Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Hook plate fixation for volar plate avulsion fractures of the middle phalanges in Korea: a case series
- Kang-San Lee, Sang-Woo Son, Hee-June Kim, Hyun-Joo Lee, Dong Hee Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2026;39(1):48-53. Published online January 25, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00339

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Volar plate avulsion fractures in phalanges are relatively common injuries. While surgical treatment can help reduce limitations in motion after injury, the small size of the fracture fragment can make the procedure challenging. In this study, we used hook plate fixation as a surgical technique for treating volar avulsion fractures in phalanges and evaluated its radiological and clinical outcomes.
Methods
The medical records of eight patients (nine digits) with volar plate avulsion fractures of the middle phalanx were retrospectively reviewed. All fractures were treated with a 1.5-mm hook plate after open reduction. Radiologic evaluations were performed using simple radiographs, and clinical outcomes were assessed through range of motion, instability, and pain.
Results
The mean follow-up period was 4.89 months (range, 1–9 months). All nine digits achieved bone union at the final follow-up. The mean union time was 2.2 months (range, 1–4 months). In all patients, the range of motion in the proximal interphalangeal joint was 85° (range, 70°–100°) before implant removal and 89.4° (range, 80°–100°) after implant removal. All patients demonstrated no joint instability and no residual pain.
Conclusion
Using a hook plate for volar plate avulsion fractures presents a promising alternative to existing fixation methods. Its biomechanical advantages and ease of fabrication make it a valuable tool in hand surgery. Level of evidence: IV.
- 191 View
- 8 Download

Technical Note
- Rim plate-assisted intramedullary nail and plate combination technique for complex tibial plateau-to-diaphysis fractures: a technical note and case series
- Whee Sung Son
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2026;39(1):62-71. Published online December 4, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00290
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
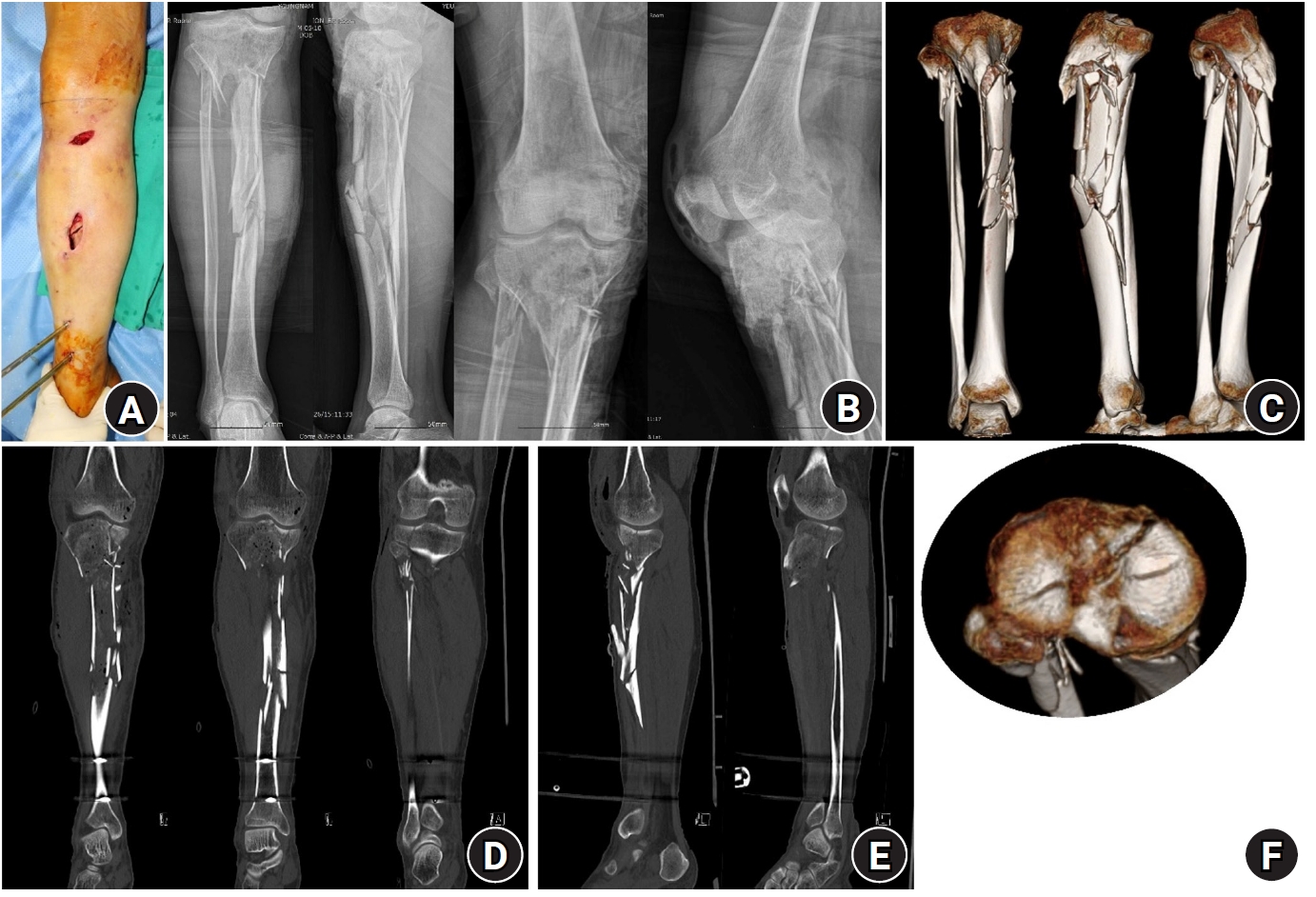
PDF - Complex tibial plateau-to-diaphysis fractures present a significant surgical challenge due to their intricate fracture patterns and frequent association with severe soft tissue damage and concomitant injuries. This technical note introduces a novel fixation strategy: the rim plate-assisted intramedullary nail-plate combination (NPC) technique. In this approach, a rim plate simplifies the conventional NPC procedure by unifying the tibial plateau fracture into a single structural segment. This modification eliminates the need to address the articular and diaphyseal components simultaneously while enhancing articular stability. Furthermore, the technique preserves soft tissue integrity and promotes early rehabilitation. Clinical case examples demonstrate its successful application in managing complex tibial plateau-to-diaphysis injuries. Level of evidence: V.
- 524 View
- 22 Download

Original Articles
- Comparison of outcomes of reinforced tension band wiring and precontoured plate and screw fixation in the management of Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures
- Hyun Goo Kang, Tong Joo Lee, Samuel Jaeyoon Won
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):96-101. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00059
- Correction in: J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(3):168

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures are characterized by significant displacement and comminution, presenting a challenge in selecting the appropriate fixation technique. This study compared the clinical and radiographic outcomes, complications, and reoperation rates of reinforced tension band wiring (TBW) and precontoured plate and screw fixation (PF) in the surgical treatment of Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures.
Methods
This retrospective review analyzed 24 patients diagnosed with Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures, who were treated between 2005 and 2023. Of these, 11 patients underwent reinforced TBW, and 13 received precontoured PF. Clinical outcomes were assessed using Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) scores and the Mayo Elbow Performance Score (MEPS). Radiographic outcomes focused on fracture union. Operative times, complication rates, and reoperation rates were compared between the groups.
Results
Both the reinforced TBW and PF groups achieved satisfactory clinical outcomes, with no significant between-group differences in DASH and MEPS scores (P>0.05). Radiographic union was achieved in all patients. The reinforced TBW group demonstrated a significantly shorter operative time than the PF group (93.6±7.4 min vs. 132.3±13.7 min; P<0.001). Complication rates were similar between the two groups (reinforced TBW, 38.4%; PF, 36.3%), but hardware-related irritation occurred more frequently in the reinforced TBW group. Reoperations were required in 15.8% of the reinforced TBW group due to hardware irritation, whereas no reoperations were necessary in the PF group.
Conclusions
Reinforced TBW and PF are both effective surgical options for managing Mayo type IIIB olecranon fractures, yielding comparable clinical and radiographic outcomes. While reinforced TBW offers shorter operative times and lower costs, PF is associated with fewer hardware-related complications. Further prospective studies are needed to optimize treatment strategies for these complex fractures. Level of Evidence: Level III. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Are posterior olecranon locking plates a problem for patients after fracture healing because of prominence?
Reva Qiu, Mallika Makkar, Richard Buckley
Injury.2025; 56(11): 112769. CrossRef
- Are posterior olecranon locking plates a problem for patients after fracture healing because of prominence?
- 2,292 View
- 51 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Outcomes of open reduction and internal fixation using 2.0/2.4 mm locking compression plate in isolated greater tuberosity fractures of humerus
- Sung Choi, Dongju Shin, Sangwoo Kim, Byung Hoon Kwack
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(1):32-39. Published online January 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
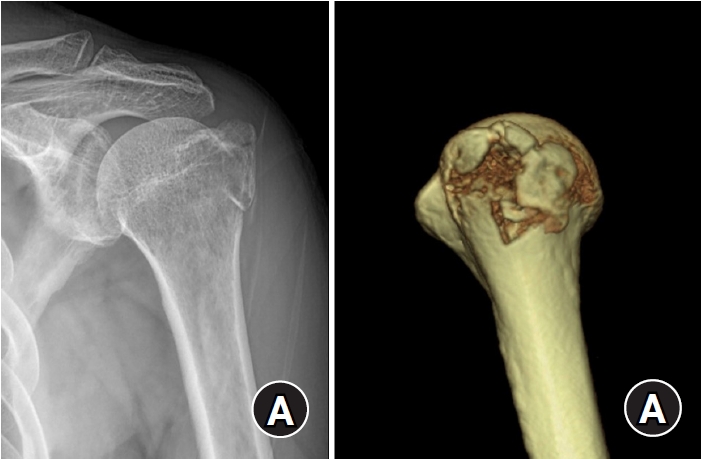
The purpose of this study was to retrospectively evaluate the radiographic and clinical results of a small single or double low-profile plate fixation of 2.0/2.4 mm locking compression plate (LCP) in treating isolated greater tuberosity (GT) fractures of the humerus. Methods: From June 2015 to October 2022, patients who underwent LCP in treating isolated GT fractures of the humerus were included in this study. The radiological and clinical results were analyzed in 15 patients who underwent open reduction and internal fixation used 2.0/2.4 mm LCP. Results: Bone union was achieved in 14 patients (93.3%) and one failed case was treated with a 2.4 mm single LCP fixation. Radiological union was achieved within 10–20 weeks. Complications occurred in two patients (13.3%), including the reduction failure and shoulder stiffness. At the final follow-up, the average clinical scores were as follows: a visual analog scale for pain of 2.1 (range, 0–5) and a University of California, Los Angeles score of 27.2 (range, 18–31). Regarding range of motion (ROM), the average active ROMs were 142° for forward flexion (range, 120°–150°), 147.1° for abduction (range, 120°– 180°), and 59.3° for external rotation (range, 45°–80°). For internal rotation, the average was observed to reach the 10th thoracic vertebra (range, 1st lumbar vertebra–7th thoracic vertebra). Conclusions: The clinical and radiologic outcomes of treating isolated GT fracture using 2.0/2.4 mm LCP were favorable, and double low-profile plate fixation may be beneficial for sufficient fracture stability if possible. Level of evidence: Level IV, case series.
- 2,048 View
- 59 Download

- Comparing Outcomes of Retrograde Intramedullary Nail and Locking Plate Fixation in Distal Femoral Fractures
- Byung-Ho Yoon, Bo Kwon Hwang, Hyoung-Keun Oh, Suk Kyu Choo, Jong Min Sohn, Yerl-Bo Sung
- J Korean Fract Soc 2021;34(4):131-136. Published online October 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2021.34.4.131
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
We compared the radiological and clinical results of fixation for distal femoral fracture (DFF) using a locking compression plate (LCP) or a retrograde intramedullary nail (RIN).
Materials and Methods
From October 2003 to February 2020, 52 cases of DFF with a minimum 1-year follow-up (with a mean follow-up of 19.1 months) were included: 31 were treated with LCP and 21 with RIN. The operation time, blood loss, and hospitalization period were compared, and the incidence of postoperative nonunion, malunion, delayed union and metal failure and other post-operative complications were evaluated and compared.
Results
There was no significant difference in the operating time between the two groups, but the mean blood loss was significantly higher in the LCP group (LCP 683.5 ml vs RIN; 134.9 ml; p=0.015). In 49 out of 52 cases, bone union was achieved without additional surgery in an average of 6.8 months, and a complete union was achieved after additional surgery in three cases of nonunion (LCP 2 cases vs RIN 1 case; p=0.065). One case of malunion and superficial infection was confirmed in each group.
Conclusion
Internal fixation using LCP and RIN give good outcomes with a low complication rate and can therefore be considered useful surgical treatments for DFF.
- 480 View
- 6 Download

- Risk Factors for Knee Stiffness in Distal Femoral Fractures
- Dong Wook Son, Hyoung Soo Kim, Woo Young Choi
- J Korean Fract Soc 2018;31(4):123-131. Published online October 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.4.123
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
The aims of this study were to evaluate risk factors for knee stiffness after the fixation of distal femoral fractures, and to analyze the clinical and radiologic outcomes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This is a retrospective case control study of 104 consecutive patients who have a distal femoral fracture and were treated with a submuscular locking plate. The case group comprised of patients with 12-month postoperative range of motion (ROM) ≤90° or a history of manipulation under anesthesia. The case group was compared with the control group of patients with a 12-month postoperative ROM >90°. The possible risk factors were evaluated by univariate and logistic regression analysis. The postoperative ROM and Knee Society clinical rating system was evaluated for the clinical assessment and the distal femoral angle on a whole-extremity scanogram was measured for radiologic assessments.
RESULTS
Fifty-four patients were included in the study (14 in the case group, 40 in the control group). Univariate analysis showed that comminuted fracture, intra-articular fracture, open fracture, temporary external fixation, severe osteoarthritis, and prolonged immobilization placed patients at an increased risk for knee stiffness. On the other hand, multivariate logistic regression showed that an extensor mechanism injury was the only significant predictor (p=0.001; odds ratio, 42.0; 95% confidence interval, 5.0–350.7). The ROM and Knee Society score were significantly lower in the case group; however, the coronal alignment was similar in the case and control group.
CONCLUSION
Various factors that delay postoperative knee motion place patients at increased risk of knee stiffness. Understanding these risk factors may help surgeons prevent postoperative knee stiffness after distal femoral fractures. In particular, extensor mechanism injury, such as patella fracture or open quadriceps injury, was found to be an independent predictable factor associated with knee stiffness. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comprehensive Approach to Stiffness in Total Knee Arthroplasty
Brian P. Chalmers, Linda I. Suleiman, Peter K. Sculco, Matthew P. Abdel
The Journal of Arthroplasty.2025; 40(9): S59. CrossRef - Staged Management for Distal Femur Fractures: Impacts on Reoperation, Stiffness, and Overall Outcomes
Matthew T. Yeager, Robert W. Rutz, Alex Roszman, Gerald McGwin, James E. Darnley, Joseph P. Johnson, Clay A. Spitler
Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma.2024; 38(11): 577. CrossRef - Outcome of the Masquelet Technique for Complex Bilateral Distal Femoral Bone Defects
Ziad A Aljaafri, Abdullah Alzahrani, Ali Alshehri, Ahmed AlHussain, Faisal Alzahrani, Khalid Alsheikh
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of non-operative treatment of patients with knee arthrofibrosis using high-intensity home mechanical therapy: a retrospective review of 11,000+ patients
Shaun K. Stinton, Samantha J. Beckley, Thomas P. Branch
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Distal Femoral Replacement and Extensor Mechanism Repair Reinforced With Synthetic Mesh for Distal Femur Fracture With Patellar Ligament Avulsion
Charles Powell, Kristopher Sanders, Neal Huang, Luis Felipe Colón, Colton Norton
Arthroplasty Today.2022; 16: 31. CrossRef - The fragility of statistical significance in distal femur fractures: systematic review of randomized controlled trials
Michael Megafu, Hassan Mian, Emmanuel Megafu, Sulabh Singhal, Alexander Lee, Richawna Cassie, Paul Tornetta, Robert Parisien
European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology.2022; 33(6): 2411. CrossRef - Association Between Femoral “Spike” Size After Intramedullary Nailing and Subsequent Knee Motion Surgery
Michael G. Schloss, Nathan N. O'Hara, Syed M. R. Zaidi, Zachary D. Hannan, Dimitrius Marinos, Jared Atchison, Alexandra Mulliken, Jason W. Nascone, Robert V. O'Toole
Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma.2021; 35(2): 100. CrossRef - Distal Femur Replacement Versus Surgical Fixation for the Treatment of Geriatric Distal Femur Fractures: A Systematic Review
Brett P. Salazar, Aaron R. Babian, Malcolm R. DeBaun, Michael F. Githens, Gustavo A. Chavez, L. Henry Goodnough, Michael J. Gardner, Julius A. Bishop
Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma.2021; 35(1): 2. CrossRef
- A Comprehensive Approach to Stiffness in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- 687 View
- 10 Download
- 8 Crossref

- A Retrospective Comparative Study of Internal Fixation with Reconstruction Plate Versus Anatomical Locking Compression Plate in Displaced Intercondylar Fractures of Humerus
- Tong Joo Lee, Young Tae Kim, Dae Gyu Kwon, Ju Yong Park
- J Korean Fract Soc 2014;27(4):294-300. Published online October 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.4.294
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To analyze the clinical result of a conventional reconstruction plate (CRP) fixation and locking compressive plate (LCP) fixation on the surgical treatment of an adult's displaced intercondylar fracture of humerus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 40 patients enrolled in the study were treated between August 2002 and May 2012. Fixation with a CRP was performed in 20 patients (group A) and anatomical locking compression plate fixation was performed in 20 patients (group B). The clinical and functional evaluation was performed according to the Mayo elbow performance score and Cassebaum classification of elbow range of motion (ROM), disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand score.
RESULTS
The Mayo elbow functional evaluation scores, eight cases were excellent, 10 cases were good, and two cases were fair in group A, and 12 cases were excellent, seven cases good, and one case fair in group B; both groups showed satisfactory results. The durations of attaining 90 to 120 degrees of the ROM of joints postoperatively were 8.3 days on average (6 to 15 days) in group A and 5.5 days on average (5 to 9 days) in group B, demonstrating a significant difference between the two groups (p=0.04). Although the correlations of clinical results according to the difference of bone mineral densities (BMDs) were not statistically significant between the two groups (p=0.35), loss of fixation occurred due to loosening of screws in two patients with low BMDs in whose operations reconstruction plates were used.
CONCLUSION
The use of locking compressive plate on the surgical treatment of an diaplaced intercondylar fracture of humerus have a good clinical results because that permits early rehabilitation through good fixation and reduces the complications such as loosening of screws.
- 414 View
- 0 Download

- Treatment of the Distal Femoral Fracture with Anatomical Bone Plate
- Sung Ho Hahn, Bo Kyu Yang, Seung Rim Yi, Shun Wook Chung, Je Oh Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(2):258-266. Published online April 30, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.2.258
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
: In this paper, we have intended to evaluate the types of fracture of the distal femur treated with anatomical bone plate, simple and user's friendly apparatus and to assess their clinical results.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
: We retrospectively reviewed 21 cases in 20 patients who were followed up over 1 year among the patients that had distal femoral fractures treated with anantomical bone plate. We analysed their fracture types in AO classification and assessed clinical results according to Neer system. The average duration of follow-up was 30 months(range, 14months to 49 months).
RESULTS
: Ont of twenty-one cases, twelve were A type(A1, 3 cases;A2, 4cases;A3, 5 cases)and nine were C type(C1, cases;C2, 4cases; C3, 3 cases). But B type was none.
CONCLUSIONS
: This study demonstrate that the operation with anatomical bone plate is not only simple and user's friendly technique but also widely appleicable method to treat A and C types of the distal femoral fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Surgical Treatment of Distal Femur Medial Condyle Fracture Using Lateral Anatomical Plate of Opposite Side through Medial Approach
Sung-Sik Ha, Jae-Chun Sim, Ki-Do Hong, Jae-Young Kim, Kwang-Hee Park, Yoon-Ho Choi
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(4): 246. CrossRef
- The Surgical Treatment of Distal Femur Medial Condyle Fracture Using Lateral Anatomical Plate of Opposite Side through Medial Approach
- 673 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Clinical study of may anatomical bone plate in distal tibial fractures
- Seung Gyun Cha, Won Seuk Lee, Oue Joong Kim, Jin Hak Kim
- J Korean Soc Fract 1991;4(1):94-99. Published online May 31, 1991
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1991.4.1.94
- 361 View
- 0 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


