Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Articles
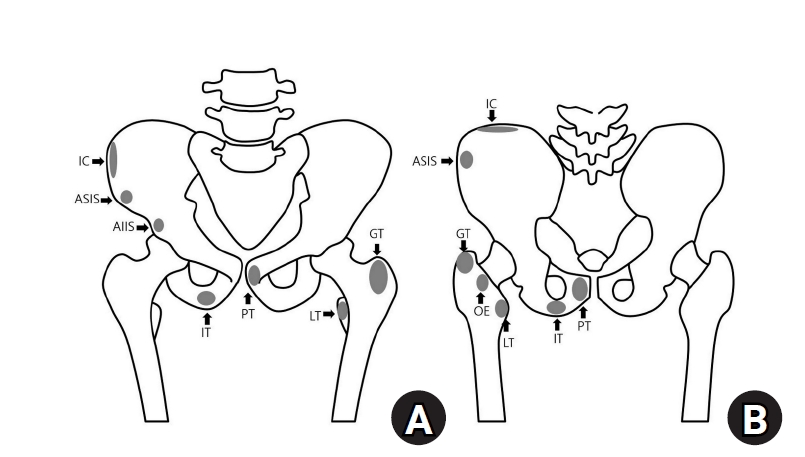
- Avulsion fractures around the hip joint and pelvis
- Won-Sik Choy, Yonghan Cha, Jung-Taek Kim, Jun-Il Yoo, Jin-Woo Kim
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(2):53-62. Published online March 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fractures occur when tendons or ligaments are subjected to forces greater than they can withstand at the apophysis or enthesis, regardless of fusion status. The pelvis and hip joint are vulnerable to these injuries due to the diverse muscular structures in these structures, which serve as origins for multiple muscles leading to the lower extremities. Pelvic avulsion fractures commonly affect young athletes, but can also occur in adults. The diagnosis typically involves assessing trauma history, a clinical examination, and radiographic imaging. If the diagnosis is unclear, additional tests such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging may assist in the diagnosis and provide useful information for treatment decisions. While most avulsion fractures respond well to conservative treatment, surgical intervention may be preferred in severe displacements, cases of significant retraction in active athletes, or when a faster recovery is necessary. Chronic or neglected injuries may lead to excessive osseous formation around the pelvis, causing impingement syndromes. Recognizing characteristic radiological findings based on pelvic anatomy helps to make an accurate diagnosis, as chronic injuries can mimic tumors or infectious conditions, necessitating a careful differential diagnosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Avulsion Fracture of the Lesser Trochanter and the Use of Conservative Treatment
Dawid Bartosik, Bartlomiej Cwikla, Anna Kowalczyk, Michalina Loson-Kawalec, Anna Palka-Szymaniec, Bartosz Starzynski, Alina Keska, Jakub Szkuta, Klaudia Wojcik
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Avulsion Fracture of the Lesser Trochanter and the Use of Conservative Treatment
- 9,160 View
- 137 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Treatment of Avulsion Fractures around the Knee
- Sumin Lim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2024;37(2):117-124. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2024.37.2.117
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Avulsion fractures are common in athletes and result from high-impact or sudden, forceful movements involving the separation of a bone fragment at the ligament or tendon attachment site. The key focus areas include the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments, medial collateral ligament, anterolateral complex, arcuate complex, medial patellofemoral ligament, patellar tendon, and quadriceps tendon. Diagnostic approaches combine radiography with advanced imaging techniques, such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, to elucidate the extent of injury and guide treatment decisions. Treatment ranges from conservative management for non-displaced fractures to surgical intervention for displaced fractures, with strategies customized based on the specific ligament involved and the nature of the fracture.
- 1,316 View
- 10 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA TOTA
TOTA TOTS
TOTS

 First
First Prev
Prev


