Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Comparative results of the femoral neck system versus the dynamic hip screw for stable femoral neck fractures in older adults in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
- Byung-Chan Choi, Byung-Woo Min, Kyung-Jae Lee, Jun-Sik Hong
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):203-211. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00276
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
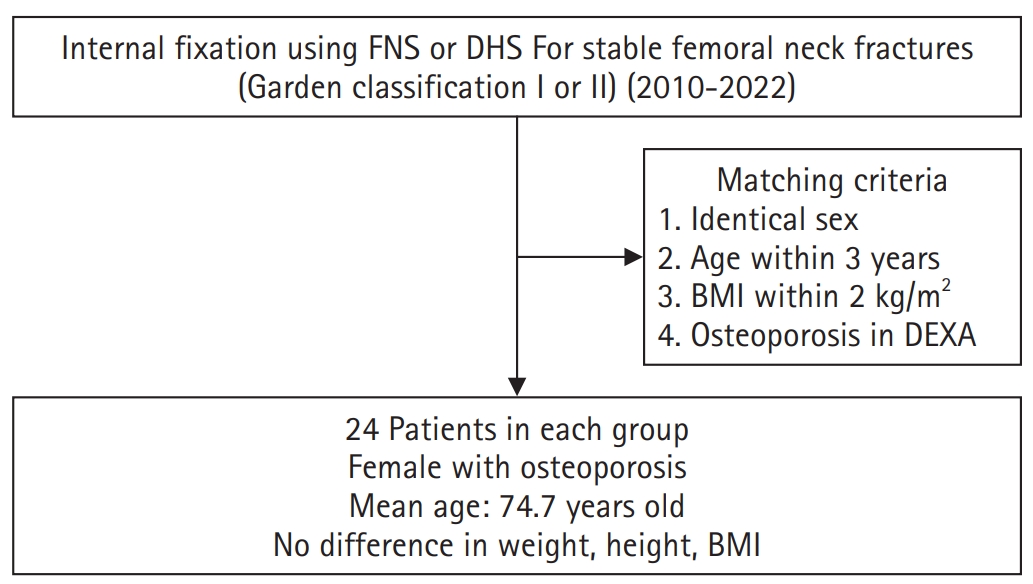
This study aimed to compare the clinical and radiological outcomes of the femoral neck system (FNS) and the dynamic hip screw (DHS) for the internal fixation of stable femoral neck fractures in older adults.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study included 48 matched older adult patients based on sex, age, BMI, and osteoporosis status, who had undergone internal fixation with either FNS or DHS for stable femoral neck fractures between January 2010 and December 2022. To minimize selection bias, a 1:1 case-control matching was performed based on sex, age, body mass index (BMI), and the presence of osteoporosis. A total of 48 patients (24 in each group) were included. We compared perioperative data (operation time, hemoglobin change, transfusion rate), functional outcomes using the Koval score, and radiological outcomes, including union rate, femoral neck shortening, and complication rates.
Results
The mean operation time was significantly shorter in the FNS group than in the DHS group (60.9 minutes vs. 70.8 minutes; P=0.007). There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in the union rate (87.5% in FNS vs. 95.8% in DHS), femoral neck shortening, final Koval score distribution, or overall complication rates (12.5% in both groups).
Conclusions
For treating stable femoral neck fractures in older adults, the FNS demonstrated comparable clinical and radiological outcomes to the DHS, with the distinct advantage of a shorter operation time. While these findings suggest that the FNS is a promising and safe alternative that may reduce the surgical burden, definitive conclusions are precluded by the small sample size, warranting further research to corroborate these results. Level of evidence: IV.
- 142 View
- 4 Download

- Correlation of bone mineral density with ankle fractures in older adults in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
- Seung Hyun Lee, Chae Hun Lee, Seo Jin Park, Jun Young Lee
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):186-192. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00150
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
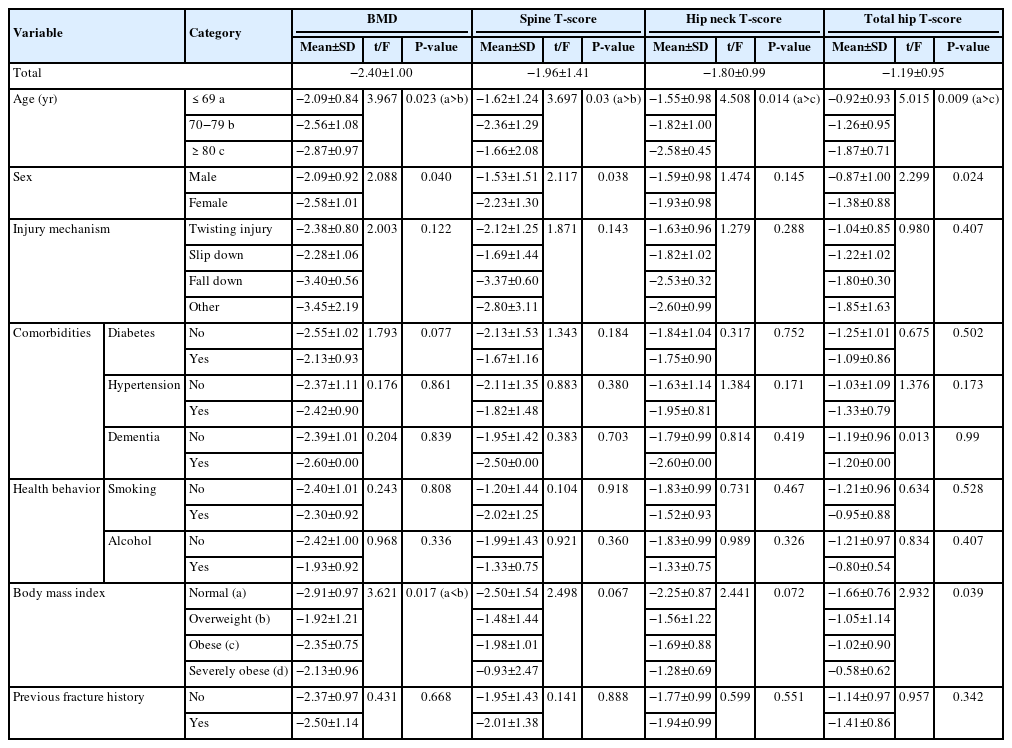
Bone mineral density (BMD) is well-documented in relation to fractures of the spine, hip, distal radius, and proximal humerus; however, its correlations with other fracture types are less established. This study aimed to analyze BMD and associated risk factors in older adults (≥65 years of age) with osteoporotic ankle fractures. These fractures involve low-energy trauma, resulting from falls from a standing height or lower, and occur from impacts which typically do not cause fractures in individuals with normal bone.
Methods
This retrospective study analyzed data from 1,411 patients diagnosed with ankle fractures admitted to Chosun University Hospital between February 2012 and April 2023. After applying inclusion criteria (age ≥65 years; low energy ankle fracture) and exclusion criteria (high energy trauma, open/multiple fractures, missing dual X-ray absorptiometry [DXA]), 73 of 1,411 patients were analyzed. Lumbar spine, femoral neck, and total hip T scores were obtained with a Horizon Wi DXA scanner, and associations with age, sex, mechanism of injury, comorbidities, smoking status, alcohol consumption, body mass index (BMI), and history of fractures were tested by ANOVA with Scheffe post hoc and Fisher exact tests.
Results
Lower BMD correlated significantly with older age, female sex, and lower BMI (P<0.05) in older adults with ankle fractures. No significant associations were observed for comorbidities (diabetes, hypertension, dementia), smoking, alcohol consumption, injury mechanism, or prior fractures.
Conclusion
These results indicate that older age, female, and lower BMI are linked to reduced BMD in ankle fracture patients over 65 years of age. Focused osteoporosis screening and management may therefore be most beneficial for older, low BMI women presenting with ankle fractures. Level of evidence: IV.
- 96 View
- 8 Download

- Risk factors for ankle fractures in older adults based on clinical components of the Fracture Risk Assessment (FRAX) tool and comorbidities in Korea: a retrospective case-control study
- Myeong Jun Song, Se Woong Jang, Jun Young Lee, Seojin Park
- J Musculoskelet Trauma 2025;38(4):193-202. Published online October 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jmt.2025.00143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
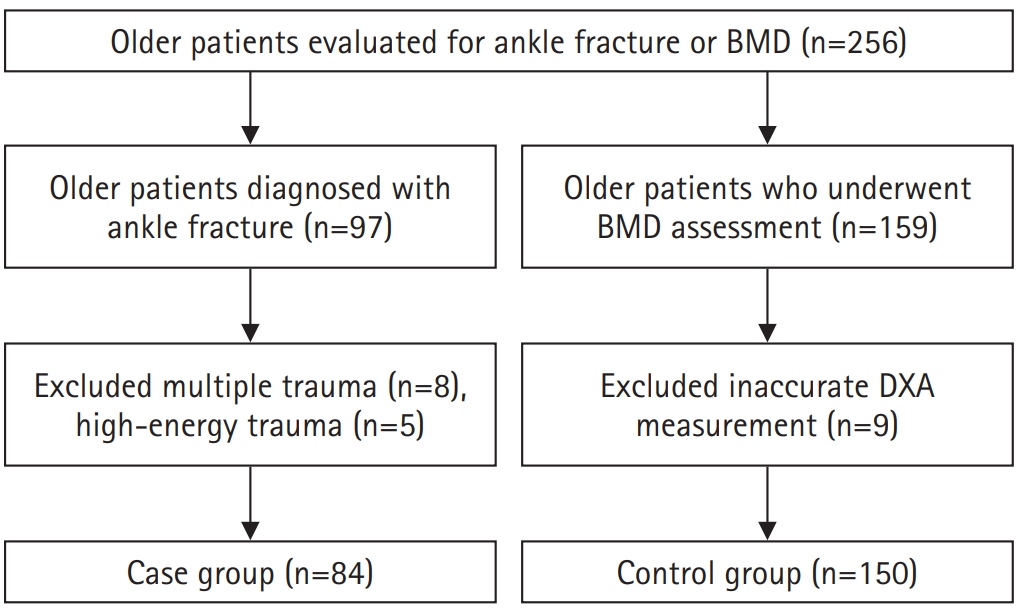
Ankle fractures are common in older adults; however, their relationship with osteoporotic fractures remains unclear. This study aimed to evaluate potential risk factors for ankle fractures in older adults by analyzing individual clinical components of the Fracture Risk Assessment (FRAX) tool and comorbidities.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective case-control study including 84 patients aged ≥65 years with ankle fractures and 150 controls who underwent bone mineral density (BMD) testing without prior ankle fractures. The variables analyzed included age, sex, body mass index, smoking, alcohol consumption, prior fracture history, and comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and dementia. BMD was measured at the spine, total hip, and femoral neck.
Results
Univariate analysis showed that alcohol consumption, diabetes mellitus, and total hip T-score categories were significantly associated with ankle fractures. In binary logistic regression, alcohol consumption remained significantly associated with higher ankle fracture risk (odds ratio [OR], 5.302; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.778–15.811; P=0.003), and both osteopenia and osteoporosis at the total hip were also associated with increased risk (OR, 3.260, P=0.049; OR, 3.561, P=0.031, respectively). Diabetes mellitus did not reach statistical significance in the adjusted model (P=0.074). Model fit was adequate (Hosmer-Lemeshow P=0.377), and post hoc power analysis confirmed sufficient sample size.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that lower total hip BMD and alcohol-related factors may be associated with ankle fracture risk in older adults. The FRAX score itself was not calculated; instead, this study focused on analyzing selected clinical components. Limitations include the retrospective design, lack of fall and medication data, and cross-sectional BMD assessment. Level of evidence: III.
- 105 View
- 7 Download

- Comparison of a Novel Box-Frame External Fixator and Conventional Delta-Frame External Fixator in the Staged Treatment of Distal Tibia Fractures
- Yong-Cheol Yoon, MinKyu Shin, Chang-Wug Oh, Jong-Keon Oh
- J Korean Fract Soc 2020;33(3):125-133. Published online July 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2020.33.3.125
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purpose
Distal tibia fractures with severe soft-tissue edema or intra-articular fractures are treated by staged operations using external fixators. Definitive surgery that maintains ligamentotaxis has been difficult using existing fixators. This study introduced a novel ‘box-frame’ external fixator and evaluated its clinical usefulness.
Materials and Methods
This study included 45 patients (32 males, 13 females) diagnosed with distal tibia fractures who underwent staged operations between March 2012 and March 2016, with a follow-up of at least one year. The patients were divided into two groups. In one group, fixation was performed with a box-frame external fixator (Group A). In the other group, fixation was performed with a delta-frame external fixator (Group B). The following outcomes were evaluated: the time until definitive surgery, operative time of the definitive surgery, radiation exposure time, bone union, time to achieve bone union, postsurgical complications, American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society anklehindfoot score, and ankle range of motion.
Results
Compared to the delta-frame, the box-frame showed a statistically significant reduction in the mean radiation-exposure time and operative time during the definitive surgery by 58 seconds and 25 minutes, respectively. The differences in the time until definitive surgery, bone union, time to achieve bone union, postsurgical complications, and functional scores were not significant.
Conclusion
The box-frame external fixator can be a useful treatment method in the staged surgery of distal tibia fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Temporary Circular External Fixation for Spanning the Traumatized Ankle Joint
Nando Ferreira, Niel Bruwer, Adriaan Jansen van Rensburg, Ernest Muserere, Shao-Ting Jerry Tsang
JBJS Essential Surgical Techniques.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Temporary circular external fixation for spanning the traumatised ankle joint: A cohort comparison study
William D. Harrison, Franklin Fortuin, Matthieu Durand-Hill, Etienne Joubert, Nando Ferreira
Injury.2022; 53(10): 3525. CrossRef
- Temporary Circular External Fixation for Spanning the Traumatized Ankle Joint
- 1,133 View
- 10 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The Result of Conservative Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fracture in Elderly Patients
- Seung Gil Baek, Chang Wug Oh, Young Soo Byun, Jong Keon Oh, Joon Woo Kim, Jong Pil Yoon, Hyun Joo Lee, Hyung Sub Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2013;26(4):292-298. Published online October 31, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.292
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
With the increase in the old age population, proximal humerus fractures have been increasing recently. However, complications after operative treatment, such as fixation failure, are common because of osteoporosis. We treated proximal humerus fractures in patients with osteoporosis conservatively, and evaluated the radiographic and functional results by analyzing the factors affecting the results.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Nineteen out of 30 cases for whom the clinical follow-up was over 1 year were included in this retrospective study. There were 17 females and 2 males, and the mean age was 73.2 years. The causes were slip from a short height (18 cases) and a minor car accident (1 case). We evaluated the union period, nonunion, malunion and the Constant score and analyzed several factors affecting the functional result, such as age, fracture pattern, and malunion.
RESULTS
Seventeen cases (89.5%) obtained union within 12.8 weeks on average. Neck-shaft angle was 125.3degrees on average, with seven cases of malunion. The Constant score was 84.1 on average, and there were excellent scores in 11 cases, good scores in 4 cases, and fair scores in 2 cases. Fracture pattern, neck-shaft angle, or malunion did not affect the functional outcome, and elderly patients showed poorer shoulder function.
CONCLUSION
Proximal humeral fractures with osteoporosis may achieve a high rate of bony union when treated with conservative methods. Despite the common occurrence of malunion, a satisfactory functional outcome may be expected.
- 425 View
- 4 Download

- Staged Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis of Proximal Tibial Fracture
- Joon Woo Kim, Chang Wug Oh, Jong Keon Oh, Hee Soo Kyung, Woo Kie Min, Byung Chul Park, Kyung Hoon Kim, Hee Joon Kim
- J Korean Fract Soc 2009;22(1):6-12. Published online January 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2009.22.1.6
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To assess the results of staged MIPO (Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis) for proximal tibial fractures with compromised soft tissue.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eighteen proximal tibial fractures (AO 41:9 cases, AO 42:9 cases) included this study. Ten were open fractures. After temporary external fixation until soft tissue healed (mean 27.3 days), MIPO was performed secondarily without bone graft. We assessed the bony union and knee function, and affecting factors of the results were investigated.
RESULTS
All fractures united at 20 weeks (range, 11~32) except 1 case. Mean range of knee flexion was 134.4degrees and mean IOWA knee score was 89.1. There were 2 superficial and 2 delayed deep infections from open fractures (grade II:1 case, grade III:3 cases), although they healed after implant removal. Open fractures seem to influence the infection rate. Otherwise, there was no related factor affecting the results.
CONCLUSION
MIPO after temporary external fixation can provide favorable results in proximal tibial fractures with soft tissue injuries, but attention of delayed infection should be paid in open fractures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- MINIMALLY INVASIVE OSTEOSYNTHESIS WITH PLATE OR NAIL FOR META-DIAPHYSEAL TIBIAL FRACTURES - WHAT IS BETTER?
B. Makelov
Trakia Journal of Sciences.2023; 21(4): 357. CrossRef - Effect of Korean Medicine Treatments in Patients with Proximal Tibia Fracture: A Retrospective Observational Study
Jung Min Lee, Eun-Jung Lee
Journal of Korean Medicine Rehabilitation.2020; 30(3): 141. CrossRef - Comparison of Time to Operation and Efficacies of Ultrasound-Guided Nerve Block and General Anesthesia in Emergency External Fixation of Lower Leg Fractures (AO 42, 43, 44)
Chan Kang, Sang-Bum Kim, Youn-Moo Heo, You-Gun Won, Byung-Hak Oh, June-Bum Jun, Gi-Soo Lee
The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery.2017; 56(5): 1019. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Proximal Tibial Shaft Fracture
Young-Soo Byun, Ki-Chul Park, Hyun-Jong Bong, Chang-Hoon Lee
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2011; 24(1): 23. CrossRef - The Use of Fresh Frozen Allogenic Bone Graft in the Impacted Tibial Plateau Fractures
Yeung Jin Kim, Soo Uk Chae, Jung Hwan Yang, Ji Wan Lee, Dae Han Wi, Duk Hwa Choi
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(1): 26. CrossRef - Management of Open Fracture
Gu-Hee Jung
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(2): 236. CrossRef - Staged Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis of Distal Tibial Fractures
Sung-Ki Park, Chang-Wug Oh, Jong-Keon Oh, Kyung-Hoon Kim, Woo-Kie Min, Byung-Chul Park, Won-Ju Jeong, Joo-Chul Ihn
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(3): 289. CrossRef - Intramedullary Nailing of Proximal Tibial Fractures
Young-Soo Byun, Dong-Ju Shin
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(3): 197. CrossRef - Proximal Tibia Fracture: Plating
Ki-Chul Park
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2009; 22(3): 206. CrossRef
- MINIMALLY INVASIVE OSTEOSYNTHESIS WITH PLATE OR NAIL FOR META-DIAPHYSEAL TIBIAL FRACTURES - WHAT IS BETTER?
- 423 View
- 0 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Treatment of High-energy Distal Tibia Intraarticular Fractures with Two-staged Delayed Minimal Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis
- Hong Moon Sohn, Jun Young Lee, Sang Ho Ha, Jae Won You, Sang Hong Lee, Kwang Chul Lee
- J Korean Fract Soc 2007;20(1):19-25. Published online January 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2007.20.1.19
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
To evaluate the short-term results of two-staged delayed minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis in high-energy intraarticular fractures of the distal tibia.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirteen patients, who underwent two-staged delayed minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis for intraarticular fractures of the distal tibia between January 2002 and July 2004, were followed for more than one year. The mean interval time between first stage and second stage of the procedures was 28.6 days (range, 14~34 days). By Ruedi-Allgower classification, there were two cases in type I, three cases in type II, and eight cases in type III. There were six cases in type B and seven cases in type C patients according to AO/OTA classification. Radiographs were graded by the criteria of Burwell and Charnley and ankle functions were graded by the criteria of Mast and Teipner. Union time and postoperative complications were also analysed.
RESULTS
Average union time was 16.9 weeks (range, 14~20 weeks) in twelve of the thirteen fractures, but there was one fracture resulting in soft tissue complication and infected nonunion. At the latest follow-up, review of the radiographic results showed that ten cases of fractures (77%) achieved an anatomic reduction, two cases (15%) achieved fair reduction and one case (8%) achieved a poor reduction. And clinical functional assessment showed that nine cases (69%) were good results, three cases were (23%) fair results and one case (8%) was poor result.
CONCLUSION
Two-staged delayed minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis is an excellent option for the treatment of high-energy intraarticular fractures of the distal tibia. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Staged Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis of Distal Tibial Fractures
Sung-Ki Park, Chang-Wug Oh, Jong-Keon Oh, Kyung-Hoon Kim, Woo-Kie Min, Byung-Chul Park, Won-Ju Jeong, Joo-Chul Ihn
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(3): 289. CrossRef - The Comparison of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis and Intramedullary Nailing in the Treatment of the Proximal and Distal Tibia Fracture
Joon Soon Kang, Seung Rim Park, Sang Rim Kim, Yong Geun Park, Jae Ho Jung, Sung Wook Choi
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2010; 23(2): 172. CrossRef - Two-staged Delayed Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis for Distal Tibial Open Fractures
Jung Hwan Yang, Seok Hyun Kweon, Jeung Woo Kim, Jin Young Park, Hyun Jun Kim, Chul Min Lim
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2008; 21(1): 24. CrossRef
- Staged Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis of Distal Tibial Fractures
- 362 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Two stage Operative Treatment of Supracondylar Open Comminuted Fracture of Femur: Temporary fixation with Transarticular Ender nails
- Song Lee, Dong Ki Ahn, Seung Hwan Kim, Sung Wook Chun
- J Korean Soc Fract 2000;13(3):470-478. Published online July 31, 2000
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.2000.13.3.470
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - PURPOSE
In many cases of open comminuted supracondylar fracture, it is very hard to apply traditional methods. So we have used Ender nails for temporary transarticular fixation. We thought that it could provide enough stability to control the wound and didn't promote further soft tissue damage or infection. We performed 2nd stage rigid fixation and bone graft after soft tissue healing. We have studied to prove this staged operation valuable to treat the very severe open comminuted supracondylar fracture of femur.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We analysed 16 cases which have been treated with such staged operation method from April 1992 to April 1996 about complication, union time and functional result in retrospective method.
RESULTS
We could prevent severe wound infection in all cases. We performed 2nd stage rigid fixation and bone graft average 6 weeks after first stage temporary fixation. The average union time was 8 months and average range of motion was 10degrees flexion contracture and 100degrees further flexion.
CONCLUSION
In patients with very severe open comminuted supracondylar fracture of femur, the temporary fixation with transarticular Ender nails allowed the successful initial management for the secondary rigid fixation and bone graft and time could be saved for management of concomitant injuries. So this new staged operation is considered as a good method for safety, union time and functional result.
- 262 View
- 0 Download

Case Report
- Scapulothoracic Dissociation: Two cases report
- Man Ho Byun, Sung Seok Seo, Hyun Duk Yu, Young Chang Kim, Jang Seok Choi, Young Ku Lee
- J Korean Soc Fract 1995;8(3):467-470. Published online July 31, 1995
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12671/jksf.1995.8.3.467
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Scapulothoracic dissociation is rare injury and as a result of severe shoulder girdle trauma. muptiple fractures of the upper extremity and closed disruption of scapula from the thorax are combined with damage to the local neurovascular structures, brachial plexus and subclavian artery. Tracitionally, above-the-elbow amputation and shoulder arthrodesis have been used to treat the flail upper extremity. Now we experienced two cases of scapulothoracic dissociation managed by forequarter amputation, shoulder and above-the elbow amputation and then present two cases of scapulothoracic dissociation through case and textbook review.
- 211 View
- 0 Download


 E-submission
E-submission KOTA
KOTA

 First
First Prev
Prev


