Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Surgical outcomes of the coracoid process fracture associated with the acromioclavicular joint injury in Korea: a case series
- Dongju Shin, Sung Choi, Sangwoo Kim, Byung Hoon Kwack
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2026;39(1):54-61. Published online January 14, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00346
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
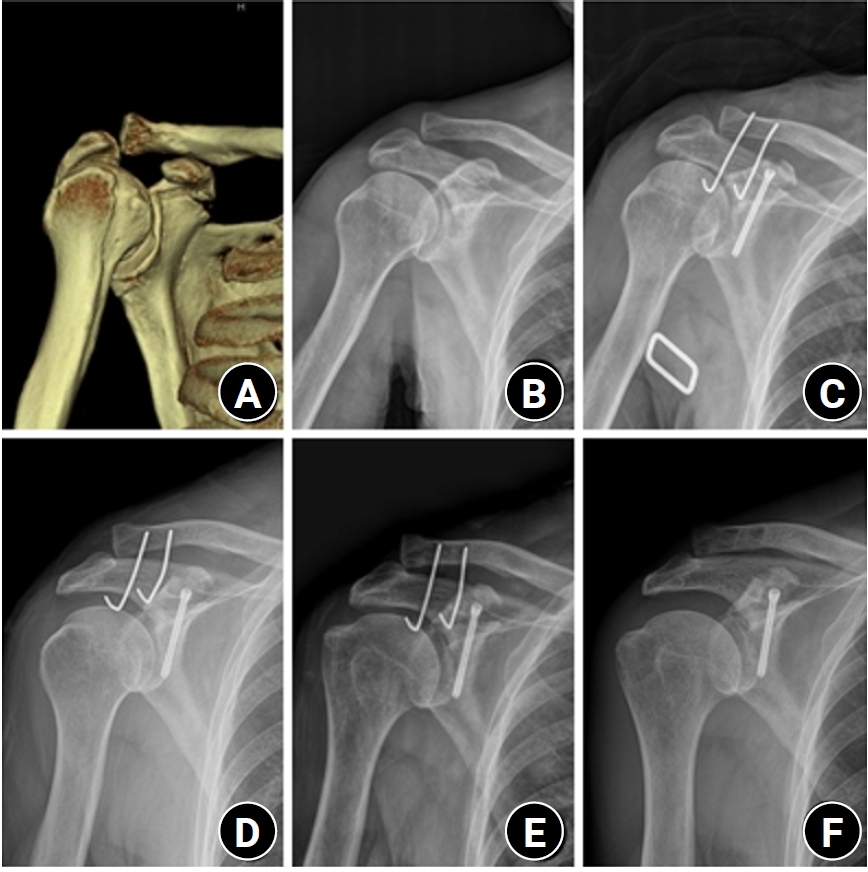
Excluding technical reports and isolated case reports, there are no published studies evaluating coracoid process fixation with or without an acromioclavicular joint (ACJ) stabilization procedure for coracoid process fractures associated with ACJ injury. The purpose of this study was to assess the surgical outcomes of coracoid process fractures associated with ACJ injuries and to determine the usefulness of coracoid process fixation with or without an ACJ stabilization procedure.
Methods
From February 2006 to December 2015, patients with coracoid process fractures associated with ACJ injuries were enrolled. Radiological and clinical outcomes were analyzed in 12 patients who underwent coracoid process fixation with or without an ACJ stabilization procedure. A 3.5-mm cannulated screw with a washer or a 3.0-mm headless compression screw was used for coracoid process fixation, and either a clavicle hook plate or Kirschner (K)-wires were used for ACJ injuries when additional fixation was necessary.
Results
Bone union was achieved in 11 patients (91.7%), while one case was determined to be a nonunion at 6 months. Radiological union occurred at an average of 3 months (range, 1.5–4 months) in all patients except the nonunion case. At the final follow-up, the average clinical scores were a visual analogue scale (VAS) pain score of 1.5 (range, 0–4) and a UCLA score of 30.9 (range, 28–35). Clinical outcomes were satisfactory in all patients, including the patient with nonunion.
Conclusion
The clinical and radiological outcomes of treating coracoid process fractures associated with ACJ injuries using coracoid process fixation with or without ACJ stabilization were favorable. A cannulated screw with a washer and clavicle hook plate fixation may provide sufficient stability for both the coracoid process fracture and the ACJ injury when feasible. Level of evidence: IV.
- 182 View
- 6 Download

- Outcomes of open reduction and internal fixation using 2.0/2.4 mm locking compression plate in isolated greater tuberosity fractures of humerus
- Sung Choi, Dongju Shin, Sangwoo Kim, Byung Hoon Kwack
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(1):32-39. Published online January 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
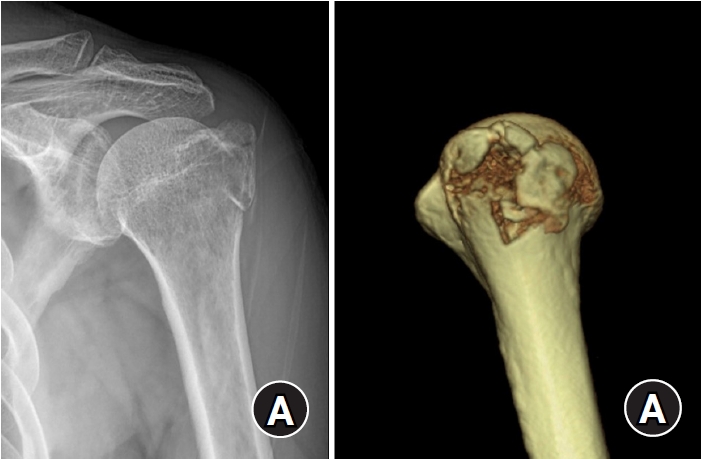
PDF - Background
The purpose of this study was to retrospectively evaluate the radiographic and clinical results of a small single or double low-profile plate fixation of 2.0/2.4 mm locking compression plate (LCP) in treating isolated greater tuberosity (GT) fractures of the humerus. Methods: From June 2015 to October 2022, patients who underwent LCP in treating isolated GT fractures of the humerus were included in this study. The radiological and clinical results were analyzed in 15 patients who underwent open reduction and internal fixation used 2.0/2.4 mm LCP. Results: Bone union was achieved in 14 patients (93.3%) and one failed case was treated with a 2.4 mm single LCP fixation. Radiological union was achieved within 10–20 weeks. Complications occurred in two patients (13.3%), including the reduction failure and shoulder stiffness. At the final follow-up, the average clinical scores were as follows: a visual analog scale for pain of 2.1 (range, 0–5) and a University of California, Los Angeles score of 27.2 (range, 18–31). Regarding range of motion (ROM), the average active ROMs were 142° for forward flexion (range, 120°–150°), 147.1° for abduction (range, 120°– 180°), and 59.3° for external rotation (range, 45°–80°). For internal rotation, the average was observed to reach the 10th thoracic vertebra (range, 1st lumbar vertebra–7th thoracic vertebra). Conclusions: The clinical and radiologic outcomes of treating isolated GT fracture using 2.0/2.4 mm LCP were favorable, and double low-profile plate fixation may be beneficial for sufficient fracture stability if possible. Level of evidence: Level IV, case series.
- 2,047 View
- 59 Download

Case Reports
- Femoral Head Fracture with Hip Dislocation Treated by Autologous Osteochondral Transfer (Mosaicplasty) - A Case Report -
- Eui-Sung Choi, Hyun-Chul Shon, Ho-Seung Jeong, Jae-Young Yang, Seok-Hyun Hong, Byung-Hyun Ahn
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(2):96-100. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.2.96
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Femoral head fractures combined with hip dislocation are very rare injuries. In most cases, they result from high-energy trauma to the hip or lower extremity during traffic accidents. Various therapy options have been suggested to treat these injuries. Especially, different joint-preserving surgical options have been described for the treatment of traumatic osteochondral injury of the femoral head in young, active patients. In this report, we present a case that a traumatic osteochondral lesion to the femoral head after hip dislocation was treated with osteochondral autografts (OATS) from the non-weight-bearing area of the ipsilateral inferior femoral head through a surgical hip dislocation. After 1 year, the clinical and radiological outcome was satisfactory with no evidence of posttraumatic osteoarthritis and no pain of patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Femoral head fracture with large crushed defect in weight-bearing area treated with autologous osteochondral transplantation (repositionplasty): A case report
Hyun-Chul Shon, Eic-Ju Lim, Jae-Young Yang, Seung-Jun Jeon
Medicine.2022; 101(52): e32569. CrossRef
- Femoral head fracture with large crushed defect in weight-bearing area treated with autologous osteochondral transplantation (repositionplasty): A case report
- 723 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Treatment of Atypical Ulnar Fracture Associated with Bisphosphonate Therapy - A Case Report -
- Dong-Soo Kim, Ji-Kang Park, Eui-Sung Choi, Ho-Seung Jeong, Seok-Hyun Hong, Byung-Hyun Ahn
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(2):101-104. Published online April 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.2.101
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Bisphosphonates can cause atypical fractures when taken for a long time. Atypical fractures appear mainly as femoral subtrochanteric or shaft fractures. On the other hand, reports of atypical fractures in the proximal ulna are relatively rare, with a high proportion of nonunion cases. This paper reports a case of nonunion after fixation for atypical fractures of the proximal ulna.
- 484 View
- 2 Download

Original Article
- Surgical Outcomes of the Monteggia Type 2 Fracture Dislocation in Adults
- Sung Choi, Daegeun Jeong, Youngsoo Byun, Taehoe Gu, Sungsoo Ha, Dongju Shin
- J Korean Fract Soc 2019;32(1):6-13. Published online January 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2019.32.1.6
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
This study examined clinical outcomes of Monteggia fracture type 2, which is the most common in adults with a high rate of accompanied injuries.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From June 2004 to November 2015, a retrospective study was performed on 12 patients diagnosed with Monteggia fracture type 2 with a follow-up period of at least 6 months after surgery. The clinical outcomes were evaluated using the Mayo elbow performance score (MEPS), and the existence of accompanied injures, radiological result, and complications were analyzed.
RESULTS
Posterior instability was confirmed in all patients and accompanied fractures were detected in 9 patients (75.0%) on the radial head, whereas 10 patients (83.3%) were found on the coronoid process. The average arc of motion was 107° (70°–130°) and the mean MEPS was 89 (45–100). Additional re-operation due to re-dislocation, radioulnar synostosis, elbow instability, ulna nonunion, and radial head nonunion were performed in 4 cases (33.3%).
CONCLUSION
The Monteggia fracture type 2 is more commonly associated with radial head fractures and coronoid process fractures rather than other types, which causes elbow instability. Because the rate of additional surgery due to complications is high, the treatment of Monteggia fracture type 2 requires careful assessments.
- 946 View
- 5 Download

Case Report
- Repeated Metal Breakage in a Femoral Shaft Fracture with Lateral Bowing: A Case Report
- Dong Soo Kim, Yong Min Kim, Eui Sung Choi, Hyun Chul Shon, Kyoung Jin Park, Byung Ki Cho, Ji Kang Park, Hyun Cheol Lee, Kyung Ho Hong
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(2):136-141. Published online April 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.2.136
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fractures of the femoral shaft with marked bowing face some obstacles in fixation of the fracture such as difficulty in insertion of the intramedullary nail (IM nail) or exact contouring plate. Locking compression plates (LCP) are an option to manage this problem. However, we experienced consecutive breakage of LCP twice and IM nail once in an 80-year-old female. Finally, union of the fracture was achieved after fixation of the IM nail and additional plate together. Fractures of the femur shaft with marked bowing are thought to have different biomechanical properties; therefore, we present this case with a review of the literature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative analysis of operation time and intraoperative fluoroscopy time in intramedullary and extramedullary fixation of trochanteric fractures
Milan Mitkovic, Sasa Milenkovic, Ivan Micic, Predrag Stojiljkovic, Igor Kostic, Milorad Mitkovic
Vojnosanitetski pregled.2022; 79(2): 177. CrossRef - Pre-operative planning for fracture fixation using locking plates: device configuration and other considerations
Alisdair R. MacLeod, Pankaj Pankaj
Injury.2018; 49: S12. CrossRef - Letter: Repeated Metal Breakage in a Femoral Shaft Fracture with Lateral Bowing - A Case Report -
Hae Seok Koh
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(3): 240. CrossRef
- Comparative analysis of operation time and intraoperative fluoroscopy time in intramedullary and extramedullary fixation of trochanteric fractures
- 608 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Crossref

Original Articles
- Surgical Treatment Using a Transolecranon Approach with a Dual Locking Plate for Unstable Intercondylar Fractures of the Humerus
- Ji Kang Park, Yong Min Kim, Dong Soo Kim, Eui Sung Choi, Hyun Chul Shon, Kyoung Jin Park, Byung Ki Cho
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(2):129-135. Published online April 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.2.129
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical outcomes of operative treatment using a transolecranon approach with a dual locking plate for unstable intercondylar fractures of the distal humerus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eighteen patients were followed for more than 1 year after surgical treatment for unstable intercondylar fractures of the humerus. Anterior transpositioning of the ulnar nerve and an early rehabilitation program to allow range of motion (ROM) exercise from postoperative week 1 were used for all cases. The clinical and functional evaluation was performed according to the Mayo Elbow Performance Index and Cassebaum's classification of ROM.
RESULTS
The range of elbow joint motion was a flexion contracture mean of 12.8 degrees to a further flexion mean of 119.3 degrees at the final follow-up. The Mayo Elbow Performance Index was an average of 88.5 points. Among the results, 6 were excellent, 9 good, 2 fair, and 1 poor. Therefore, 15 cases (83.3%) achieved satisfactory results. Fourteen cases (77.7%) achieved a satisfactory ROM according to Cassebaum's classification. All cases achieved bone union, and the interval to union was an average of 14.2 weeks.
CONCLUSION
Dual locking plate fixation through the transolecranon approach seems to be one of the effective treatment methods for unstable intercondylar fractures of the humerus because it enables the anatomical reduction and rigid fixation of articulation, and early rehabilitation exercise.
- 718 View
- 10 Download

- Bleeding Volume after Surgery for Trochanteric Fractures of the Femur in Patients Treated with Antiplatelet Agents: Comparison according to Surgical Timing
- Se Ang Jang, Young Ho Cho, Young Soo Byun, Tae Gyun Kim, Hun Sik Cho, Sung Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2012;25(2):105-109. Published online April 30, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.2.105
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
We evaluated the bleeding volume after surgery for trochanteric fractures of the femur in patients treated with antiplatelet agents according to surgical timing.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We selected 20 patients who had trochanteric fractures of the femur treated with antiplatelet agents from January 2009 to June 2010. Group I included 9 patients who discontinued antiplatelet medication and had delayed operations at an average of 6.5 days and Group II included 11 patients who underwent early operations within 24 hours. Group I included 2 males and 7 females; their average age was 77.8 years (range 59~86). Group II included 4 males and 7 females, with an average age of 73.5 years (range 61~84). We compared the two groups' volume of intraoperative bleeding, the preoperative and postoperative hemoglobin levels and the volume of postoperative transfusion. The Mann-Whitney U test was used for statistical analysis.
RESULTS
The volume of intraoperative bleeding was 88 ml in group I and 106 ml in group II (p>0.01). The difference in the hemoglobin was a decrease of 2.4 mg% in group I and a decrease of 2.2 mg% in group II (p>0.01). The volume of postoperative transfusion was 0.6 pints in group I and 1 pint in group II (p>0.01).
CONCLUSION
We found a similar bleeding volume regardless of operative timing after surgery for trochanteric fractures of the femur in patients treated with antiplatelet agents. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Is early hip fracture surgery safe for patients on clopidogrel? Systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression
B. Doleman, I.K. Moppett
Injury.2015; 46(6): 954. CrossRef - Morbidity and Mortality of the Elderly after Early Operation for Trochanteric Fractures
Se-Ang Jang, Young-Ho Cho, Young-Soo Byun, Ki-Hong Park, Hyun-Seong Yoo, Chul Jung
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2013; 26(3): 199. CrossRef
- Is early hip fracture surgery safe for patients on clopidogrel? Systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression
- 653 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Arthroscopic Treatment of Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation Using TightRope(R): Preliminary Report
- Eui Sung Choi, Kyoung Jin Park, Yong Min Kim, Dong Soo Kim, Hyun Chul Shon, Byung Ki Cho, Ji Kang Park, Hyun Chul Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2010;23(3):310-316. Published online July 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.3.310
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the clinical and radiologic results of the arthroscopic treatment using TightRope(R) (Arthrex, Inc, Naples, FL) for management of acute acromioclavicular dislocation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twelve patients with acromioclavicular joint dislocation Rockwood type V are underwent the arthroscopic acromioclavicular joint reconstruction using TightRope(R) between March, 2008 and March, 2009. The average age was 40.4 years (range 25~63 years) and mean follow-up was 10 months (range 8~16 months). The shoulders were evaluated using parameters include radiologic measurements by comparing the clavicle posteroanterior and lateral radiographs with the contralateral one. Clinical evaluation was made for pain, function, and range of joint motion by Constant score and KSS (Korean Shoulder Score).
RESULTS
All twelve patients returned to their work without pain in 3 months after operation. The average Constant score and KSS score was 98.4 (range 97~100) and 97.8 (range 97~100) at the last follow-up. Because of technical error and indication error, two patients showed failures of TightRope(R) fixation on the coracoid side and the acromioclavicular joint was redislocated, so these cases were excluded. 10 patients were satisfied with functional results and cosmetic appearance.
CONCLUSION
Considering its less morbidity, less hospitalization, excellent cosmesis, early rehabilitation, this new technique offers an attractive alternative in acromioclavicular joint stabilization if the early technical error would be overcome. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Coracoclavicular Ligament Augmentation Using Tight-Rope®for Acute Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation - Preliminary Report -
Seok Hyun Kweon, Sang Su Choi, Seong In Lee, Jeong Woo Kim, Kwang Mee Kim
The Journal of the Korean Shoulder and Elbow Society.2013; 16(2): 115. CrossRef - Coracoclavicular Ligament Augmentation Using Endobutton for Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures - Preliminary Report -
Chul-Hyun Cho, Gu-Hee Jung, Hong-Kwan Sin, Young-Kuk Lee, Jin-Hyun Park
The Journal of the Korean Shoulder and Elbow Society.2011; 14(1): 1. CrossRef
- Coracoclavicular Ligament Augmentation Using Tight-Rope®for Acute Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation - Preliminary Report -
- 649 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Comparison of Open Fixation and Closed Percutaneous Pinning in Jakob Stage II Lateral Condylar Fractures of Children
- Eui Sung Choi, Dong Soo Kim, Hyun Chul Shon, Yong Min Kim, Kyoung Jin Park, Jun Mo Jeon, Gee Kang Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2006;19(2):277-282. Published online April 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2006.19.2.277
-
 Abstract
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the results of open fixation and closed percutaneous pinning in managing Jakob stage II lateral condylar fractures of children's elbow.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Since Febuary 2000, We operated 21 children with Jakob stage II lateral condylar fractures of elbow. Eleven of the 21 were treated with closed percutaneous pinning, open fixation was done to the other 10 children. Each patient was evaluated about range of motion, carrying angle, scar satisfaction and radiologic findings for comparison between closed pinning and open fixation groups.
RESULTS
Open fixation group showed 3.8 degrees decrease of elbow motion while closed pinning group showed no significant decrease. Carrying angle and radiologic findings were not different between the two groups. Open fixation group expressed dissatisfaction to their scars (average 5.2 cm) whereas all the patients of closed pinning group were satisfied with their functional and cosmetic outcomes.
CONCLUSION
In managing Jakob stage II lateral condyle fractures of children's elbow, closed percutaneous pinning was thought to be superior to open fixation because of the same functional outcome and much better cosmetic results.
- 367 View
- 0 Download

Case Reports
- Neglected Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation in a Crutch-walking Patient: A Case Report
- Yong Min Kim, Hyun Chul Shon, Dong Soo Kim, Eui Sung Choi, Kyung Jin Park, Se Hyuk Im
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(4):474-477. Published online October 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.4.474
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Traumatic posterior hip dislocation should be reduced emergently, but diagnosis could be delayed in a patient with head trauma or in developing countries. We have experienced neglected posterior hip dislocation for three months in a crutch-walking patient who had ipsilateral tibia fracture and alert mentality. Open reduction followed by six-weeks skeletal traction was performed. At one year follow-up, the reduced hip showed good range of motion with no evidence of avascular necrosis.
- 470 View
- 1 Download

- Fat Embolism in a Patient with Multiple Fractures of Cancellous Bones: A Case Report
- Eui Sung Choi, Yong Min Kim, Dong Soo Kim, Hyun Chul Shon, Kyung Jin Park, Jun Mo Jeon
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(2):202-204. Published online April 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.2.202
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fat embolism is a rare complication of multiple long bone fracture or extensive soft tissue injury. The pathogenesis of fat embolism has been poorly understood and definite pathogenesis and treatment were not fully established. Respiratory failure associated with fat embolism is a major cause of death, but is usually self-limited, and is responsive to intensive treatment. We have experienced fat embolism in cancellous bone fracture which occurred in spine, distal radius and talus. Patient's fractures were treated with conservative management. The patient was recovered from fat embolism with supportive treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A case of fat embolism syndrome in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis patient
Kyung Hoon Kim, Ju Kyung Lee, Young Hun Choi, Woo Sun Kim, June Dong Park, Young Yull Koh, Dong In Suh
Allergy Asthma & Respiratory Disease.2013; 1(1): 94. CrossRef
- A case of fat embolism syndrome in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis patient
- 590 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Articles
- Differences of Fracture Types and Associated Injuries in Thoracolumbar Fractures Caused by Fall from Height and by In-Car Accident
- Eui Sung Choi, Yong Min Kim, Dong Soo Kim, Kyung Jin Park, Kyeong Il Jeong, Yoon Moo Hur, Young Chan Cha, Jun Mo Jeon, Jong Won VKang
- J Korean Fract Soc 2005;18(2):176-180. Published online April 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2005.18.2.176
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the differences of associated factors in thoracolumbar fractures according to the mechanism of injury, level and type of the fracture, associated injuries were investigated for comparison between injuries by fall from height and by in-car accident injury.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Medical records and X-ray findings of 249 patients with fractures of thoracolumbar spine were reviewed retrospectively. Among them, 169 patients were injured by the two main causes. McAfee classification was adopted to determine the type of fracture. Associated injuries were classified as head and neck, chest and abdomen, pelvis, proximal and distal extremity, and neurologic deficit. Statistical analysis using Chi-square method was used for comparison between the two groups.
RESULTS
In overall patients, the most common cause of thoracolumbar fracture was fall from height (44.6%) followed by in-car accident (23.3%) and fall down (16.9%). In fall-from height gruoup, burst fracture was the most common (44.1%) while flexion-distraction injury was the most popular (39.7%) in in-car accident group (p=0.05). Comparison according to height of fall showed significant increase of multiple fractures (p=0.0326). Associated injuries of distal lower and upper extremities and pelvis were common in fall-from-height group, while injuries of head and neck, proximal part of upper extremity, chest and abdomen were common in in-car accident patients.
CONCLUSION
Type of fracture and distribution of associated injuries were significantly different between the two main causes of thoracolumbar injury, which seemed to be useful for understanding the mechanical events of injury and detecting associated injuries in each victim. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Injury Severity and Patterns of Accompanying Injury in Spinal Fracture
Hun Park, Kyung-Jin Song, Kwang-Bok Lee, Joo-Hyun Sim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2012; 25(3): 203. CrossRef - Differences in Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures by Falls from Height with Associated Foot and Ankle Fractures
Chung-Shik Shin, Eea-Sub Chung, Chang-Eon Yu, Byeong-Yeol Choi
Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery.2012; 19(2): 47. CrossRef
- Injury Severity and Patterns of Accompanying Injury in Spinal Fracture
- 813 View
- 6 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Lateral Submeniscal Approach in the Treatment of Tibial Condyle Fracture
- Weon Yoo Kim, Jin Young Kim, Woo Sung Choi, Yong Hwan Kim, Bum Sung Lee, Young Mo Kim, Chang Whan Han
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(4):496-503. Published online October 31, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.4.496
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the radiologic and functional results of treatment in proximal tibial plateau fracture using lateral submeniscal approach, which is a relatively minimally invasive approach to tibial condylar articular surface.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty three cases of tibial plateau fracture which treated with submeniscal approach were analyzed with one year follow up. The results were evaluated by immediate postoperative radiographic and Hohl's clinical evaluation.
RESULTS
Tibial articular surface could be in operation field and the articular surface could be restored the anatomically by elevating the depressed articular surface and bone graft to the empty space. The postoperative radiography showed that most cases (91%) could be reduced adequately (within 2 mm). The clinical evaluation by Hohl's criteria revealed excellent 7 cases (30%), good 12 cases (52%), fair 3 cases (13%), and one poor case (4%).
CONCLUSION
Submeniscal approach can identify the articular surface and intraarticular soft tissues with minimal incision, and allows anatomical reduction, sufficient bone graft, rigid plate fixation and soft tissue treatment, therefore it is one of the good approach in treatment of proximal tibial plateau fracture.
- 373 View
- 4 Download

- Anterior Approach and Volar T-plate fixation of Distal Radius Fracture
- Woo Sung Choi, Weon Yoo Kim, Dong Won Choi, Yun Hack Shin, Jin Young Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2003;16(2):244-252. Published online April 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2003.16.2.244
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyze the radiologic and clinical results of open reduction and volar plating through anterior approach for distal radius fracture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We retrospectively analysed that 19 distal radius fracture, which would not be reduced by closed reduction or too comminuted to maintain reduction or articular surface incongruency, were treated by open reduction and volar plating through anterior approach. The results were evaluated by preoperative and immediate postoperative radiographics and clinical results were analysed using Green and O'Brien scoring system at final follow up.
RESULTS
All cases achieved anatomical articular surface reduction postoperatively. In terms of radiologic analysis, mean radial length (8.8 mm +/-4.8 mm vs. 11 mm +/-3 mm), radial inclination (15 degrees+/-5.7 degreesvs. 20degrees+/-5degrees), volar tilt (-11 degrees+/-13 degrees vs. 7 degrees+/-4 degrees) and ulnar plus variant (4 mm+/-3 mm vs. 0 mm+/-1 mm) were improved. The clinical evaluation revealed 9 excellent cases, 7 good cases, 2 fair cases and 1 poor case. The reduction loss and flexor pollicis longus rupture was occurred in one patient, who had severely displaced comminute fracture in initial injury.
CONCLUSION
Using volar plating, authors gain good radiologic and clinical results. But, additional external fixation is recommended to prevent further collapse in severly comminuted fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Is dorsal cortex drilling necessary for distal radius fractures treated with a volar locking plate? A comparative study of near-cortex-only and far-cortex drilling
Chul Hong Kim, Sung Yoon Jung, Hyeon Jun Kim, Si-Hyun Park
Journal of Trauma and Injury.2025; 38(3): 248. CrossRef - Treatment of Fractures of the Distal Radius Using Variable-Angle Volar Locking Plate
Jae-Cheon Sim, Sung-Sik Ha, Ki-Do Hong, Tae-Ho Kim, Min-Chul Sung
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2015; 28(1): 46. CrossRef
- Is dorsal cortex drilling necessary for distal radius fractures treated with a volar locking plate? A comparative study of near-cortex-only and far-cortex drilling
- 546 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Treatment of Pertrochanteric Fracture with Femoral Neck Fracture
- Weon Yoo Kim, Chang Whan Han, Woo Sung Choi, Jong Hoon Ji, Chang Youn Moon, Jin Young Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 2002;15(3):307-311. Published online July 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2002.15.3.307
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - OBJECTIVES
To establish the precise diagnosis of a comminuted pertrochanteric fracture with femoral neck fracture in a senile osteoporotic patient and report of a preliminary clinical results of early bipolar hemiarthroplasty. MATERIAL & METHODS: Consecutive seven cases of comminuted pertrochanteric fractures who were suspicious to have combination with femoral neck fracture were evaluated. All cases had routine radiographs and CT scans of proximal femur and performed with bipolar hemiarthroplasties. Observation of the retrieved femoral head to evaluate a fracture and recorded with photograph. Postoperative evaluation was done with Daubine & Postel clinical grading with medical recording and personal telephone. The clinical evaluation was focused on the recovery for preinjured walking distance.
RESULTS
All patients were proved to have combination with pertrochanteric fractures and femoral neck fractures. In addition, all patients were recovered to more than good in clinical grading and pre-injured walking distance.
CONCLUSION
To make a precise diagnosis of pertrochanteric fractures with femoral neck fracture it is recommended to perform the CT scan with prompt reading of the simple radiographs in suspicious case. An early bipolar hemiarthroplasty was also recommended to treat this kind of senile difficult fracture.
- 480 View
- 1 Download

- Operative Treatment of Intra-articular Fractures of the Calcaneus by Sanders Classification
- Jong In Yim, Bu Hwan Kim, Hee Yeong Chung, Woo Sung Choi
- J Korean Soc Fract 1995;8(3):628-637. Published online July 31, 1995
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1995.8.3.628
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The os calcis is the most frequently fractured than any other tarsal bone and the displaced intraarticular fracture account for 60-75% of them. Because of complex contour of calcaneus, it is difficult to evaluate the pattern of fracture exactuly by conventional roentgenograms. But recently, computed tomography clearly defines fracture patterns of subtalar joint and calcaneocuboid joint. From Feb. 1992 to Jan. 1994. we analyzed 18 feet in 16 patients of intraarticular calcaneal fractures after routine preoperative CT scan and Sandersclassification. All cases were operated through extensile lateral approach and internally fixed with plate and screws. The clinical and radiographic analysis were as follows: 1. Sanders classification of 18 cases were type I in 3, type I in 8, type III in 4 and type IV in 3. 2. As the fracture line moves medially, intraoperative visualization of joint, reduction becomes more difficult and the prognosis worsens in type II and IIIBC. 3. By SandersCT classification of calcaneal fracture, it help us in understanding fracture pattern more detail and in deciding of the method of treatment and in the predicting of the prognosis.
- 442 View
- 1 Download

- Comparison between Intramedullary and Plate Fixation for Subtrochanteric Fracture of the Femur
- Han Suk Ko, Byung Jik Kim, Suk Kyu Choo, Jae Sung Choi
- J Korean Soc Fract 1994;7(2):352-363. Published online November 30, 1994
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1994.7.2.352
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Management of subtrochanteric fractures of the femur is difficult because it occurs in bone that is predominantly cortical and high stress concentrates in this region. The subtrochanteric fracture is difficult for the accurate reduction and maintenance because many of these fractures are cmminuted from high velocity trauma and its proximal fragment is severely displaced by adjacent strong muscles pooling. Therefore, as a rule we prefer to treat subtrochanteric fractures by operative means if possible. Many internal fixation devices have been recomended for use in subtrochanteric fractures and their selection should be based on the individual fracture anatomy. In recent years, generally accepted two methods are intramedullary nailing and plate fixation. We have reviewed our experience using the intramedullary fixation on 14 cases of subtrochanteric femur fracture and compared the result with those of 14 cases of plate fixation. All the 28 cases were treated at the Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University in the period from March 1988 to March 1993. Intramedullary fixation were implanted with shorter operating time, smaller incisions, and less intraoperative bleeding. The intramedullary fixation group had a shorter covalescence and earlier full weight-bearing but no significant difference in fracture union rate with plate fixation group. We conclude that with careful surgical technique, the intramedullary fixation was a more suitable method for the treatment of the subtrochanteric femoral fractures.
- 462 View
- 2 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


