Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
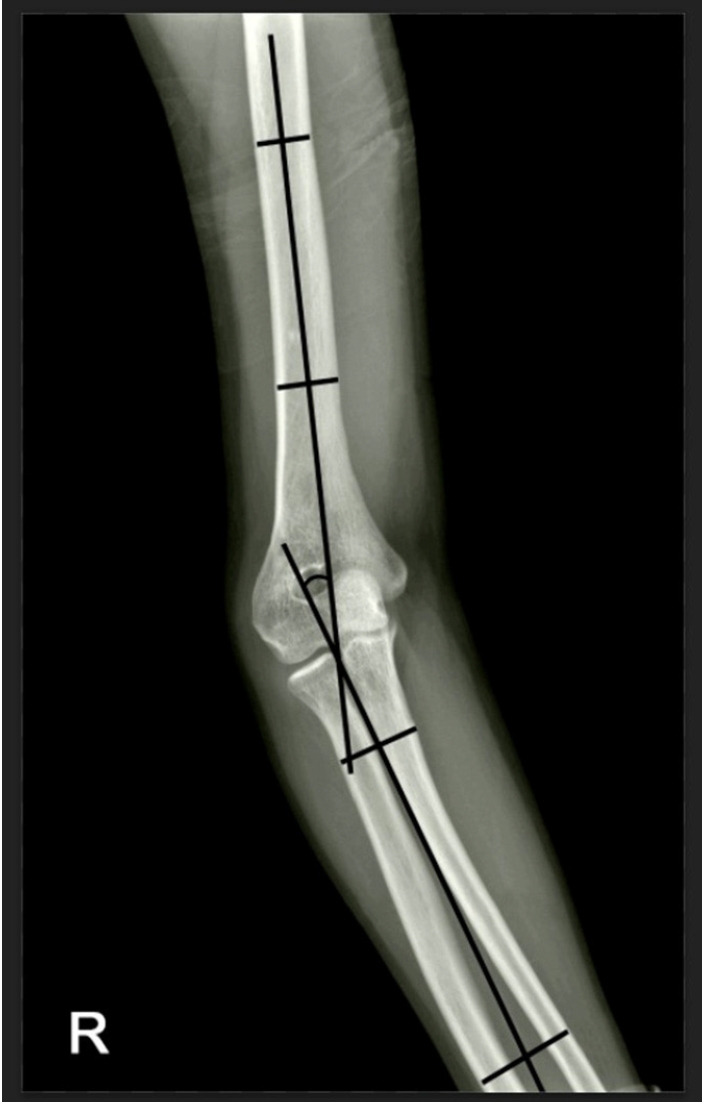
- Reverse V step-cut osteotomy for the correction of cubitus varus in adults: a retrospective study
- Jinyoung Bang, Hyung Jun Koo
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):102-108. Published online April 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00045
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Cubitus varus deformity in adults most commonly occurs as a late complication resulting from malunion of distal humeral fractures sustained during childhood. This deformity can cause cosmetic problems and anatomical deformities that hinder normal sports activities and potentially lead to long-term complications. Although various surgical techniques exist for correcting cubitus varus, this study investigated the clinical and functional outcomes of reverse V step-cut osteotomy.
Methods
In total, 15 patients underwent surgical treatment with reverse V step-cut osteotomy between 2012 and 2023. The mean age of the patients at the time of surgery was 46.3 years (range, 20–65 years). The preoperative carrying angle was ‒11.09° of varus, which was corrected to +12.81° of valgus postoperatively. The mean preoperative lateral prominence index (LPI) was ‒10.03, and the mean postoperative LPI improved to ‒4.48. A comparison to the unaffected side showed a P-value of 0.978, indicating similarity.
Results
Preoperatively, eight patients exhibited signs of posterolateral rotatory instability, and among them, three underwent concomitant lateral ulnar collateral ligament reconstruction. Seven patients reported ulnar nerve symptoms, and all underwent concurrent ulnar nerve release. Postoperatively, improvements in elbow pain, instability, and ulnar nerve symptoms were observed. One patient required reoperation due to malunion and insufficient correction, but no other complications were noted.
Conclusions
These outcomes demonstrate that reverse V step-cut osteotomy can be an effective treatment method for cubitus varus deformity in adults. Level of evidence: IV.
- 1,964 View
- 56 Download

- Analysis of the Changes in Femoral Varus Bowing and the Factors Affecting Nonunion for the Treatment of Femoral Shaft Fractures over 60 Years Old Using Piriformis Fossa Insertion Intramedullary Nailing
- Yonghan Cha, Chan Ho Park, Jun-Il Yoo, Jung-Taek Kim, WooSuk Kim, Ha-Yong Kim, Won-Sik Choy
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(2):65-71. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.2.65
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
This study examined the bony morphological changes to analyze the factors affecting bony union in the treatment of elderly femoral shaft fractures with varus bowing using piriformis fossa insertion intramedullary nailing.
Materials and Methods
This study included 26 patients over 60 years of age, who were admitted for femoral shaft fractures between January 2005 and December 2014 and treated with piriformis fossa insertion intramedullary nailing. Age, sex, height, weight, bone mineral density, injury mechanism, fracture type, diameter and length of the nail, postoperative lengthening of the femur, postoperative change in varus angle, contact between the lateral and anterior cortex, and the gap between the fracture line and the bony union were checked. The patients were divided into a varus group and nonvarus group, as well as a bone union group and nonunion group. Logistic regression analysis was performed to analyze the factors affecting nonunion.
Results
The patients were classified into 11 in the varus group and 15 in the non-varus group and 24 in the union group and 2 in the nonunion group. The varus group showed a larger increase in leg length and varus angle reduction than the non-varus group (p<0.05). The union group had more contact with the lateral cortical bone than that of the nonunion group (p<0.05). The factor affecting bone union in regression analysis was contact of the lateral cortical bone (p<0.05).
Conclusion
Treatment of a femoral shaft fracture in elderly patients with a varus deformity of the femur using piriformis fossa insertion intramedullary nail increases the length of the femur and decreases the varus deformity. For bony union, the most important thing during surgery is contact of the lateral cortical bone with the fracture site. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Straight nail insertion through a laterally shifted entry for diaphyseal atypical femoral fractures with bowing: good indications and limitations of this technique
Seong-Eun Byun, Young-Ho Cho, Young-Kyun Lee, Jung-Wee Park, Seonguk Kim, Kyung-Hoi Koo, Young Soo Byun
International Orthopaedics.2021; 45(12): 3223. CrossRef
- Straight nail insertion through a laterally shifted entry for diaphyseal atypical femoral fractures with bowing: good indications and limitations of this technique
- 1,056 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Modified Step-cut Osteotomy of Distal Humerus for the Correction of Cubitus Varus Deformity in Children
- Yeo Hon Yun, Jun Gyu Moon, Duk Moon Chung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2004;17(3):287-294. Published online July 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2004.17.3.287
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
evaluate the radiologic and clinical results of modified step-cut osteotomy for correction of cubitus varus deformity in children.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We analysed 16 children who had varus deformity preoperatively and received modified step-cut osteotomy. The results were evaluated by final follow-up radiographs and clinical results, which were humeral-elbow-wrist angle, lateral prominence, range of motion and complications.
RESULTS
The average preoperative humeral-elbow-wrist (HEW) angle was -15.8degrees and average last follow-up HEW angle was +6.7degrees Lateral prominence under 5 mm occurred in 3 cases and one children showed limited motion and transient ulna neuropathy.
CONCLUSION
The results demonstrate that modified step-cut osteotomy achieve good correction of cubitus varus without lateral bony prominence or complications.
- 403 View
- 1 Download

- The Lateral Closing Osteotomy using Threaded Steinmann Pin for the Cubitus Varus Deformity Followed by Supracondylar Fracture around the Elbow
- Jin Hak Kim, Song Lee, Byung Ki Kwon, Hyun Soo Kim, Soon Young Jeong, Dea Jung Choi
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(3):370-378. Published online July 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.3.370
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To investigate the usefulness of closing wedge osteotomy with threaded steinmann pin and wiring for the treatment of cubitus varus deformity after elbow fracture during childhood.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From February 1994 to February 2002. We performed closing wedge osteotomy with threaded steinmann pin and wiring in 16 elbows with cubitus varus deformity. There are 11 men and 5 women. Mean age was 21.6 years and mean follow-up was 19.2 months. Mean deformed carrying angle was varus 21.7 degree. Mean period from initial injury to treatment was 16.5 years.
RESULTS
Mean angle that was corrected by above operation methods was valgus 12 degree. Average periods of immobilization was 27.8 days. One tardy ulnar nerve syndrome before surgery was solved at 8 weeks after operation. 2 cases with superficial infection was treated easily. 14 cases of all were estimated as good with Oppenheim's criteria.
CONCLUSION
Closing wedge osteotomy with threaded steinmann pin and wiring makes early range of motion exercise being possible as rigid fixation. The supracondylar closing wedge osteotomy with threaded Steinmann pin and wiring is thought to be the useful method.
- 391 View
- 1 Download

- Comparison study between valgus and varus type in Neer 's 3 and 4 part proximal humerus fracture
- Chang Hyuk Choi, Koing Woo Kwon, Shin Kun Kim, Sang Wook Lee, Dong Kyu Shin, Seung Jin Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(4):558-565. Published online October 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.4.558
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
We reclassified three- and four-part proximal humerus fractures by Neer ' s classification into valgus & varus type, and compared the results of these groups. MATERIALS & METHODS: 21 cases classified as three- and four-part fracture in Neer 's classification were treated surgically and followed for 12 months. We reclassfied the 21cases valgus and varus type fractures, according to angulation of fractures, facing of humeral head, and dominant displaced tuberosity. Functional evaluation was done by UCLA shoulder rating scale.
RESULTS
Neer 's three- and four-part proximal humerus fractures could be reclassified based on angulation, facing of humeral head, and dominant tuberosity displacement. The functional results according to UCLA shoulder rating scale were good or excellant in 8 of 9 cases of valgus type(89%), and at 4 in 10 cases of varus type(40%). The clinical result of the valgus type was better than that of the varus type.
CONCLUSION
Based on reclassification system of proximal humerus fractures, clinical results and radiographic findings including angulation, facing of head, and dominant tuberosity displacement showed close relationship. Neurovascular complication were more frequent in the varus type. Therefore, careful evaluation including surgical approach and soft tissue status should be considered in the varus type of complex proximal humerus fracture.
- 514 View
- 4 Download

- Cubitus Varus Resulted from Fracture-Separation of the Distal Humeral Epiphysis
- Sung Soo Kim, Sang Hwan Park, Kyoung Sik Hwang
- J Korean Soc Fract 2001;14(4):769-775. Published online October 31, 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2001.14.4.769
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
We tried to find the cause of cubitus varus after treatment of fracture separation of the distal humeral epiphysis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed 13 cases of fracture-separation of the distal humeral epiphysis. Five cases were treated by open reduction and K-wire fixation, 8 cases were treated by closed reduction and K-wire fixation. Six cases of cubitus varus were evaluated.
RESULTS
With the average 27 months(14-96 months) of follow-up, six of 13 cases showed cubitus varus postoperatively and mean carrying angle was -6.7 degrees(range -3~-15 degrees). None of these cases showed the progression of deformity after then. Among the six cases, five cases were treated with closed reduction, and one case with open reduction. Average age of the cubitus varus cases was 31 months (14-60 months). Among the six cases, four cases were Salter-Hams type I and two cases were type II.
CONCLUSION
Incomplete reduction seems to be the cause of cubitus varus in fracture-separation of the distal humeral epiphysis, so the anatomical reduction is important to prevent the cubitus varus.
- 385 View
- 0 Download

- Varus Stress Test and Percutaneous Fixation of the Lateral Condyle Fracture of the Humerus in Children
- Sung Soo Kim, Sang Ki Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(4):1053-1060. Published online October 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.4.1053
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The current study is planned to evaluate varus stress test and a result of percutaneous K-wire fixation in the minimally displaced lateral condyle fracture of humerus in children.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We have analyzed seven patients of Jakob stage I or II lateral condylar fracture of the humerus clinically and radiologically who were managed with closed reduction and percutaneous K-wire fixation from July 1996 to June 1999. Their ages at the time of injury ranged 2.5 to 11.7 years (average 6.3 years). We checked varus stress view for evaluating fracture stability and treatment plan.
RESULTS
The patients were followed up for average 13 months postoperatively and showed no differences in carrying angle, range of motion and physical activity compared with contralateral elbow. K-wires were removed average 6 weeks postoperatively. The fractures were united at average 5.9 weeks (5-9 weeks). There were minor complications ; one case of bony overgrowth, three cases of bony spur and one case of pin site infection. The treatment results according to Hardacre's assessment were excellent in all cases.
CONCLUSION
Varus stress view is necessary to evaluate the fracture stability and to make treatment plan in minimally displaced lateral condyle fracture, and closed reduction followed by percutaneous K-wire fixation can be used successfully in the cases of unstable Jakob stage I and reducible Jakob stage II.
- 314 View
- 0 Download

- Causative Factor for Cubitus Varus Deformity in Severely Displaced Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children : s Rotational Deformity of Distal Fragment Needed to be Acurately Reduced?
- Seung Woo Suh, Jeong Ho Park, Jong Gun Oh, Seung Ju Chun, Jeong Ro Yoon, Seok Hyun Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 1997;10(3):712-717. Published online July 31, 1997
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1997.10.3.712
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We reviewed retrospectively 53 cases of supracondylar fracture of humerus in children which were severely displaced(Gartland type III). All patients were treated with closed reduction and percutaneous pinning. Purpose of this study is to evaluate the residual effect of incompletely reduced fragment, especially of rotation of distal fragment(represented by fish-tail sign) on clinical relults. The quality of reduction was determined by carrying angle, varus tilting, existence of fish-tail sign and medial displacement. Of the 53 elbows, fish tail signs only presented in twelve cases(50.0%), medial tilting combined with fish tail in five(20.8%) and medial displacements in seven cases(29.2%). Final results by Flynn et al. were as follows; Excellent was in 40 cases(15.9%), Good in 6(11.3%), Fair in 1(1.8%), poor in 6(11.3%). Six cases of poor outcomes resulted from cubitus varus deformed elbow, of which cubitus varus deformity developed in 5 cases of medial tilted distal fragment, one developed in medially displaced fragment, and cases presented with fish tail sign(rotation of distal fragment) had no contribution to cubitus varus deformity yielding acceptable clinical results. In conclusion, even though the quantification of fish tail sign is needed, fish tail sign only presenting on fluorscopy might be acceptable in operative room.
- 366 View
- 0 Download

- Treatment of Cubitus Varus Using Tension Band Wiring after the Supracondylar Osteotomy
- Dne Yong Han, Hui Wan Park, Dong Eun Shin, Ki Won Suh
- J Korean Soc Fract 1997;10(3):678-684. Published online July 31, 1997
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1997.10.3.678
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cubitus varus is the most common angular deformity that results from supracondylar fractures in children. Although this deformity rarely limit elbow function, the correction is frequently requested due to cosmetic problem. This paper was prepared to describe the operative method and to evaluate the clinical results of tension band wirinB after distal humeral supracondylar osteotomy for cubitus varus. The result was evaluated using Oppenheim criteria. Excellent or good cases were 94.4%. We concluded that tension band wiring is a satisfactory method of treatment for cubitus varus.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of tension-band osteosynthesis for cubitus varus deformity in pediatric patients: A retrospective review
Man Duc Minh Phan, Terry Richard Light, Tiep Van Phan, Phi Duong Nguyen
Journal of Hand and Microsurgery.2025; 17(2): 100213. CrossRef
- Evaluation of tension-band osteosynthesis for cubitus varus deformity in pediatric patients: A retrospective review
- 444 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Supracondylar Osteotomy for Cubitus Varus and Valgus
- Duk Seop Shin, Jong Chul Ahn, Se Dong Kim, Yong Seok Choi
- J Korean Soc Fract 1994;7(1):49-57. Published online May 31, 1994
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1994.7.1.49
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Between December 1989 and january 1944, 17 corrective supracondylar osteotomy of humerus for cubitus varus and valgus were performed at department of orthopaedic surgery in Yeugnam University. Supracondylar fracture was the most common cause of deformity Average age at operation was 18.6 years old and average follow up period was 14 months. The operation was done under the comprehensive preoperative plan, and Internal fixation was done with K-w,res ,n younger patients, and with plates and screws in elder ones(77%). Period for external fixation could be shortened by firm internal fixation. The result was exllent in nine cases, good in four, and poor in four. No ulna and radial nerve palsy were found in operation of cubitus varus. There were three tardy ulna nerve palsy In cubitus valgus, then anterior transposition of ulna nerve was done.
- 449 View
- 3 Download

- Supracondylar Osteotomy for Cubitus Vnrus Deformity by Using Plate in Adults
- Hyun Ki Yoon, Sung Seok Soe, Young Ku Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 1992;5(2):319-324. Published online November 30, 1992
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1992.5.2.319
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cubitus varus deformity is the most common complication of supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. For the correction of this deformity, three basic types of osteotomies were known. Among them, the lateral closing wedge osteotomy is the easiest, safest and the most stable method. After osteotomy, the methods of fixation are plate fixation, crossed kirschner wires, staple, and French techniques. Between 1987 and 1991, 15 corrective supracondylar osteotomy of the humerus in adults were perromed at department of orthopaedic surgery inje University, Paik hoshpital Pusan, Korea. All were fixed with plate and screws. From this small series of retrospective study, the authors concluded that plate fixation is good method for the prevention of complication after osteotomy and results are satisfactory.
- 352 View
- 0 Download

- Supracondylar osteotomy for cubitus varus deformity in adult
- Ik Dong Kim, Poong Taek Kim, Byung Chul Park, Young Goo Lyu, Il Hyung Park, Byung Guk Min
- J Korean Soc Fract 1991;4(1):22-29. Published online May 31, 1991
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1991.4.1.22
- 535 View
- 0 Download

- The Supracondylar Osteotomy for the Angular Dformity followed by a Fracture Around the Elbow
- Soo Ill Kang, Kang Hyung Lee, Chan Su Park, Myung Ku Kim, Myung Seon Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1990;3(1):103-109. Published online May 31, 1990
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1990.3.1.103
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The fracture around the elbow is frequent in the children. The cubitus varus and cubitus valgus deformities are the common late complications of the elbow fracture. The reason of correction for these problem is not the elbow fuction, but the cosmetic problem of tardy ulnar nerve palsy. We performed five supracondylar osteotomies that are modification of Milch osteotomy from Mar, 1988 to Jan, 1989 of which four cases were cubitus varus and one case was cubitus valgus at In Chon Christian Hospital. The results were as follows; 1. the cubitus varus deformities were four cases and the cubitus balus deformity was one. 2. The injuries were supracondylar fractures of the humerus for the cubitus varus and lateral condyle fracture of the humerus for the cubitus valgus. 3. The result was excellent by modified Milch osteotomy with derotation in the case of rotational deformity. 4. In adult, the bone healing was promoted by deepening the triangular shaped notch in the Milch osteotomy by widening the contact surface.
- 409 View
- 1 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


