clinical outcomes. Complications were also evaluated. Results: All cases achieved complete bony union with mean healing time of 17.6 weeks (range, 14–22 weeks). The mean clavicle length difference was significantly decreased from 9.1 mm preoperatively to 2.6 mm postoperatively (P<0.001). The mean UCLA and ASES scores were significantly improved from 18.1 and 52.2 before surgery to 30.6 and 88.6 after surgery (both P<0.001), respectively. The mean final Quick-DASH score was 18.0. Three cases (17.6%) developed postoperative complications including two cases of shoulder stiffness and one case of screw irritation. Conclusions: Interpositional tricortical iliac bone graft with plate fixation for the clavicle midshaft nonunion demonstrated excellent radiological and clinical outcomes. In cases of atrophic nonunion combined with bone defect, this technique is an effective option that can provide structural support and restore clavicle length. Level of evidence: Level IV, case series.
- 2,025 View
- 44 Download

Review Article
- Fracture-Related Complication: Fat Embolism Syndrome
- Beom-Soo Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2023;36(3):95-102. Published online July 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2023.36.3.95
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fat embolization is a common occurrence after trauma or during orthopedic procedures involving intramedullary manipulation. Although uncommon, fat embolism syndrome (FES) with respiratory failure, neurologic dysfunction, and petechial rash can be fatal to patients. Two theories are proposed for the manifestation of FES: in the mechanical theory, FES occurs when fat tissue in the bone marrow enters the bloodstream and mechanically blocks it; the biochemical theory proposes that FES occurs due to an inflammatory reaction caused by free fatty acids. There are currently no clear diagnostic criteria for FES, and symptoms and signs are typically nonspecific. For the treatment of FES, conservative and supportive management is performed for the specific symptoms, and close monitoring of the respiratory and neurologic systems is required in high-risk groups. Early fracture fixation of long bones helps prevent and reduce the severity of fat embolism.
- 943 View
- 11 Download

Original Articles
- Minimal Invasive Fixation Methods for the Metacarpal Fracture
- Ki Youn Kwon, Jin Rok Oh, Ji Woong Kwak
- J Korean Fract Soc 2022;35(1):9-15. Published online January 31, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2022.35.1.9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study compared the radiologic and clinical outcomes of metacarpal fractures treated with two minimally invasive surgical techniques: Kirschner wire (K-wire) fixation and headless screw fixation.
Materials and Methods
This study included 52 patients (46 males and 6 females; age 18-55 years) with distal metacarpal fractures (middle and distal shaft, including the neck) who had undergone K-wire fixation or headless screw fixation. All subjects were followed up for at least six months. The radiologic assessments were performed to evaluate the angular deformity and shortenings. The total active motion (TAM), grip strength, and patients’ subjective functional assessment were measured to evaluate the hand function. The time taken to return to work (RTW) and adverse events were analyzed.
Results
Of the 52 cases, metacarpal fractures treated with headless screw fixation and K-wire fixation showed a significant difference associated with early RTW (p<0.05). There were no significant differences between the subjects treated with K-wire fixation and those with headless screw fixation in terms of the radiologic measurement, hand function examinations, complications, and adverse events (p>0.05).
Conclusion
After a six-month follow-up, minimally invasive K-wire fixation and headless screw fixation produced similar clinical and radiologic outcomes in subjects with metacarpal fractures. Compared to K-wire fixation, however, headless screw fixation led to earlier functional recovery and might be a better option for treating metacarpal fractures in this regard.
- 559 View
- 5 Download

- Operative Treatment of Pediatric Distal Forearm Bothbone Fracture
- Sang Uk Lee, Changhoon Jeong, Il Jung Park, Jaeyoung Lee, Seman Oh, Kyung Hoon Lee, Sanghyun Jeon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2015;28(4):237-244. Published online October 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2015.28.4.237
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Pediatric patients with distal forearm bothbone fractures of surgical indication were treated with the Kapandji reduction technique for radius and flexible intramedullary nail for ulna at our institution. The purpose of this study is to evaluate clinical and radiological results.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From February 2012 to June 2014, we retrospectively evaluated 16 out of 18 cases with distal forearm bothbone fractures treated with the Kapandji reduction technique for radius and flexible intramedullary nail for ulna with at least 1-year follow-up. The average age at operation was 9.1 years (7-13 years).
RESULTS
Adequate reduction for both radius and ulna was achieved for all cases, and none of the cases showed re-displacement until the last follow-up. Mean 6.6 weeks lapsed until bony union was observed for the radius. For the ulna, the mean was 6.5 weeks. All patients gained full wrist range of motion at the last visit.
CONCLUSION
For pediatric distal forearm bothbone fractures, intrafocal Kapandji reduction and internal fixation with Kirschner wire for radius and reduction and internal fixation with a flexible intramedullary nail for ulna is the technique for handy reduction. Use of this technique can prevent re-displacement during the union process and achieve excellent clinical and radiologic results.
- 429 View
- 1 Download

- Effect of Fracture Gap on Biomechanical Stability of Compression Bone-Plate Fixation System after Bone Fracture Augmentation
- Duk Young Jung, Sung Jae Lee, Seon Chil Kim, Jong Keon Oh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(2):220-226. Published online April 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.2.220
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The goal of this study using the biomechanical test was to evaluate the mechanical stability of the bone-plate fixation system according to changes of the fracture gap sizes and widths.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
For mechanical test, four types with different fracture models simulating the clinical situations were constructed depending on the gap size (FGS, mm) and the gap width (FGW, %) at the fracture site: 0 mm/0%, 1 mm/100%, 4 mm/100%, 4 mm/50%. For analyzing the effects of fracture gap on the biomechanical stability of the bone-plate fixation system, 4-point bending test was performed under all same conditions.
RESULTS
It was found that the fracture gap sizes of 1 and 4 mm decreased mechanical stiffness by about 50~60% or more. Furthermore, even without fracture gap size, 50% or more fracture gap width considerably decreased mechanical stiffness and suggested the possibility of plate damage through strain results.
CONCLUSION
Our findings suggested that at least 50% contact of the fracture faces in a fracture surgery would be maintained to increase the mechanical stability of the bone-plate fixation system.
- 662 View
- 5 Download

- A Finite Element Analysis of Biomechanical Stability of Compression Plate Fixation System in according to Existing of Fracture Gap after Bone Fracture Augmentation
- Duk Young Jung, Bong Ju Kim, Jong Keon Oh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(1):83-89. Published online January 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.1.83
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study using the finite element analysis (FEA) focused on evaluating the biomechanical stability of the LC-DCP in accordance with existing of the fracture gap at the facture site after bone fracture augmentation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
For FEM analysis, total eleven types with different fracture models considering clinical fracture cases were constructed according to the fracture gap sizes (0, 1, 4 mm)/widths (0, 25, 50, 75, 100%). Limited contact dynamic compression plate (LC-DCP) fixation system was used in this FEM analysis, and three types of load were applied to the bone-plate fixation system: compressive, torsional, bending load.
RESULTS
The results in FEM analysis showed that the 1, 4 mm fracture gap sizes and 75% or more fracture gap widths increased considerably the peak von Mises stress (PVMS) both the plate and the screw under all loading conditions. PVMS were concentrated on the center of the LC-DCP bone-plate, and around the necks of screws.
CONCLUSION
Based on the our findings, we recommend at least 50% contact of the fracture faces in a fracture surgery using the compression bone-plate system. Moreover, if x-ray observation after surgery finds 100% fracture gap or 50% or more fracture gap width, supplementary measures to improve biomechanical stability must be taken, such as restriction of walking of the patient or plastering. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Application of Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Orthopedic Splint for Bone Fracture in Small Breed Dogs
Kwangsik Jang, Eun Joo Jang, Yo Han Min, Kyung Mi Shim, Chunsik Bae, Seong Soo Kang, Se Eun Kim
Journal of Veterinary Clinics.2023; 40(4): 268. CrossRef
- Application of Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Orthopedic Splint for Bone Fracture in Small Breed Dogs
- 684 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Pediatric Forearm Bone Fractures Treated with Flexible Intramedullary Nail
- Suk Kyu Choo, Jin Hwan Kim, Hyung Keun Oh, Dong Hyun Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(2):190-195. Published online April 30, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.2.190
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To determine the usefulness of flexible intramedullary fixation in pediatric forearm diaphyseal fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed 22 cases of forearm diaphyseal fractures treated with flexible intramedullary nail and K-wire. The radiographic assessment was based on the time to union, maintenance of reduction and angular deformity. The functional outcome was assessed with the range of motion and complications at last follow up.
RESULTS
Average length of follow up was 13.9 months with mean age of 10.8 years and the time to union was 5.2 weeks. There were no angular deformity and fuctional results were excellent in all cases. There were 5 cases of soft tissue irritation of nail insertion site as post operative complication which was resolved after nail removal.
CONCLUSION
Flexible intramedullary for pediatric forearm bone fractures is an effective and safe method which gives a good functional outcome.
- 504 View
- 4 Download

Case Report
- Complete Rupture of Sciatic Nerve by Protruded Kuncher Nail in Pelvic Bone Fracture: A Case Report
- Yong Sik Kim, Nam Yong Choi, Suk Ku Han
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(4):486-489. Published online October 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.4.486
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- Rupture of sciatic nerve is a rare injury in minimally displaced pelvic bone fracture. We report one case of complete rupture of sciatic nerve that were resulted from the extremely protruded Kuncher nail inserted before accident and the preexisting heterotopic ossification with a review of the relevant literature.
- 388 View
- 0 Download

Original Articles
- Flexible Intramedullary Pin Fixation of Both Forearm Bone Fractures in Children
- Young Jin Sohn, Yong Woon Shin, Hyung Jin Chung, Sang lim Lee, Jae Kwang Yum, Yerl Bo Sung, Jong Kuk An, Eul O Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(2):271-276. Published online April 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.2.271
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the efficacy of Flexible intramedullary pin fixation in pediatric forearm diaphyseal fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In this retrospective study, we reviewed 15 cases of forearm diaphyseal fractures operated using flexible intra-medullary nail fixation technique between January 2000 and December 2004. Of these 15 children, there were 11 boys and 4 girls with an average age of 11.6 years (range, 7~15 years). The implants were introduced in the distal radius and proximal ulna in all patients. An average duration of fixation was 5.3 months in the radius, 4.7 months in the ulna. After operation, all patient were applied with a long arm cast and the duration of immobilization was 5.2 weeks (range, 4~6 weeks) on average.
RESULTS
All fractures in this series healed with normal range of supination (average 80.0) and pronation (average, 71.6 degrees). Average operation time including anesthesia was 123 minutes and hospital stay was 5.4 days. Time to union was 8.4 weeks on average. Range of motion and functional results were satisfactory in all cases. There were one case of incomplete ulnar nerve injury and two cases of refracture which were treated conservatively without any permanent complication.
CONCLUSION
Flexible intramedullary pin fixation technique is a good method in case of unstable displaced fracture and difficult or failed closed treatment.
- 471 View
- 0 Download

- Treatment of Diaphyseal Fractures of Forearm Both Bones: Comparison between Plate Fixation and Rush Pin Intramedullary Nailing
- Myung Ho Kim, Moon Jib Yoo, Hong Geun Jung, Hee Gon Park, Woo Sup Byun, Ji Yong Chun, Suk Ha Jeon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(2):215-220. Published online April 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.2.215
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the functional results between the plate fixation and Rush pin insertion for the treatment of diaphyseal fractures of the forearm both bones.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed 51 patients who were treated for diaphyseal fractures of the both forearm bones from 1995 to 2003, and evaluated them with Anderson's method. Eighteen patients were treated with plate fixation of both bones (group I), 14 patients treated with of the Rush pin insertion of the radius and plate fixation of the ulna (group II), 11 patients treated with plate fixation of the radius and Rush pin insertion of the ulna (group III), and 8 patients treated with Rush pin insertion of forearm both bones (group IV).
RESULTS
Seventeen out of eighteen cases obtained favorable result (94.4%) in group I, 12 out of 14 cases (85.7%) in group II, 7 out of 11 cases (63.3%) in group III, and 4 out of 8 cases (50.0%) in group IV with statistically significant differences between the groups (p=0.04).
CONCLUSION
Plate fixation of forearm both bones yield the best result. Thus, plate fixation of both forearm bones is recommended in treating the diaphyseal fractures of both forearm bones. At least one bone is recommended to be fixed with a plate if it is not possible to fix both forearm bones with plates. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Shaft Fractures of Both Forearm Bones: The Outcomes of Surgical Treatment with Plating Only and Combined Plating and Intramedullary Nailing
Sang Bum Kim, Youn Moo Heo, Jin Woong Yi, Jung Bum Lee, Byoung Gu Lim
Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.2015; 7(3): 282. CrossRef - Treatment of Forearm Shaft Fracture with Modified Interlocking Intramedullary Nail
Kwang-Yul Kim, Moon-Sup Lim, Shin-Kwon Choi, Hyeong-Jo Yoon
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2008; 21(2): 157. CrossRef
- Shaft Fractures of Both Forearm Bones: The Outcomes of Surgical Treatment with Plating Only and Combined Plating and Intramedullary Nailing
- 644 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Delayed Operative Treatment of Long Bone Fractures in Patients with Brain Injury
- Hong Moon Sohn, Sang Ho Ha, Jun Young Lee, Young Kwan Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(2):157-162. Published online April 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.2.157
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the postoperative progress and outcomes of bone injured patients with long bone fracture showing callus formation and deformity due to delayed surgical treatment.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
10 cases with more than 1 year follow up were chosen from 12 patients with long bone fracture whose surgical treatment was delayed due to brain injury. Exuberant callus formation and deformations were observed. Average delayed period was 6.7 weeks (4~10 weeks). Preoperative callus formation, shortening and angulation were evaluated using plain radiographs. Total operation time and transfusion amount were compared with that from operations done within 2 weeks following accident. Postoperative bone union was checked.
RESULTS
In all cases, preformed angulation and hypertrophic ossification made reduction difficult and this increased total operation time and transfusion amount but had no statistical importance. In patients with humerus and femur fractures accompanying brain injury, massive hypertrophic ossification was observed both in preoperative period and in postoperative period. Average bone union period was 13.5 weeks in humerus fractures, 17.9 weeks in femur fractures. The bone union period was shorter in subject group but had no statistical importance.
CONCLUSION
Early surgical treatment is essential to patients with long bone fracture accompanying brain injury but if early surgical treatment can not be done, proper immobilization to fracture site should be done. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Alterations in Serum Levels of Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-κB Ligand and Osteoprotegerin in Patients with Head Injury and Fracture
Shin Young Park, Kuen Tak Suh, Chang Hoon Ryu, Seung Hun Woo, Jung Sub Lee, Seong-Gang Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2008; 21(2): 145. CrossRef
- Alterations in Serum Levels of Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-κB Ligand and Osteoprotegerin in Patients with Head Injury and Fracture
- 924 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Report
- Fat Embolism in a Patient with Multiple Fractures of Cancellous Bones: A Case Report
- Eui Sung Choi, Yong Min Kim, Dong Soo Kim, Hyun Chul Shon, Kyung Jin Park, Jun Mo Jeon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(2):202-204. Published online April 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.2.202
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fat embolism is a rare complication of multiple long bone fracture or extensive soft tissue injury. The pathogenesis of fat embolism has been poorly understood and definite pathogenesis and treatment were not fully established. Respiratory failure associated with fat embolism is a major cause of death, but is usually self-limited, and is responsive to intensive treatment. We have experienced fat embolism in cancellous bone fracture which occurred in spine, distal radius and talus. Patient's fractures were treated with conservative management. The patient was recovered from fat embolism with supportive treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A case of fat embolism syndrome in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis patient
Kyung Hoon Kim, Ju Kyung Lee, Young Hun Choi, Woo Sun Kim, June Dong Park, Young Yull Koh, Dong In Suh
Allergy Asthma & Respiratory Disease.2013; 1(1): 94. CrossRef
- A case of fat embolism syndrome in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis patient
- 588 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- Reduction of Pediatric Forearm Diaphyseal Fractures by Pin Leverage Technique
- Soo Hong Han, Duck Yun Cho, Hyung Ku Yoon, Byung Soon Kim, Sung Hoon Kang, Tae Hyung Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(1):59-63. Published online January 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.1.59
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
Although the majority of children's forearm diaphyseal fractures may be treated conservatively with closed reduction and cast immobilization, unstable or irreducible fractures are usually treated by surgical management. Authors performed percutaneous pin leverage reduction technique for irreducible displaced diaphyseal fractures. The aim of this study is to determine the efficacy of pin leverage technique in pediatric forearm diaphyseal fractures MATERIALS AND METHODS: In this retrospective study, we reviewed 22 cases of forearm diaphyseal fractures reduced by percutaneous pin leverage technique between 1997 and 2002. We analyzed radiographs, operation time, hospital stay and immobilization period, range of motion, postoperative complications and functional results by Thomas.
RESULTS
Average length of follow up was 28 months with mean age of 10.5 years. All fractures in this series healed less than 2 degrees of diaphyseal angulation. Average operation time including anesthesia was 42 minutes and hospital stay was 4.6 days. Time to union was 49.6 days in average and range of motion and functional results were satisfactory in all cases except one case of congenital radioulnar synostosis. There was one case of superficial pin track infection as complication.
CONCLUSION
In operative treatment of children's diaphyseal fractures of forearm bones, percutaneous pin leverage reduction technique is a good alternative method prior to open reduction in case of difficult closed reduction. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pediatric Forearm Bone Fractures Treated with Flexible Intramedullary Nail
Suk Kyu Choo, Jin Hwan Kim, Hyung Keun Oh, Dong Hyun Kim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2007; 20(2): 190. CrossRef
- Pediatric Forearm Bone Fractures Treated with Flexible Intramedullary Nail
- 584 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Surgical Treatment of Unstable Pelvic Bone Fracture Involving Sacroiliac Joint
- Myung Ho Kim, Hee Gon Park, Moon jib Yoo, Jin Woo An
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(4):433-440. Published online October 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.4.433
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the results of surgical method using plate and screws in the treatment of unstable pelvic bone fracture involving Sacroiliac Joint.
MATERIALS AND METHOD
Authors reviewed 21 patients treated by surgical method from 1998 to 2002. Mean follow-up period was 15 months (12~24 month). Male were 16 and female were 5. We used plate and screws in 18 cases, just screws in 3 cases. We classified the type of fracture by Tile's classification and evaluated the results with Moon's criteria that based on reduction state in simple x-ray and patient's subjective satisfaction.
RESULTS
We got the bony union in all cases. By Moon's criteria, 10 cases were good, 7 cases were fair and 4 cases were poor. In 17 cases (80.9%), we got the results over fair. Mean weight bearing exercise periods were 6.4 weeks. There were 2 infection and 2 sacroiliac arthritis after operation.
CONCLUSION
As a method of surgical treatment on unstable pelvic bone fracture involving sacroiliac joint, we recommend open reduction and internal fixation with plate and screws and it may has particular advantages in early ambulation and satisfactory functional outcome.
- 467 View
- 1 Download

- Use of Cancellous Bone Allograft in the Treatment of Long bone Fractures
- Keun Bae Lee, Taek Rim Yoon, Jae Yoon Chung, Sung Taek Jung, Jae Joon Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 2001;14(4):776-782. Published online October 31, 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2001.14.4.776
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The goal of our study was to evaluate the usefulness of frozen cancellous bone allograft in the treatment of long bone fractures that had bone defect and nonunion.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
22 cases of long bone fractures(femur and tibia) with severe comminution or bone defect and nonunion were treated by operation using frozen cancellous bone allograft from March 1998 through May 2000. Thirteen were male and nine were female. The average age was 55 years old (range, 17-76 years) and the mean duration of follow-up was 20.1 months(range, 10-37 months). Eleven cases were femoral fractures, 7 cases of tibial fractures, and 4 cases of nonunion. Allografts were achieved from the patients of femoral neck fracture or osteoarthritis of the hip, and cadaveric donors. The specimens were carefully evaluated based on medical history and laboratory examination about the acute or chronic infection, and bloodtransmitted diseases. The results were evaluated by clinically, such as infection, pain at fracture site, immunological rejection and by radiologically union or resorption of allografts.
RESULTS
Radiologically, bone union was obtained in 14 cases(63.6%) at 6 months after operation, in all except two cases(90.9%) at 9 months after operation. Clinically, pain at fracture site, infection, and immunologic rejection were not observed.
CONCLUSION
In the treatment of severe comminuted fracture or nonunion of long bones, cancellous allograft transplantation after strict donor selection and appropriate screening was a good substitution for autograft avoiding of donor site morbidity or limitation in quantity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Process Conditions on the Quality Characteristics of Beef-Bone Broth
Byung-Su Kim, Gye-Won Kim, Jae-Yong Shim
Food Engineering Progress.2014; 18(1): 15. CrossRef
- Influence of Process Conditions on the Quality Characteristics of Beef-Bone Broth
- 586 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Treatment by Composite Fixation of Fractures in Osteoporotic Patients Aged over 60Years
- Keun Woo Kim, Yong Hoon Kim, Hak Jin Min, Ui Seoung Yoon, Hee Oh Kim, Young Joon Ahn, Yoon Jong Kim, Ki Chan Yoo, Sang Rim Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2001;14(1):121-127. Published online January 31, 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2001.14.1.121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study summarizes the satisfactory results obtained using a composite fixation method for the surgical treatment of long bone fractures in elderly patients with osteoporosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed 10 cases of long bone fractures, that were treated by composite fixation, involving patients over 60 years of age that presented with radiological osteoporosis. Composite fixation was applied incorporating, traditional plate and screw fixation in conjunction with bone graft, plate or intramedullary bone cement at four cases of humeral shaft fractures, three cases of femur supracondylar fractures, two cases of femur shaft fractures, and one case of tibia shaft fracture. Results were evaluated in methods of ambulation, range of motion, bony union and complications.
RESULTS
Satisfactory ambulation and range of motion was observed in all cases, which showed bony union without early implant failure. No re-operation were necessary due to nonunion. No medical complication was noted.
CONCLUSION
The results shows that the composite fixation method provided a stable reduction and a rigid fixation, which facilitated bony union, and allowed elderly patients with osteoporosis an early range of motion and mobility after the surgical treatment of long bone fractures.
- 420 View
- 0 Download

- Pelvic Bone Fractures in Children
- Byoung Suck Kim, Ye Yeon Won, Weon Ik Lee, Myeong Ryeol Song, Jae In Ahn
- J Korean Soc Fract 1998;11(1):107-114. Published online January 31, 1998
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1998.11.1.107
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The pelvic bone fractures in children were uncommon, except for avulsion injuries in the literature and authors had 21 cases of children's pelvic bone fracture, ranging from 1 to 15 years. The mode of injury, type of fracture, associated injuries, morbidity and mortality, and out-come were retrospectively analyzed. The majority of injuries were from automobile-pedestrian collisions (81.0%). the Torode and Zieg type IV injury had the greatest morbidity, mortality, and complications. sixteen patients had non-orthopedic, associated injuries and fourteen required blood transfusions within initial 48 hours after injury. Two of them passed away due to hematologic unstableness. Twenty patients were managed by conservative method, except for one operative case by using of an external fixation device. This study included only 13 cases had average 1 year of follow-up. One acetabular dysplasia of 5 acetabular fractures was found at 12 months after injury. The nonoperative approach for the pelvic bone injury has had a satisfactory outcome in our hospital. so, authors think that if conservative methods will be properly applied, it may be one of the methods of treatment for the children's pelvic bone fracture. Even though there is no symptoms, long-term follow-up will be inevitable for checking more severe acetabular dysplasia and leg length discrepancy.
- 435 View
- 0 Download

- Treatment of Carpal Bone Fracture-Dislocation using the Small-External Fixator and Internal Fixation
- Chil Soo Kwon, Young Uck Kim, Byung Hyun Jung, Kyeong Seog Kong
- J Korean Soc Fract 1995;8(1):228-233. Published online January 31, 1995
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1995.8.1.228
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Authors reviewed 3 cases of carpal bone fracture-dislocation treated with samll-external fixator and internal fixation such as K-wires or screws from October 1991 to March 1993 with above 1 year follow up. The results were as follows; 1. Mean ages were 25 years, all patients were male. 2. The causes of injury were the fall down in 2 cases and the sports injury in 1 case. 3. Cases were a palmar transscaphoid lunate dislocation, a Neglected volar dislocation of lunate, and a doral transscaphoid perilunar dislocation. 4. Advantages are as follows 1) minimize surgical dissection 2) maintenance of reduction is easy 3) ROM: full 4) painless 5) results are excellent We would like to recomment to use the small-external fixator and limited internal fixation instead of other methods for the treatment of carpal bone fracture-dislocation.
- 375 View
- 0 Download

- Surgical Treatment of Concomitant Ipsilateral Humerus and Forearm Fractures
- Jeung Tak Suh, Sung Hun Kim, Chong Il Yoo
- J Korean Soc Fract 1994;7(2):316-321. Published online November 30, 1994
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1994.7.2.316
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The term "floating elbow" refers to concomitant ipsilateral humeral and forearm bone fractures. This type of fractures is relatively rare and has few guidelines for treatment. Author reviewed 14 cases of these fractures which were treated by open reduction and rigid internal fixation in Pusan National University Hospital from January 1983 to January 1993. In follow up study, Author obtained that good results in 10 cases(71%) of patient, and fair results in 3 cases of patient. Author advocate the patient with concomitant ipsilateral humerus and forearm bone fractures should requires open reduction and stable internal fixation of the both humerus and forearm bone, as soon as possible.
- 402 View
- 0 Download

- Treatment of the Long Bone fractures Assuiated with Vascular Injuries
- Myun Whan Ahn, Yong Seok Choi, Jong Chal Ahn
- J Korean Soc Fract 1994;7(1):113-121. Published online May 31, 1994
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1994.7.1.113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Vascular injuries combined with long bone fractures have been infrequent and difficult to manage. Despite of recent advancement in the vacular repalr and fixation of fracutres, it is not easy to save the limb. In order to identify the factor associated with amputation or salvage of the affected limb, a retrospective study of 14 patients whose injured vessels were repaired primarily at the time of bone fixation was perfomed. The ischemic time, the degree of soft tissue or bone injury and the method of treatment were evaluated with relation to the limb salvage, 4(28.6%) of that 14 long bone fractures needed secondary amputation due to a vascular insufficiency. In 3 of 4 fractures, in which vascular repair were delayed over 24 hours, afftected limbs were amputated later. Thus, the ischemnic time was determined as an important factor for limb salvage after the vascular injury associated with the long bone fracture(p<0.05). However, the dogree of the soft tissue of bone injury and the method of treatment were not correlated with the limb salvage.
- 319 View
- 0 Download

- Medullary fixation with rush pin of fracture of the forearm bone in adults
- Young Chang Kim, Hae Ill Jung
- J Korean Soc Fract 1991;4(2):340-346. Published online November 30, 1991
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1991.4.2.340
- 405 View
- 1 Download

- Treatment of Intractable Nonunion of the Long Bone with the Invasive Electrical Stimulation
- Myung Chul Yoo, Dae Kyung Bae, Yong Girl Rhee, Deok Ho Ahn, Goong Hee Cho
- J Korean Soc Fract 1989;2(1):82-90. Published online June 30, 1989
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1989.2.1.82
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Nonunion of the long bone is one of the difficult porbloems in orthopaedic surgery. We studied the effect of the electrical stimulation. From July, 1980 to August, 1988, 30 nonunions of the long bones were treated with the invasive type electrical stimulator. The range of follow-up period was from 3 months to 7 years(average, 25 months). The results were as foloowings: 1. The good bony union has occurred in 26 cases(86.7%). 2. The previous infection was in 11 cases and its union rate was 100% 3. The average duration of bone union in over-all cases was 5. months and in previous infeted cases, was 5.5 months. 4. The average duration of bone union in open fracture was 5.5 months and in closed fracture, was 5 months. 5. The invasive electrical stimulation was a good technique to treat the intractable nonunion as the result of long bone fracture.
- 342 View
- 0 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


