Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Musculoskelet Trauma > Volume 21(4); 2008 > Article
-
Original Article
- Cause and Treatment of Extraarticular Proximal Tibial Nonunion
- Sung Soo Kim, M.D., Sung Keun Shon, M.D., Kyu Yeol Lee, M.D., Chul Hong Kim, M.D., Myung Jin Lee, M.D., Min Soo Kang, M.D., Lih Wang, M.D., Im Sic Ha, M.D.
-
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society 2008;21(4):279-285.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.4.279
Published online: October 31, 2008
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea.
*Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Dong-Eui Medical Center, Busan, Korea.
- Address reprint requests to: Lih Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, 3-1, Dongdaesin-dong, Seo-gu, Busan 602-715, Korea. Tel: 82-51-240-2593, Fax: 82-51-254-6757, libi33@dau.ac.kr
Copyright © 2008 The Korean Fracture Society. All rights reserved.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 482 Views
- 2 Download
Abstract
-
Purpose
- To analyze the factors affecting the nonunion of extraarticular proximal tibial fracture and the outcome of nonunion treatment.
-
Materials and Methods
- We investigated 51 cases of extraarticular proximal tibial fractures from June 2002 to May 2006. The nonunion rate was assessed in relation to several risk factors and the treatment outcome of nonunion using plate fixation with bone graft was assessed by Klemm and Börner functional rating system.
-
Results
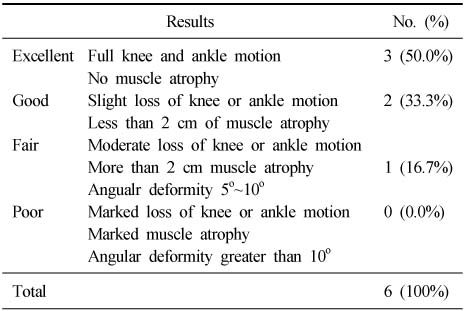
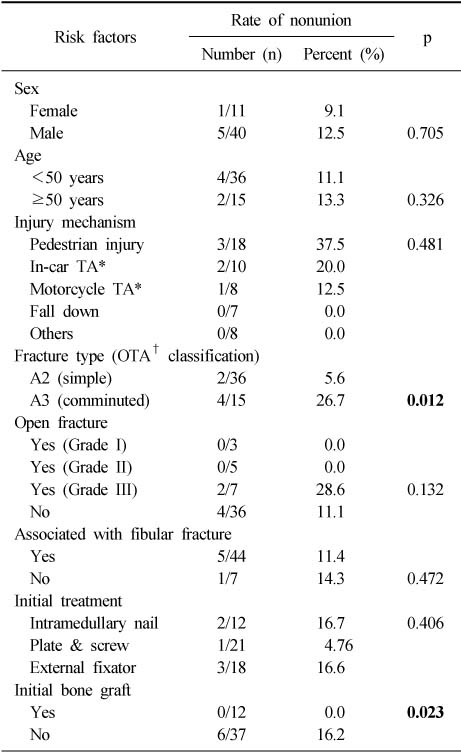
- 6 cases of nonunion (11.8%) was noted among 51 cases, and the risk factors examined, OTA A3 comminuted fracture was associated with a high nonunion rate with statistical significance and initial bone graft had a significant effect in bone healing. Excellent and good results were obtained in 5 cases (83.3%) and bone union was achieved in all nonunion cases.
-
Conclusion
- Comminution was found to be an important factor affecting the nonunion in extraarticular proximal tibial fracture, and bone graft in primary operation could reduce the chance of nonunion. Accurate plate fixation with bone graft is a reliable option in nonunion treatment.
- 1. Blick SS, Brumback RJ, Lakatos R, Poka A, Burgess AR. Early prophylactic bone grafting of high-energy tibial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1989;240:21-41.Article
- 2. Borrelli J Jr, Prickett W, Song E, Becker D, Ricci W. Extraosseous blood supply of the tibia and the effects of different plating techniques: a human cadaveric study. J Orthop Trauma, 2002;16:691-695.Article
- 3. Boyd HB, Lipinski SW, Wiley JH. Observations on non-union of the shafts of the long bones with a statistical analysis of 842 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1961;43:159-168.Article
- 4. Bradley GW, Mckenna GB, Dunn HK, Daniels AU, Statton WO. Effects of flexural rigidity of plates on bone healing. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1979;61:866-872.Article
- 5. Carpenter CA, Jupiter JB. Blade plate reconstruction of metaphyseal nonunion of the tibia. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1996;332:23-28.Article
- 6. Cattaneo R, Catagni M, Johnson EE. The treatment of infected nonunions and segmental defects of the tibia by the methods of Ilizarov. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1992;280:143-152.Article
- 7. Charnley J. Fractures of the shaft of the tibia. the closed treatment of common fractures. 3rd ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone; 1961. p. 209-249.
- 8. Ebraheim NA, Skie MC, Jackson WT. The treatment of tibial nonunion with angular deformity using an Ilizarov device. J Trauma, 1995;38:111-117.Article
- 9. Edwards CC, Jaworski MF, Solaria J, Aronson BS. Management of compound tibial fractures using external fixation. Am Surg, 1979;45:190-203.
- 10. Gardner MJ, Toro-Arbelaez JB, Boraiah S, Lorich DG, Helfet DL. Surgical treatment and outcomes of extraarticular proximal tibial nonunions. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 2008;128:833-839.PDF
- 11. Gershuni DH, Halma G. The A-O external skeletal fixator in the treatment of severe tibia fractures. J Trauma, 1983;23:986-990.
- 12. Helfet DL, Shonnard PY, Levine D, Borrelli J Jr. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of distal fracture of tibia. Injury, 1997;28:Suppl 1. A42-A47.
- 13. Kim KH, Wee KH, Back SH. A clinical study of non-union and delayed union. J Korean Orthop Assoc, 1983;18:921-929.PDF
- 14. Klemm KW, Börner M. Interkocking nailing of complex fractures of the femur and tibia. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1986;212:89-100.
- 15. Laflamme GY, Heimlich D, Stephen D, Kreder HJ, Whyne CM. Proximal tibial fracture stability with intramedullary nail fixation using olique interlocking screws. J Orthop Trauma, 2003;17:496-502.
- 16. Lee HJ, Park YU. Treatment of proximal tibial non-union after IM nailing in conjunction with anterior buttress plating. J Korean Fract Soc, 2004;17:138-141.
- 17. Lee HS, Kim JJ, Oh SK, Ahn HS. Treatment of distal tibial metaphyseal fracture using MIPPO technique. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc, 2004;8:166-170.
- 18. McLaren AC, Blokker CP. Locked intramedullary fixation for metaphyseal malunion and nonunion. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1991;265:253-260.
- 19. Moon MS, Woo YK, Ha KY, Yeon G. A clinical analysis of nonunion of the long bones in lower extremity. J Korean Orthop Assoc, 1989;24:15-26.PDF
- 20. Morandi M, Zembo MM, Ciotti M. Infected tibia pseudarthrosis. A 2-year follow up on patients treated by Ilizarov technique. Orthopedics, 1989;12:497-508.
- 21. Mueller CA, Eingarner C, Scheitmueller E, et al. Primary stability of various forms of osteosynthesis in the treatment of fractures of the proximal tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2005;87:426-432.
- 22. Nork SE, Barei DP, Schildhauer TA, et al. Intramedullary nailing of proximal quarter tibial fractures. J Orthop Trauma, 2006;20:523-528.
- 23. Oh JK, Oh CW, Jeon IH, et al. Percutaneous plate stabilization of proximal tibial fractures. J Trauma, 2005;59:431-437.
- 24. Paley D, Chaudray M, Pirone AM, Lentz P, Kautz D. Treatment of malunions and malnonunions of the femur and tibia by detailed preoperative planning and the Ilizarov techniques. Orthop Clin North Am, 1990;21:667-691.
- 25. Phieffer LS, Goulet JA. Delayed unions of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2006;88:206-216.
- 26. Stegemann P, Lorio M, Soriano R, Bone L. Management protocol for unreamed interlocking tibial nails for open tibial fractures. J Orthop Trauma, 1995;9:117-120.
REFERENCES
A 27-year-old male involved in a incar traffic accident suffered a closed comminuted (OTA A3) proximal tibial fracture.
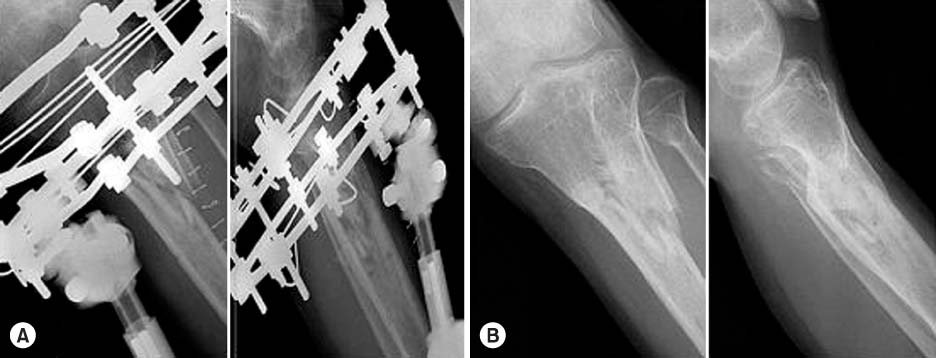
(A) A 55-year-old male involved in a pedestrian traffic accident suffered a open comminuted (G-A Grade II, OTA A3) proximal tibial fracture.
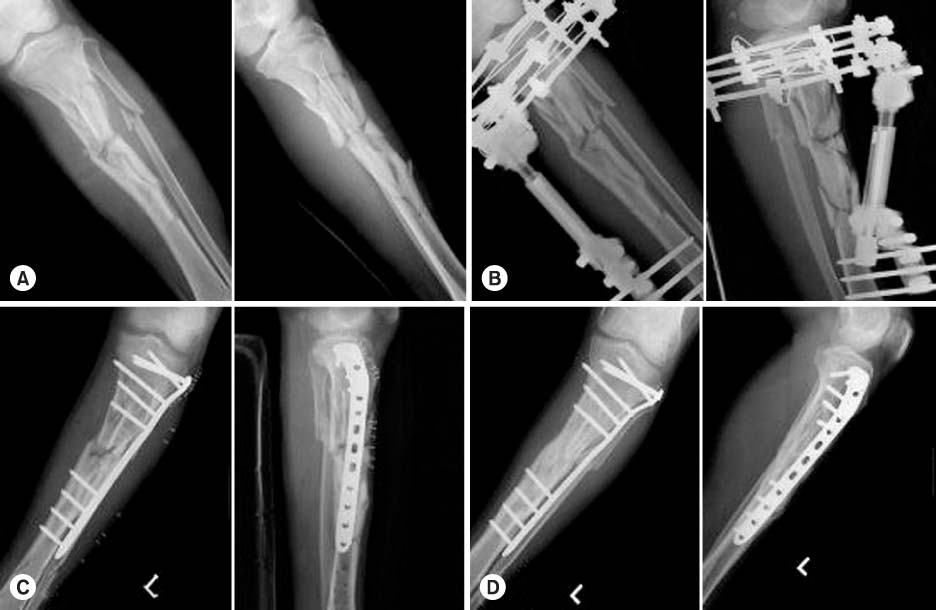
Figure & Data
REFERENCES
Citations

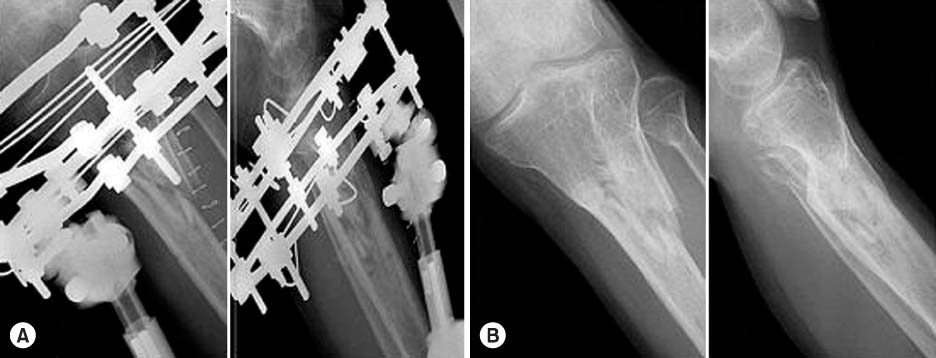
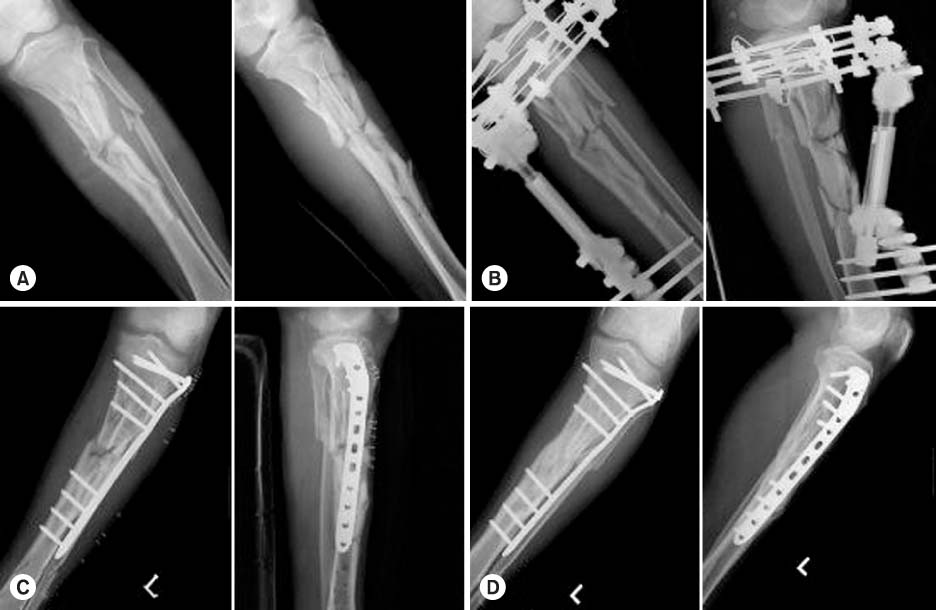
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Functional results of the nonunion patients by Klemm and Börner classification
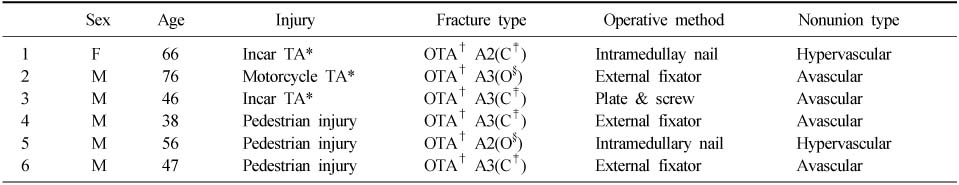
Data analysis of proximal tibial nonunion patients
*TA: Traffic accident, †OTA: Orthopedic Trauma Association, ‡C: Closed fracture, §O: Open fracture.
Statistic analysis of nonunion rate related to risk factors
*TA: Traffic accident, †OTA: Orthopedic Trauma Association.
*TA: Traffic accident, †OTA: Orthopedic Trauma Association, ‡C: Closed fracture, §O: Open fracture.
*TA: Traffic accident, †OTA: Orthopedic Trauma Association.

 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS
 Cite
Cite

