Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 22(4); 2009 > Article
-
Original Article
- The Surgical Treatment of Distal Femur Medial Condyle Fracture Using Lateral Anatomical Plate of Opposite Side through Medial Approach
- Sung-Sik Ha, M.D., Jae-Chun Sim, M.D., Ki-Do Hong, M.D., Jae-Young Kim, M.D., Kwang-Hee Park, M.D., Yoon-Ho Choi, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2009;22(4):246-251.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.4.246
Published online: October 30, 2009
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Samyook Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Jae-Chun Sim, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Samyook Medical Center, 29-1, Hwigyoung-2-dong, Dongdaemoon-gu, Seoul 130-711, Korea. Tel: 82-2-2210-3581, Fax: 82-2-2217-1897, cyh143@freechal.com
• Received: April 27, 2009 • Revised: July 17, 2009 • Accepted: October 6, 2009
Copyright © 2009 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 1,368 Views
- 21 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To evaluate clinical and radiological results of surgical treatment of distal femur medial condyle fracture using lateral anatomical plate of opposite side through medial approach.
-
Materials and Methods
- This study reviewed the results of 9 cases of distal femur medial condyle fracture treated with lateral anatomical plate of opposite side through medial approach from December 2005 to June 2007, after a follow up of more than 12 months. There were 2 males and 7 females with a mean age of 63.1 (57~72) years. The clinical results were evaluated using the Schatzker's criteria, and the radiographic results were evaluated using the bone union time.
-
Results
- Using the Schatzker's criteria, 7 cases of the 9 patients (78%) showed exellent results. The mean time for bone union was 13.4 (11~15) weeks. There were 3 cases of pain on full weight bearing same as previous operative state by degenerative osteoarthritis. There weren't complications as joint stiffness, infection, varus & rotational deformity, malunion, nonunion, and metal failure.
-
Conclusion
- Plate fixation using medial approach provides the proper anatomical reduction and stronger fixation, and outcome good results.
- 1. Borgen D, Sprague BL. Treatment of distal femoral fractures with early weight-bearing. A preliminary report. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1975;111:156-162.
- 2. Butt MS, Krikler SJ, Ali MS. Displaced fractures of the distal femur in elderly patients. Operative versus non-operative treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1996;78:110-114.
- 3. Chiron HS, Trémoulet J, Casey P, Müller M. Fractures of the distal third of the femur treated by internal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1974;100:160-170.Article
- 4. Giles JB, DeLee JC, Heckman JD, Keever JE. Supracondylar-intercondylar fractures of the femur treated with a supracondylar plate and lag screw. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1982;64:864-870.Article
- 5. Hahn SH, Yang BK, Yi SR, Chung SW, Lee JO. Treatment of the distal femoral fracture with anatomical bone plate. J Korean Soc Fract, 2000;13:258-266.Article
- 6. Healy WL, Brooker AF Jr. Distal femoral fractures. Comparison of open and closed methods of treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1983;174:166-171.
- 7. Höntzsch D. Distal femoral fracture--Clinical possibilities. Kongressbd Dtsch Ges Chir Kongr, 2001;118:371-374.
- 8. Johnson KD, Hicken G. Distal femoral fractures. Orthop Clin North Am, 1987;18:115-132.Article
- 9. Kwon H, Kim DW, Sohn CS, et al. Metal failure after plate fixation for femur fracture. J Korean Soc Fract, 1997;10:371-378.Article
- 10. Mize RD. Surgical management of comlex fractures of the distal femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1989;(240):77-86.
- 11. Moon ES, Lee KB, Jeong JW. Anatomical plate fixation for distal femur fracture. J Korean Soc Fract, 1999;12:294-300.Article
- 12. Ostermann PA, Neumann K, Ekkernkamp A, Muhr G. Long term results of unicondylar fractures of the femur. J Orthop Trauma, 1994;8:142-146.Article
- 13. Ostrum RF, Geel C. Indirect reduction and internal fixation of supracondylar femur fractures without bone graft. J Orthop Trauma, 1995;9:278-284.Article
- 14. Schatzker J. Fractures of the distal femur revisited. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1998;347:43-56.Article
- 15. Schatzker J, Home G, Waddell J. The Toronto experience with the supracondylar fracture of the femur, 1966-72. Injury, 1974;6:113-128.Article
- 16. Schatzker J, Lambert DC. Supracondylar fractures of the femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1979;138:77-83.Article
- 17. Schatzker J, Tile M. The rationale of operative fracture care. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer-Verlg; 1996. p. 395.
- 18. Shewring DJ, Meggitt BF. Fractures of the distal femur treated with the AO dynamic condylar screw. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1992;74:122-125.ArticlePDF
- 19. Siliski JM, Mahring M, Hofer HP. Supracondylar-intercondylar fractures of the femur. Treatment by internal fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1989;71:95-114.Article
- 20. Stewart MJ, Sisk TD, Walace SL Jr. Fractures of the distal third of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg, 1966;48:784-807.Article
- 21. Stover M. Distal femur fractures: current treatment, results and problems. Injury, 2001;32:SC3-SC13.
- 22. Vallier HA, Hennessey TA, Sontich JK, Patterson BM. Failure of LCP condylar plate fixation in the distal part of the femur. A report of six cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2006;88:846-853.
- 23. Volpin G, Dowd GS, Stein H, Bentley G. Degenerative arthritis after intra-articular fractures of the knee. Long-term results. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1990;72:634-638.PDF
- 24. Yune SH, Rhee KJ, Park CH, Byun KY, Lee SY, Rho SK. Importance of maintenance medial buttress in treatment of supra-condylar and inter-condylar (T-condylar) fracture of the femur. J Korean Soc Fract, 1996;9:567-573.
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
(A) Preoperative radiographs show posterior displacement and rotational deformity of medial condyle of 69-year-old woman with right femur medial condyle fracture after traffic accident.
(B) Immediate postoperative radiographs show the plate fixation using lateral anatomical plate of opposite side through medial approach.
(C) Postoperative 27 months radiographs show complete bone union, good by Schaztker's criteria, and 5~130° knee ROM.


Fig. 2
(A) Preoperative radiographs show posterior displacement and valgus deformity of medial condyle of 70-year-old woman with right femur medial condyle fracture after slip down.
(B) Immediate postoperative radiographs show the plate fixation using lateral anatomical plate of opposite side through medial approach.
(C) Postoperative 26 months radiographs show complete bone union, excellent by Schaztker's criteria, and 0~125° knee ROM.


Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Medial Plating of Distal Femoral Fracture with Locking Compression Plate-Proximal Lateral Tibia: Cases' Report
Se-Ang Jang, Young-Soo Byun, In-Ho Han, Dongju Shin
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2016; 29(3): 206. CrossRef
The Surgical Treatment of Distal Femur Medial Condyle Fracture Using Lateral Anatomical Plate of Opposite Side through Medial Approach
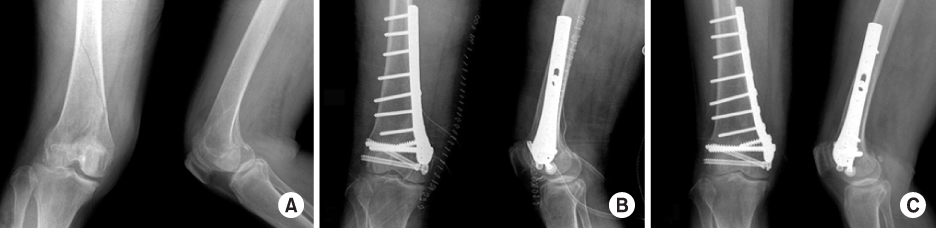

Fig. 1
(A) Preoperative radiographs show posterior displacement and rotational deformity of medial condyle of 69-year-old woman with right femur medial condyle fracture after traffic accident.
(B) Immediate postoperative radiographs show the plate fixation using lateral anatomical plate of opposite side through medial approach.
(C) Postoperative 27 months radiographs show complete bone union, good by Schaztker's criteria, and 5~130° knee ROM.
Fig. 2
(A) Preoperative radiographs show posterior displacement and valgus deformity of medial condyle of 70-year-old woman with right femur medial condyle fracture after slip down.
(B) Immediate postoperative radiographs show the plate fixation using lateral anatomical plate of opposite side through medial approach.
(C) Postoperative 26 months radiographs show complete bone union, excellent by Schaztker's criteria, and 0~125° knee ROM.
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
The Surgical Treatment of Distal Femur Medial Condyle Fracture Using Lateral Anatomical Plate of Opposite Side through Medial Approach
Schatzker's criteria
Patients of distal femur medial condyle fracture using lateral anatomical plate of opposite side through medial approach
Table 1
Schatzker's criteria
Table 2
Patients of distal femur medial condyle fracture using lateral anatomical plate of opposite side through medial approach

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS


 Cite
Cite

